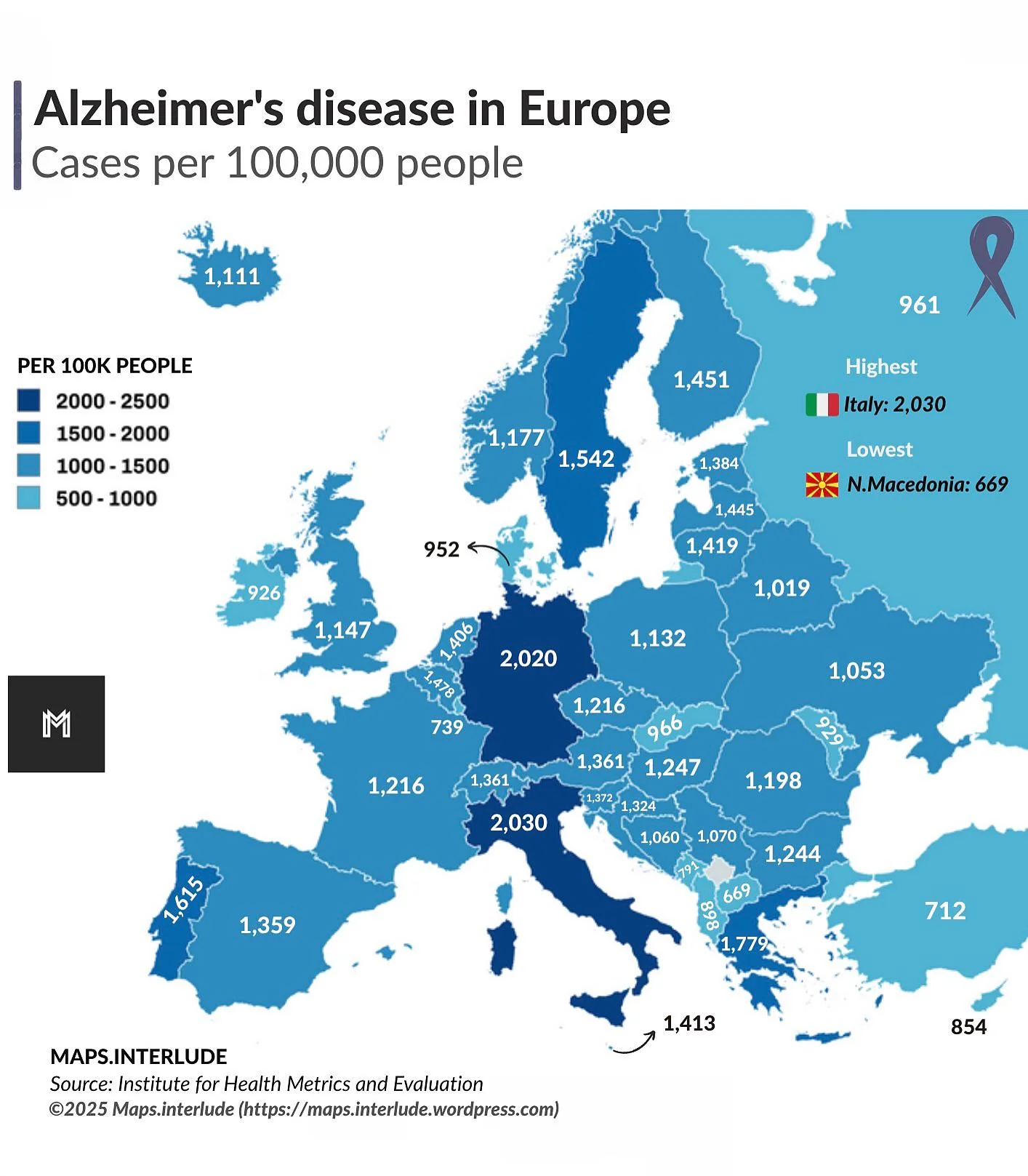
Alzheimer's Disease Prevalence Map in Europe

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Alzheimer's Disease Prevalence in Europe" visually represents the varying rates of Alzheimer's disease across different European countries. The color-coded regions highlight areas with high, medium, and low prevalence rates, providing a clear picture of how this neurodegenerative disease affects populations across the continent. However, this map is not just a collection of statistics; it serves as a critical tool for understanding the broader implications of Alzheimer's disease in Europe.
Deep Dive into Alzheimer's Disease in Europe
Alzheimer's disease, a progressive neurological disorder, is primarily characterized by memory loss, cognitive decline, and changes in behavior. It accounts for 60-80% of dementia cases, making it a significant public health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of people living with dementia is expected to rise to 78 million by 2030, and this number could reach 139 million by 2050. What's fascinating is that the prevalence of Alzheimer's varies widely in Europe, influenced by factors such as age demographics, genetics, healthcare systems, and lifestyle choices.
In examining the specifics, countries such as Germany and Italy report some of the highest prevalence rates, with estimates suggesting that over 1 million individuals in each country are living with Alzheimer's. In contrast, Eastern European nations like Poland and Hungary show relatively lower prevalence rates, which may be attributed to differences in healthcare access, early diagnosis, and public awareness.
Interestingly, while age is the primary risk factor for Alzheimer's, with the majority of cases occurring in people aged 65 and older, other factors also come into play. For example, studies have shown that women are disproportionately affected, comprising nearly two-thirds of individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer's. This gender disparity raises questions about the biological and social factors that might contribute to the higher incidence among women.
Moreover, lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and social engagement can significantly influence the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's. Countries with healthier diets, such as those in the Mediterranean region, may exhibit lower prevalence rates, highlighting the importance of preventative measures. Research indicates that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can contribute to better cognitive health.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map regionally, several noteworthy patterns emerge. Western Europe, particularly the Scandinavian countries like Sweden and Norway, showcases a mix of high awareness and advanced healthcare systems, potentially leading to higher reported prevalence rates. However, this does not necessarily indicate a higher actual incidence; it could also reflect better diagnostic practices and support systems in place.
Southern Europe presents a different scenario. Countries like Spain and Italy not only report significant numbers of Alzheimer's patients but also face increasing challenges as their populations age. Italy, for instance, has a high proportion of elderly citizens, which correlates with its elevated prevalence rates.
In contrast, the Baltic states display lower prevalence rates. Countries such as Estonia and Latvia have made concerted efforts in public health awareness and early detection programs, which may contribute to these lower numbers. Additionally, the socio-economic factors in these regions can impact overall health, thereby influencing Alzheimer's statistics.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the prevalence of Alzheimer's disease across Europe is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it informs policymakers about the necessity of allocating resources for healthcare services, research, and support systems for those affected and their families. The economic burden of Alzheimer's is staggering, costing European countries billions annually due to healthcare expenses and lost productivity.
Moreover, as the population ages, the implications of Alzheimer's disease will become even more pronounced. Current trends suggest that without significant advancements in treatment and prevention, the number of cases will continue to rise. Therefore, it is imperative to foster awareness, improve healthcare access, and encourage lifestyle changes that could mitigate the risk of developing Alzheimer's.
In conclusion, the map of Alzheimer's disease prevalence in Europe serves not only as a representation of data but also as a call to action. It highlights the urgent need for awareness, research, and enhanced healthcare strategies to tackle this growing health crisis. As we move forward, understanding these geographical patterns will be key to addressing the challenges posed by Alzheimer’s disease across Europe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 7, 2025
- Views
- 44
Comments
Loading comments...