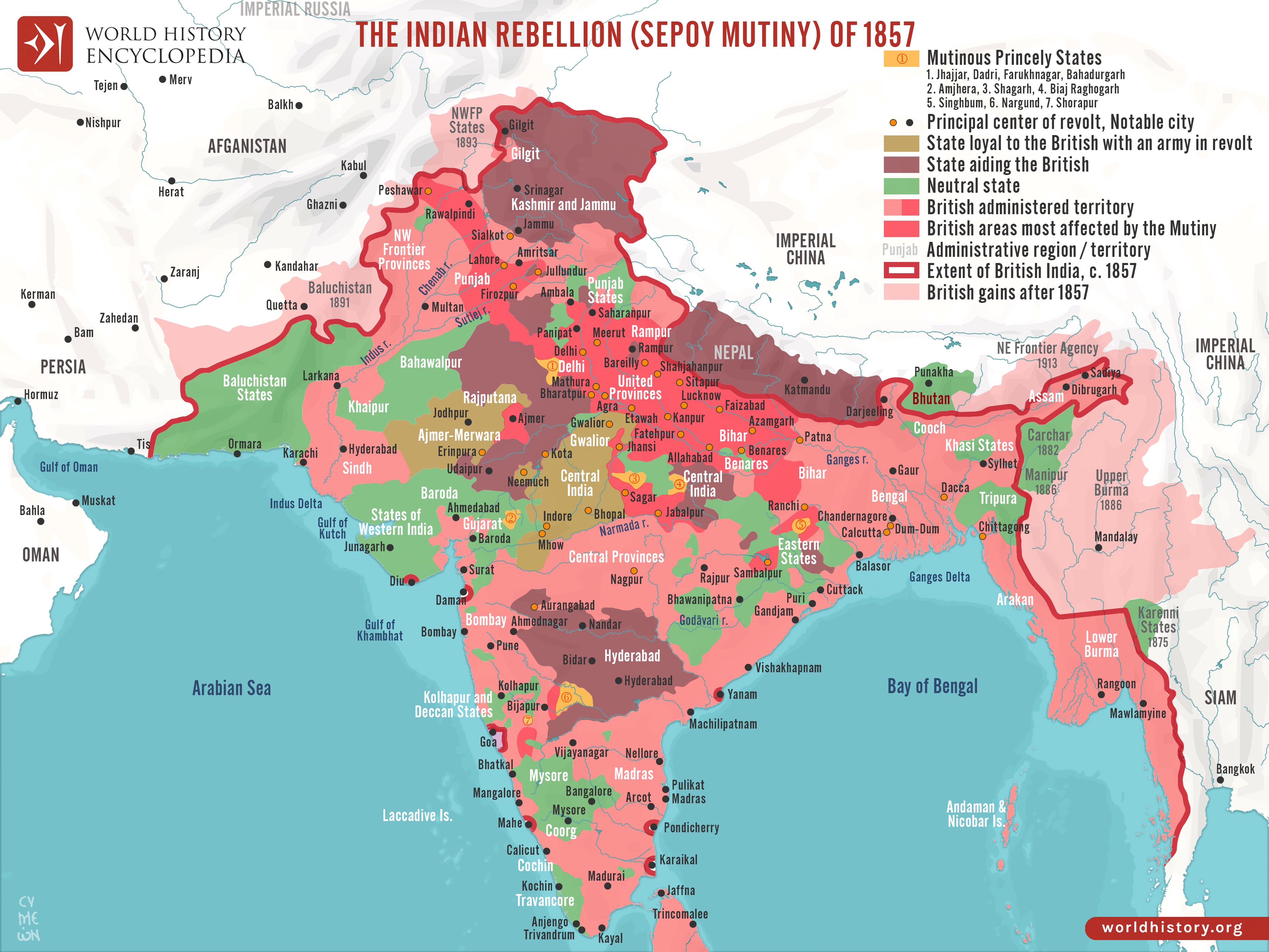
Map of the Indian Subcontinent during the Sepoy Mutiny of 1857

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The 'Map of the Indian Subcontinent during the Sepoy Mutiny of 1857' provides a detailed geographical representation of the regions affected by one of the most significant uprisings against British colonial rule in India. The map outlines key locations where critical events unfolded, showcasing major cities, military movements, and areas of intense conflict. It offers insight into the geographical context of the mutiny, highlighting how the topography and urban centers played crucial roles in the uprising's dynamics.
Deep Dive into the Sepoy Mutiny
The Sepoy Mutiny, also known as the First War of Independence, was a pivotal event in Indian history that marked a major turning point in the struggle against British colonialism. The uprising began in May 1857 and spread across Northern India, with significant episodes occurring in cities such as Delhi, Kanpur, and Lucknow. The map vividly illustrates these key locations and their strategic importance.
Interestingly, the causes of the Sepoy Mutiny were multifaceted. Discontent among the sepoys, or Indian soldiers, was fueled by a combination of factors, including cultural insensitivity from the British, the introduction of new rifle cartridges rumored to be greased with animal fat, and a growing resentment towards British authority. This discontent was not solely limited to the military; it extended to various social groups, including peasants and landlords, who felt threatened by British policies.
The geographical layout of the subcontinent played a significant role in how the mutiny developed. The Ganges River, which flows through many of the affected areas, was not just a physical barrier but also a vital lifeline that facilitated troop movements and supply routes. The map illustrates how control over these waterways was crucial for both the British and the rebelling sepoys.
Additionally, the diverse landscape of the region influenced the nature of the conflict. For instance, urban centers like Delhi became focal points of the rebellion, while rural areas experienced different dynamics. The urban rebellions were marked by intense street fighting and guerrilla tactics, while rural uprisings often involved large gatherings of peasants rallying against oppressive land revenue systems imposed by the British.
Regional Analysis
Analyzing the map reveals distinct regional disparities in the intensity of the uprising. In Northern India, particularly in the regions around Delhi, Meerut, and Kanpur, the revolt was most pronounced. Delhi, as the historical capital, saw fierce battles, with sepoys declaring it as a center of resistance against British rule. Have you noticed how the layout of the city, with its forts and narrow lanes, provided strategic advantages for those involved in the rebellion?
In contrast, areas further south, such as Punjab, experienced a more subdued response. The British had implemented a more conciliatory approach in Punjab, which helped maintain relative peace. However, regions like Awadh were hotspots of rebellion due to the deep-seated grievances against British policies. The map clearly delineates these differences, showcasing the geographical contours that played into the varying levels of resistance.
Significance and Impact
The significance of the Sepoy Mutiny extends beyond its immediate consequences. It was a watershed moment that altered the trajectory of British colonial policy in India. The uprising led to the dissolution of the British East India Company and the establishment of direct British rule, marking the beginning of the British Raj.
What's fascinating is that the 1857 revolt laid the groundwork for future movements for independence, inspiring generations of Indian leaders, including Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru. The map serves as a reminder of how geographical contexts can shape historical events and catalyze social change. Today, as India continues to grapple with its colonial past, understanding the geographical dynamics of the Sepoy Mutiny provides valuable insights into the ongoing discussions around identity, nationalism, and historical memory. The legacies of this pivotal moment in history still resonate, influencing contemporary Indian society.
In conclusion, the 'Map of the Indian Subcontinent during the Sepoy Mutiny of 1857' is not just a visual representation; it's a window into the historical complexities that defined a crucial chapter in Indian history. By examining the geographical factors at play, we gain a deeper appreciation of the events that led to India's ongoing struggle for independence and the lasting impact of colonialism on the subcontinent.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 13, 2025
- Views
- 22
Comments
Loading comments...