5G Standalone Global Coverage Map 2024-2025

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
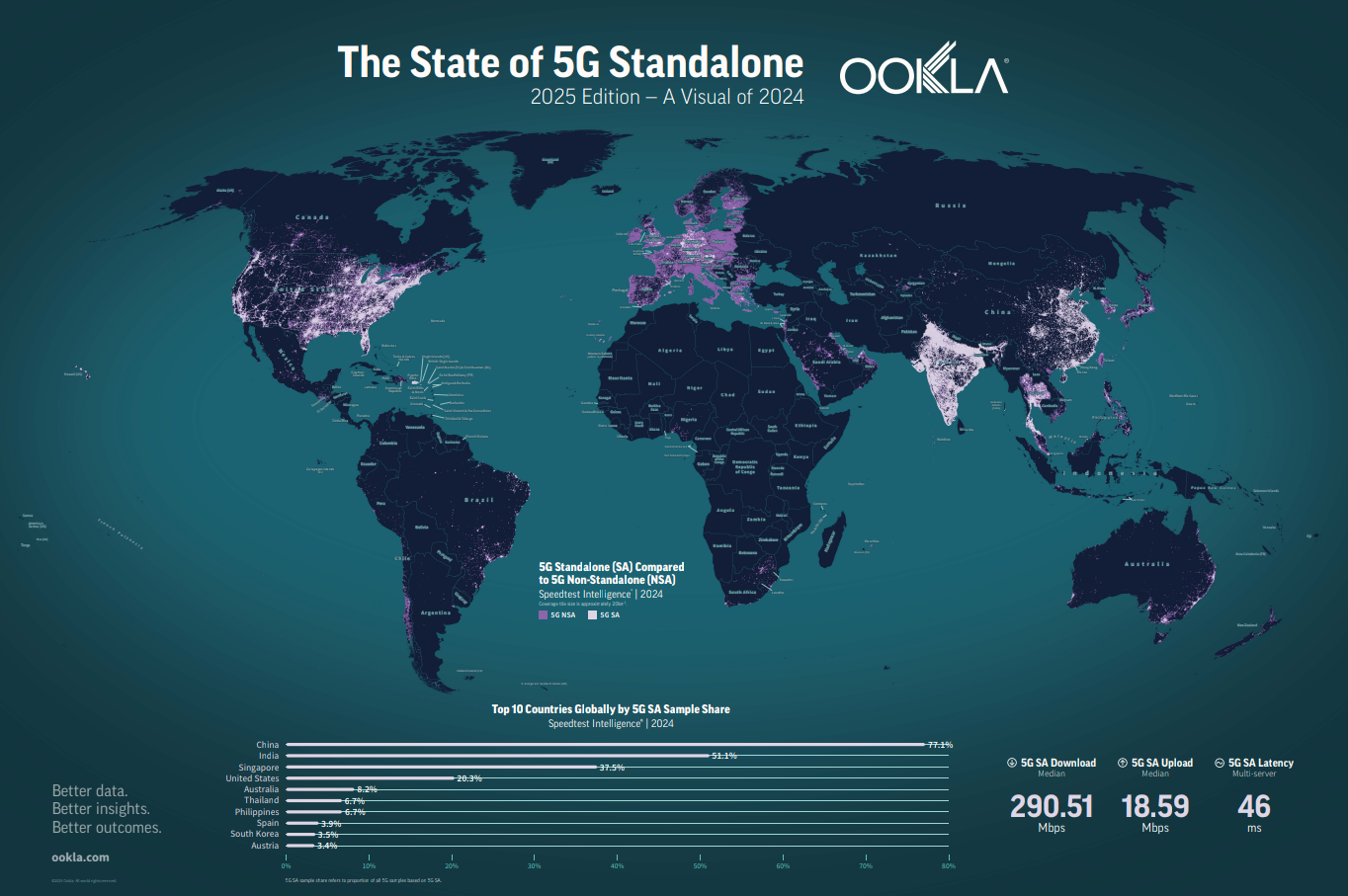
What This Map Shows
The "State of 5G Standalone Worldwide as of 2024-25" map provides a comprehensive overview of the global landscape of 5G standalone (SA) networks. Unlike non-standalone 5G, which relies on existing 4G infrastructure, 5G SA represents a complete transition to next-generation technology, allowing for lower latency, increased capacity, and enhanced reliability. This map visually represents the countries that have successfully implemented 5G SA networks, highlighting areas of rapid technological advancement and investment in telecommunication infrastructures.
Deep Dive into 5G Standalone Technology
5G technology is more than just a faster mobile internet; it is a transformative force capable of reshaping industries, economies, and our daily lives. The standalone version is designed to facilitate ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), which is crucial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices that require instantaneous data exchange.
Interestingly, while many countries have begun rolling out 5G networks, only a handful have adopted the standalone approach due to the significant investment and infrastructure overhaul required. As of early 2025, countries like the United States, South Korea, and parts of Europe have emerged as leaders in this domain, illustrating a clear divergence in global telecommunications capabilities.
In terms of implementation, 5G SA relies on a new core network architecture, which must be developed from the ground up. This transition represents a significant leap from 4G LTE, necessitating substantial investment in new hardware and software solutions. The benefits, however, are significant. For instance, 5G SA networks can support a greater number of connected devices per square kilometer than their predecessors, making them ideal for dense urban environments where IoT applications thrive.
Moreover, as more countries adopt this technology, we can expect to see a domino effect. Regions that lag in 5G SA deployment may face competitiveness challenges in the global market. Countries that have embraced this technology are already witnessing economic growth fueled by tech-driven innovation and improved telecommunications framework.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals interesting regional disparities. North America and parts of East Asia, particularly South Korea and Japan, are at the forefront of 5G SA implementation. The United States has invested heavily in building a robust 5G infrastructure, with major telecommunications companies continuously expanding their networks. According to recent statistics, over 30% of the U.S. population is now covered by 5G SA, a figure that is expected to rise rapidly.
In contrast, Europe shows a mixed picture. While countries like Germany and the UK have made strides in 5G SA deployment, others are still grappling with regulatory challenges and slower rollout processes. Interestingly, Scandinavian countries appear to be leading the charge in Europe, with extensive investments in both urban and rural areas, ensuring that 5G SA benefits are widely distributed.
Meanwhile, emerging economies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are starting to catch up, with several countries beginning pilots of 5G SA networks. For instance, India has launched initiatives to test 5G SA in select metropolitan areas, aiming to boost its digital economy. This is a critical development, as it underscores the global push towards a more interconnected world, where digital equity can be realized.
Significance and Impact
The deployment of 5G SA technology is not merely about enhancing connectivity; it represents a paradigm shift in how societies function. As industries adopt this technology, we can anticipate significant advancements in various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and entertainment. For example, in healthcare, the ability to perform remote surgeries with minimal latency could revolutionize patient care, especially in underserved regions.
However, there are challenges to consider. The rapid deployment of 5G SA raises concerns about cybersecurity, as increased connectivity can lead to vulnerabilities. Moreover, there is a growing debate about the environmental impact of the necessary infrastructure expansions. Policymakers must navigate these complexities to ensure that the transition to 5G SA is both beneficial and sustainable.
Looking ahead, the global race for 5G SA deployment will likely define the technological landscape of the next decade. As countries invest in this technology, the implications for economic growth, innovation, and societal advancement will be profound. This map serves as a snapshot of where the world stands today, but it also hints at the possibilities that lie ahead in our increasingly connected future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 13, 2025
- Views
- 64
Comments
Loading comments...