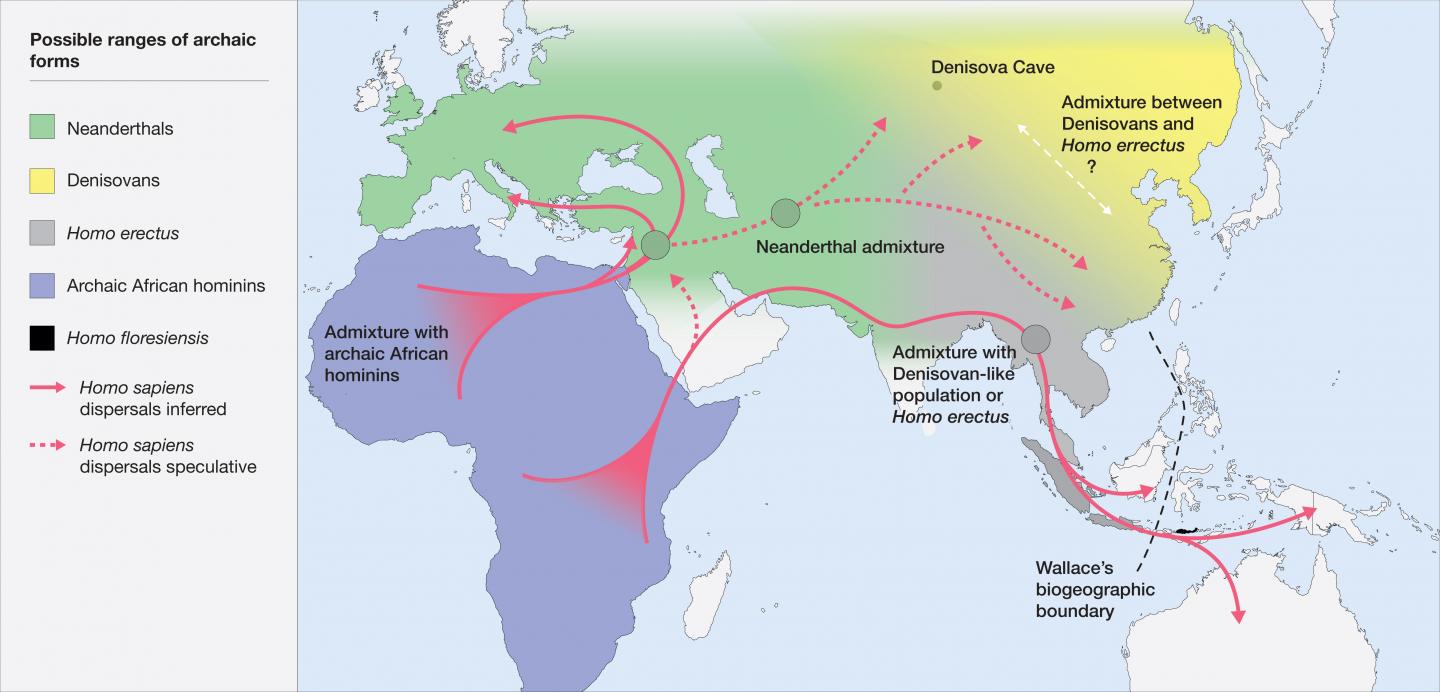
Hominin Distribution Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The Hominin Distribution Map provides a visual representation of the geographical spread of hominin species over time. This map identifies key fossil sites and archaeological findings that shed light on where early humans and their ancestors lived, migrated, and evolved. By combining archaeological data with geological evidence, this map serves as a crucial tool in understanding our evolutionary history.
Deep Dive into Hominin Evolution and Distribution
Hominins, which include all species on the human branch of the evolutionary tree after our split from the chimpanzee lineage, have a rich and varied distribution across the globe. The story of hominin migration is one of adaptation, survival, and exploration. Early hominins began to emerge in Africa around six to seven million years ago, with notable species like *Australopithecus afarensis*, exemplified by the famous fossil Lucy. As we delve deeper into the hominin lineage, we encounter other significant species such as *Homo habilis*, *Homo erectus*, and eventually, *Homo sapiens*.
Interestingly, the map reveals that while Africa served as the cradle of humanity, it was not the only significant region for hominin development. For instance, *Homo erectus* was one of the first hominins to exhibit a migratory pattern, spreading from Africa into parts of Asia and Europe approximately 1.9 million years ago. The adaptability of these early species is highlighted in various archaeological sites across Europe, such as the well-preserved remains found in Spain and Italy.
What’s fascinating is that the map does not just highlight the locations of fossils but also indicates the age of these findings. This temporal aspect allows researchers to track the movement and evolution of hominins through different epochs. For example, the emergence of *Homo sapiens* around 300,000 years ago in Africa is a significant marker. This species then spread across the globe, reaching Europe, Asia, and eventually the Americas.
Another critical point of interest is the role of climate and environment in shaping hominin distribution. During periods of glaciation, for instance, land bridges emerged, allowing for easier migration between continents. Conversely, during warmer interglacial periods, some areas became inhospitable, leading to population contractions. The interaction between climate change and human migration patterns is an ongoing area of research that continues to evolve with new discoveries.
Regional Analysis
Examining regional variations in hominin distribution can reveal much about how different environmental conditions influenced their survival and evolution. In Africa, the high concentration of fossil sites highlights the continent's importance as the evolutionary birthplace. Regions like East Africa, particularly the Great Rift Valley, are rich in hominin fossils, showcasing a timeline of human evolution spanning millions of years.
In contrast, Europe presents a different picture. The discovery of *Neanderthal* remains in areas like the Neander Valley in Germany and the presence of *Homo sapiens* in caves across France indicates a complex interaction between different hominin species. Here, the climatic fluctuations of the Pleistocene era created a dynamic environment that shaped human adaptation and cohabitation.
Asia also plays a crucial role in the story of hominin distribution. The map shows significant findings in regions such as China and Indonesia, where species like *Homo floresiensis* were discovered. These unique hominins adapted to local environments, raising intriguing questions about how geography influenced their physical development and cultural practices.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of hominins is not just an academic exercise; it holds profound implications for our understanding of human history and identity. It informs us about how early humans adapted to diverse environments, which in turn can shed light on our responses to contemporary challenges like climate change and migration.
As we advance our archaeological techniques and technologies, the potential to uncover new sites and information is growing. Future projections indicate that as we delve deeper into uncharted territories, we may find evidence that could reshape our understanding of human evolution. The ongoing study of hominin distribution not only enriches our knowledge of the past but also provides insights into the complexities of human survival in the face of changing environments.
In conclusion, the Hominin Distribution Map serves as a vital resource for researchers and enthusiasts alike. It encapsulates a story of migration, adaptation, and evolution that has shaped who we are today. As our understanding of these ancient species continues to evolve, so too will our appreciation of the intricate tapestry of human history that this map represents.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 6, 2025
- Views
- 44
Comments
Loading comments...