Amerindian Ancestry in the Americas Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
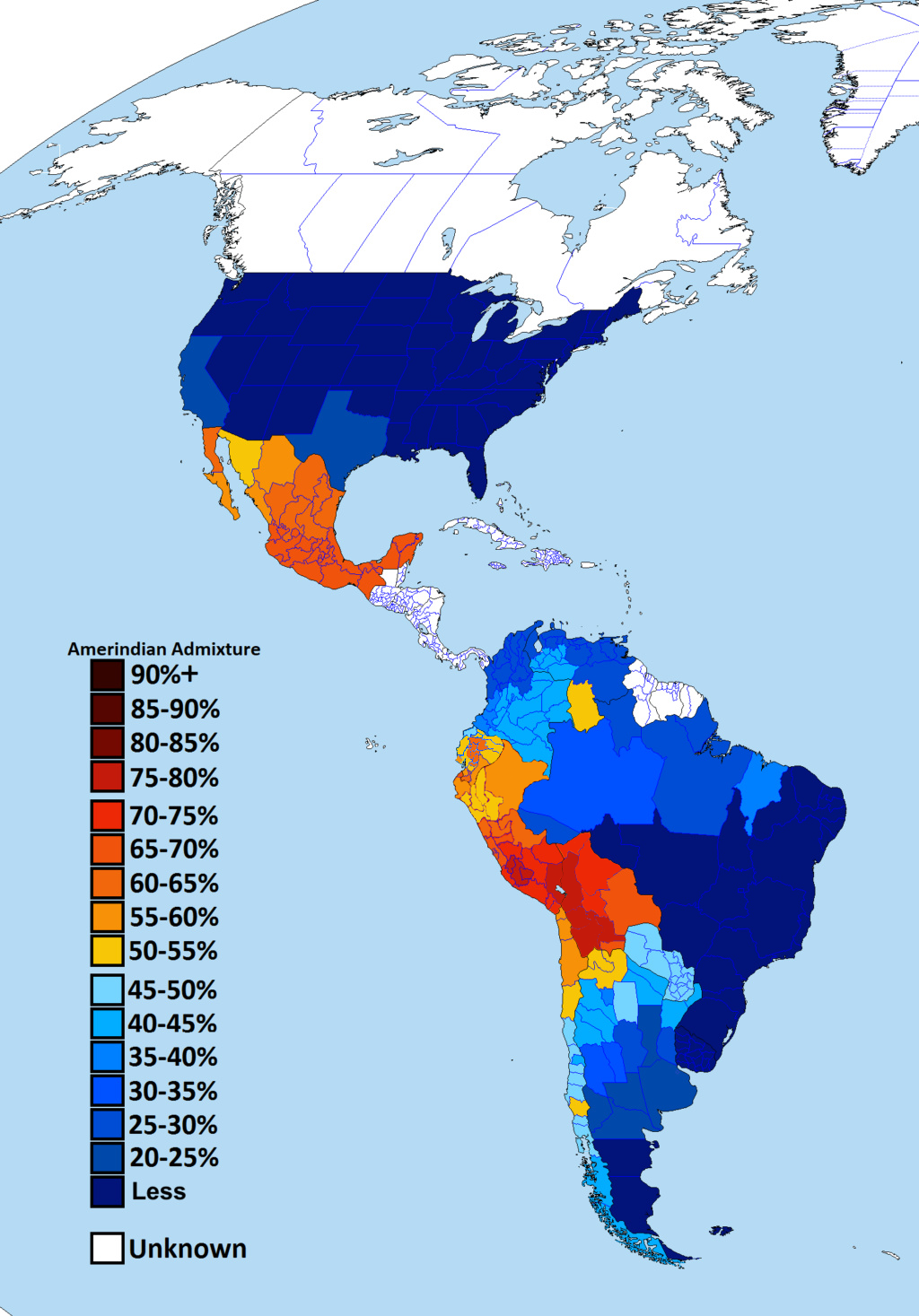
The "Amerindian Ancestry in the Americas Map" provides a comprehensive visualization of the genetic heritage of Indigenous peoples across the Americas. This map highlights the varying degrees of Amerindian admixture present in different regions, reflecting the historical and contemporary interactions between Indigenous populations and other ethnic groups. By analyzing this map, we can gain insights into the demographic evolution of the Americas, shaped by colonization, migration, and cultural exchange.
Deep Dive into Amerindian Ancestry
Amerindian ancestry refers to the genetic lineage traced back to the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. This ancestry is not only a marker of identity but also an important element of the diverse cultural tapestry that characterizes the continent. The percentage of Amerindian admixture varies significantly depending on historical factors, geographical location, and social dynamics.
What's fascinating is that genetic studies have shown that most people in Latin America possess some degree of Indigenous ancestry, a result of centuries of intermarriage among Indigenous peoples, Europeans, and Africans. For instance, a study published in the American Journal of Human Genetics indicated that individuals from Mexico have an average Amerindian ancestry of around 60%, while populations in regions like the Southern Cone may show lower percentages due to different migration patterns and historical interactions.
The genetic legacy of Indigenous peoples is evident in various ways, including health, culture, and social structures. Many Indigenous groups have contributed unique genetic traits that can influence health outcomes, such as resistance to certain diseases. Moreover, cultural practices, languages, and traditional knowledge systems rooted in Indigenous heritage continue to thrive, despite the pressures of globalization.
Interestingly, the concept of Amerindian ancestry is not just limited to the genomic aspect; it also encompasses cultural identity. For many, acknowledging Amerindian roots is a way to reconnect with ancestral traditions and practices that define their communities. This cultural revival is particularly important in a world where globalization often threatens local customs and languages.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, one can observe distinct patterns of Amerindian admixture across different regions. In Mexico, for example, states like Oaxaca and Chiapas exhibit high levels of Indigenous ancestry, reflecting the presence of numerous Indigenous groups such as the Zapotecs and Mayans. In these areas, cultural practices and languages are still vibrant, serving as a testament to the rich heritage that persists.
Contrastingly, regions like Argentina and Uruguay show lower percentages of Amerindian ancestry, which can be attributed to historical events such as the extensive European colonization and the subsequent displacement of Indigenous populations. In Argentina, the Pampas region, known for its agricultural development, has seen a significant decline in Indigenous identity due to assimilation and urbanization.
Another interesting case is found in the Andean region, particularly in Bolivia and Peru, where Indigenous populations remain prominent. Here, the map indicates higher levels of Amerindian ancestry, aligning with the demographic dominance of groups like the Quechua and Aymara. The cultural richness in these regions is palpable, with traditional customs, festivals, and languages still actively practiced.
Significance and Impact
Understanding Amerindian ancestry in the Americas is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for a deeper appreciation of the continent's historical narrative, encompassing the resilience and adaptation of Indigenous peoples. Furthermore, recognizing the Amerindian roots in modern populations can foster a sense of pride and cultural identity, especially among mixed-ancestry individuals.
Moreover, this topic has significant real-world implications. As discussions surrounding Indigenous rights and representation gain momentum, acknowledging Amerindian ancestry becomes part of broader social justice movements. It can influence policies related to land rights, cultural preservation, and health care access for Indigenous communities.
Looking forward, trends in genetic research and the growing interest in ancestry testing are likely to continue shaping our understanding of Amerindian lineage. As more people explore their roots, we may see a resurgence in Indigenous identity and advocacy, further emphasizing the need to protect and celebrate the diverse cultures that define the Americas today.
In conclusion, the Amerindian Ancestry in the Americas Map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complex interweaving of history, genetics, and culture across the continent. By examining this map, we can appreciate the rich legacy of Indigenous peoples and the ongoing journey of cultural identity in a rapidly changing world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 11, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...