Map of Indians Aged 15-24 Proficient in Word Processing

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
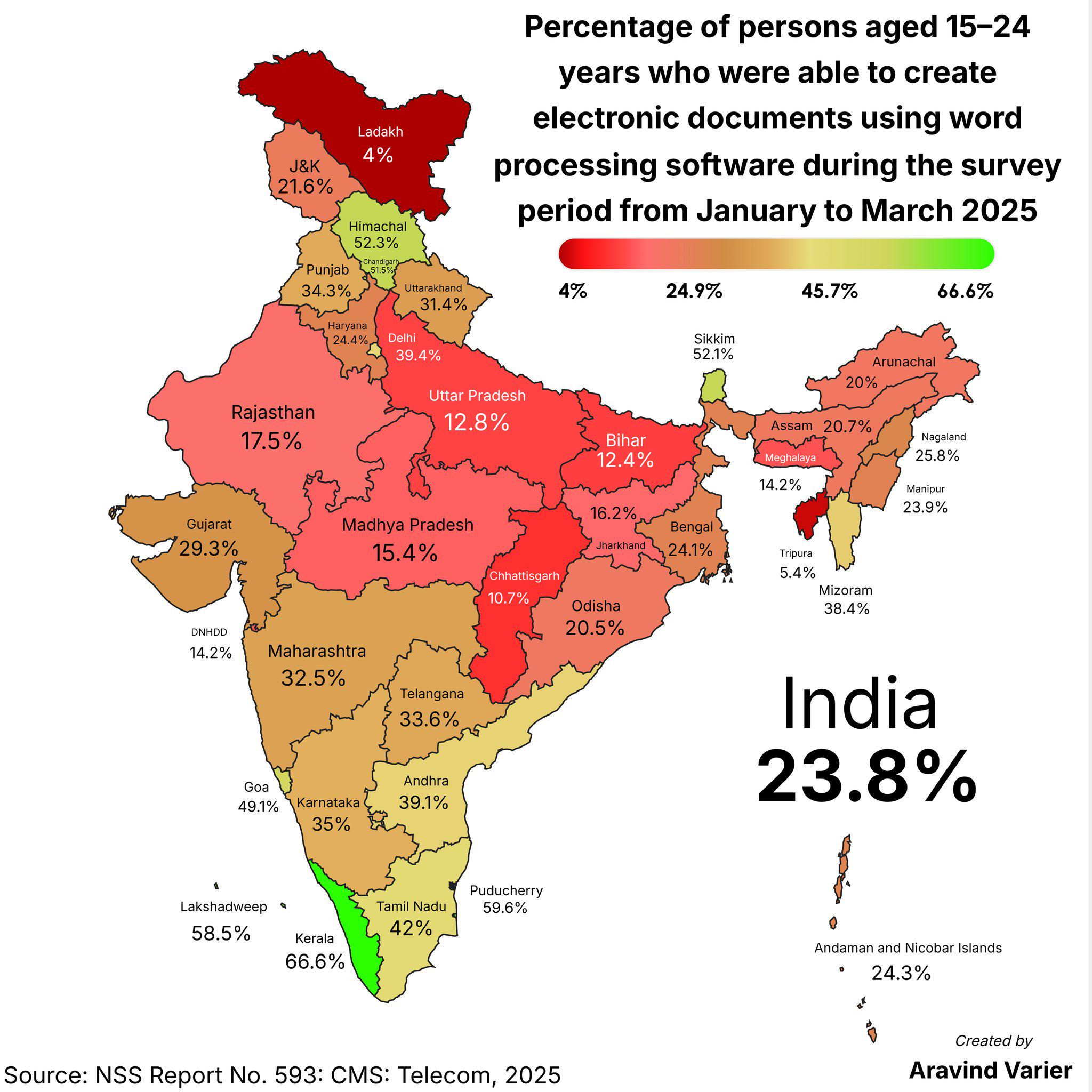
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Percentage of Indians aged 15–24 years who were able to create electronic documents using word processing softwares" provides a compelling visual representation of digital literacy among the youth in India. Specifically, it highlights the percentage of young individuals proficient in creating electronic documents with popular word processing tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and others. This visualization offers insights into the varying levels of technological competence across different regions of India and serves as a crucial indicator of the digital divide in the country.
Deep Dive into Digital Literacy in India
When we think about the digital landscape of India, it’s essential to recognize that technology has permeated various facets of life, especially for the younger generation. Digital literacy is more than just knowing how to use a computer; it encompasses a range of skills including the ability to create documents, manage files, and engage with online platforms. According to various studies, digital literacy among youth is a key driver for educational and employment opportunities.
Interestingly, the ability to create electronic documents signifies not only familiarity with technology but also an understanding of how to communicate effectively in a digital format. This skill has become increasingly vital in today’s job market, where employers often seek candidates who can demonstrate technical proficiency. For young Indians, being able to create electronic documents can open doors to internships, job opportunities, and further education, all of which are crucial for economic advancement.
Recent statistics indicate that the youth demographic (aged 15-24) is one of the largest segments in India, making up roughly 35% of the population. However, despite this potential, there are significant disparities in digital skills across different states and regions. For instance, urban areas typically showcase higher percentages of young individuals skilled in word processing compared to their rural counterparts. This digital divide can be attributed to several factors including access to resources, quality of education, and exposure to technology.
Moreover, in regions with robust educational infrastructure and access to technology, such as Delhi, Maharashtra, and Karnataka, the proficiency rates tend to be substantially higher. Conversely, states like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh often lag behind, highlighting the challenges that come with limited resources and educational opportunities. The government and various NGOs have recognized this gap and are actively working to address it through initiatives aimed at enhancing digital literacy.
Regional Analysis
As we examine the map in detail, we can see distinct regional patterns that emerge. For example, states like Tamil Nadu and Kerala stand out with higher percentages of young individuals proficient in word processing. This trend can be linked to their strong educational systems and ongoing investments in technology in schools and colleges.
On the other hand, Northern states like Punjab and Haryana show a mixed picture, with some areas exhibiting high digital literacy due to urbanization, while rural regions struggle with access to technology. Interestingly, even within well-developed states, there can be stark contrasts between urban and rural areas. In cities, initiatives such as computer literacy programs in schools have led to higher proficiency rates, while surrounding rural communities still face challenges.
Another notable observation is the influence of socio-economic factors on digital literacy. Areas with higher economic development tend to have better infrastructure, which in turn supports digital skills acquisition. For instance, Maharashtra, with its thriving IT sector in cities like Pune and Mumbai, boasts one of the highest percentages of digitally literate youth. In contrast, states with lower GDP may find their youth facing barriers in accessing the necessary technology and training.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the levels of digital literacy, particularly in word processing, is crucial for several reasons. First, it reflects the broader trends of technological integration in education and the workforce. In a country like India, where economic growth is largely driven by the IT sector, having a digitally literate youth population can significantly enhance productivity and innovation.
Moreover, the implications of this data extend beyond just job readiness. Digital skills empower young people to participate more actively in society, facilitating better communication, access to information, and engagement with governmental processes. As we move towards a more digital economy, the ability to create documents and effectively communicate online will only become more important.
In conclusion, this map not only highlights the current state of digital literacy among young Indians but also raises important questions about equity and access to technology. As we look to the future, addressing the disparities in digital skills will be essential for ensuring that all young people have the opportunity to thrive in an increasingly digital world. The trends suggest that with continued investment in education and technology, we can expect to see improvements in these statistics, which will ultimately benefit the entire nation.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 14, 2025
- Views
- 34
Comments
Loading comments...