Inbreeding by Country 2025 Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
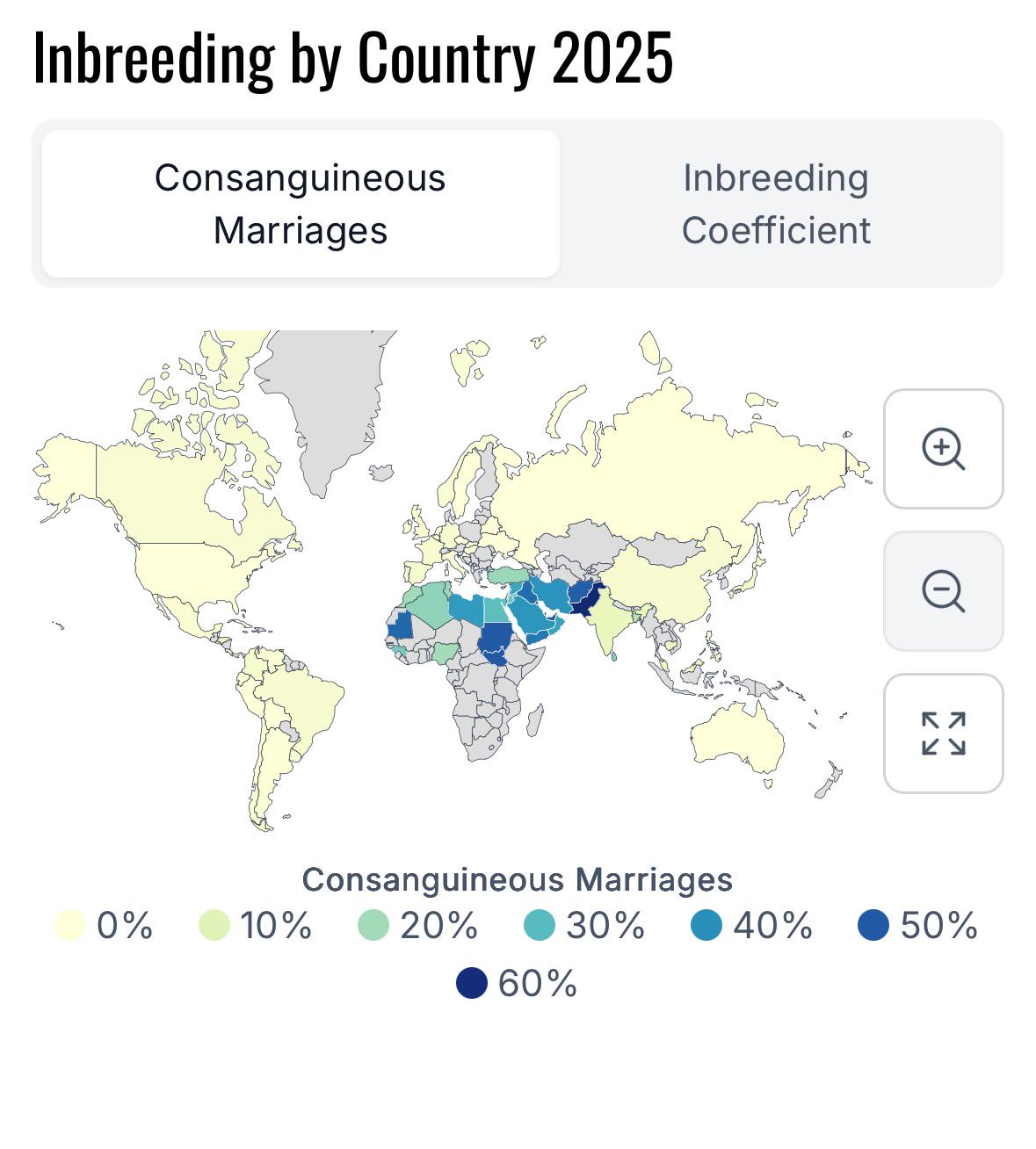
What This Map Shows
The "Inbreeding by Country 2025 Map" provides a visual representation of inbreeding rates across various nations. This map highlights the prevalence of inbreeding, which is often defined as the mating of individuals who are closely related genetically. The map utilizes data sourced from global studies to showcase the percentage of the population that may be affected by this phenomenon in different countries. With varying rates ranging from negligible to significantly high, it presents a striking overview of how inbreeding practices vary worldwide.
Deep Dive into Inbreeding
Inbreeding occurs when closely related individuals reproduce, leading to a higher probability of offspring inheriting genetic defects. This practice can have profound implications for genetic diversity and population health. Interestingly, inbreeding is not just a topic of concern in genetics; it also intersects with cultural, social, and even economic factors.
The prevalence of inbreeding varies significantly across different cultures and regions. For instance, societies with strong traditions of cousin marriage may exhibit higher rates of inbreeding. In some parts of the Middle East and North Africa, cousin marriages are culturally accepted and can lead to increased inbreeding coefficients within communities. Conversely, in regions like Northern Europe, where there are strict societal taboos against such practices, the inbreeding rates are much lower, often falling below 1%.
One of the most significant concerns regarding inbreeding is its impact on genetic health. Studies suggest that populations with high inbreeding rates may experience an increase in genetic disorders. For example, in certain communities in Pakistan, the prevalence of congenital disabilities and genetic diseases is notably higher, a direct correlation to the commonality of cousin marriages. Moreover, this phenomenon raises questions about the long-term viability of such populations, as genetic diversity is crucial for resilience against diseases and environmental changes.
Interestingly, the effects of inbreeding are not uniform; they can vary based on the level of inbreeding and the genetic background of the individuals involved. For instance, some individuals may carry recessive alleles that are harmful when expressed, but remain benign in a heterozygous state. This genetic complexity highlights the necessity of understanding local contexts when analyzing inbreeding's effects.
Regional Analysis
Diving deeper into the map, we can observe distinct regional patterns. In South Asia, particularly in countries like Afghanistan and Pakistan, inbreeding rates can soar as high as 60-70% in some communities. This is often linked to cultural practices that favor marriages within extended families. On the other hand, in more diverse societies such as the United States and Canada, where multiculturalism is prevalent, inbreeding rates are significantly lower, often below 1%. Here, the diversity of the population reduces the likelihood of closely related individuals marrying.
The Middle East presents a complex picture as well. Nations like Saudi Arabia and Jordan see varying rates of inbreeding, with some tribes practicing cousin marriage, while others do not. For example, the Bedouin tribes often engage in cousin marriages, contributing to higher inbreeding rates, while urban populations may exhibit lower rates due to increased social mobility and marriage outside of close familial ties.
In Europe, particularly in Scandinavia, inbreeding is virtually non-existent due to strict societal norms and laws prohibiting such practices. This has resulted in healthier populations with lower incidences of genetic disorders compared to regions with higher inbreeding rates.
Significance and Impact
Understanding inbreeding is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it has substantial implications for public health, particularly in regions where genetic disorders are rampant due to inbreeding. The increased prevalence of certain health issues can strain healthcare systems and impact community well-being.
Moreover, inbreeding can influence the genetic landscape of populations, affecting their adaptability to changes, whether environmental or disease-related. As climate change continues to alter habitats, populations with greater genetic diversity are likely to adapt more readily than those with high levels of inbreeding.
In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the need for genetic counseling in high inbreeding communities. Programs aimed at educating individuals about the potential risks associated with inbreeding are crucial for promoting healthier reproductive choices. With advancements in genetic testing, communities can better understand their genetic health and mitigate the risks associated with inbreeding.
In conclusion, the "Inbreeding by Country 2025 Map" is more than just a visualization; it reflects complex social, cultural, and genetic dynamics that resonate throughout human history. By understanding the implications of inbreeding, we can foster healthier populations and advocate for informed choices across various communities around the globe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 8, 2025
- Views
- 42
Comments
Loading comments...