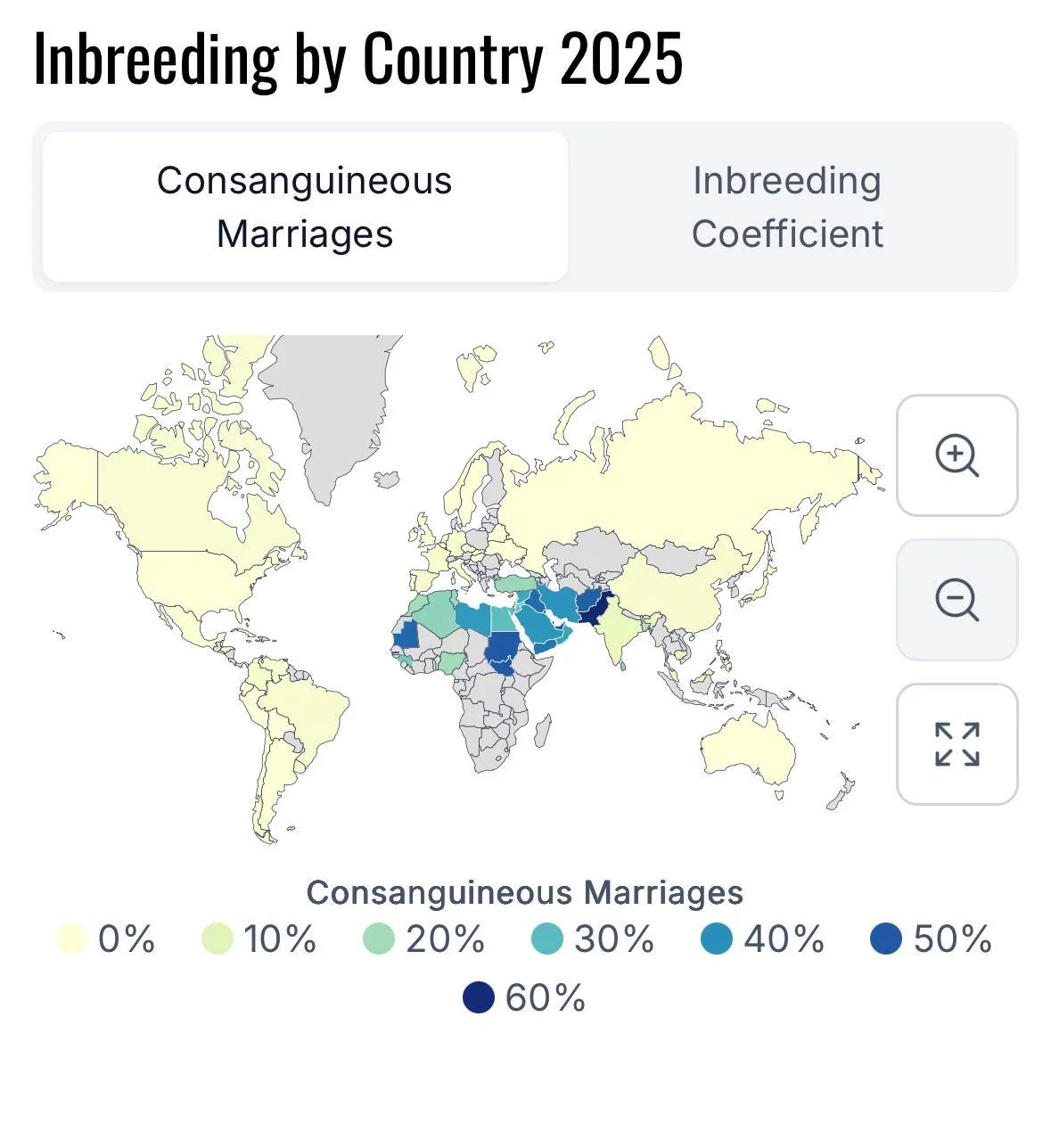
Consanguineous Marriage by Country Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the prevalence of consanguineous marriages—unions between relatives—across different countries. Consanguinity is a sociocultural phenomenon that can have significant implications for genetics, health, and societal development. The visualization highlights regions where such marriages are more common, giving us a clearer picture of cultural practices and their possible consequences on population genetics.
Deep Dive into Consanguineous Marriage
Consanguineous marriage involves unions between individuals who share a common ancestor. These relationships can range from first cousins to more distant relatives, and their prevalence varies widely across cultures and geographical regions. Interestingly, this practice is often rooted in tradition, economic considerations, and social structures, fostering familial bonds and maintaining cultural identity.
Globally, it's estimated that about 10% of all marriages are consanguineous, but this statistic varies dramatically from region to region. For example, countries in the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Asia demonstrate significantly higher rates of consanguinity, often exceeding 50% in certain communities. In contrast, Western countries generally report lower rates, often below 1%. This disparity raises questions about cultural norms and genetic health risks associated with such unions.
Genetically, consanguineous marriages can increase the probability of inheriting genetic disorders, as recessive genes from both parents have a higher chance of manifesting in their offspring. This phenomenon is particularly critical in regions where cousin marriages are common, as it can lead to an increased prevalence of autosomal recessive diseases. For instance, conditions such as cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, and various forms of congenital heart disease may become more prevalent in populations with high rates of consanguinity.
Interestingly, the dynamics of consanguineous marriage are not entirely negative. Some studies suggest that these unions can enhance social cohesion and familial support, providing economic stability within tightly-knit communities. Furthermore, in some cultures, these marriages are seen as a way to preserve land and wealth within the family, which may explain their continued prevalence despite potential health risks.
Regional Analysis
The map reveals stark contrasts in the prevalence of consanguineous marriages across the globe. In the Middle East, for instance, countries like Saudi Arabia and Jordan report rates of consanguinity as high as 50-60%. These practices are often influenced by tradition and the desire to strengthen familial ties. In South Asia, particularly in Pakistan and India, cousin marriages are common, with rates often hovering around 30-40%.
Conversely, in Europe and North America, the rates of such marriages are significantly lower. Countries like Sweden and Denmark show rates around 1%, reflecting a different cultural approach to marriage and family structures. The variation in these practices can also be attributed to legal frameworks and public health initiatives that raise awareness about the potential genetic implications of consanguinity.
In Africa, the situation is mixed. While some regions exhibit high rates of consanguineous marriages, others, particularly urbanized areas, are seeing a decline as modernity influences social norms. Countries like Nigeria present a complex scenario where traditional practices coexist with contemporary views on marriage.
Significance and Impact
The implications of consanguineous marriage are profound. Understanding this phenomenon is crucial for public health initiatives, particularly in regions with high rates of genetic disorders stemming from such unions. As global migration patterns change and cultures intermingle, the conversation surrounding consanguinity must evolve, addressing both its cultural significance and its health consequences.
Moreover, as nations grapple with genetic diversity and public health, the impact of consanguineous marriages will continue to be a relevant topic. Current trends indicate a gradual decline in consanguineous marriages in some regions, influenced by education and awareness campaigns. However, in many cultures, the practice remains deeply embedded in social structures, making it a complex issue that requires nuanced understanding and respectful dialogue.
As we examine the prevalence of consanguineous marriage through this map, we gain insights into the intricate tapestry of cultural practices and their implications for health and society. It's a reminder of how diverse human relationships can be and how they shape the genetic landscape of populations around the world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 13, 2025
- Views
- 16
Comments
Loading comments...