Map of the Main Language Families of the World

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
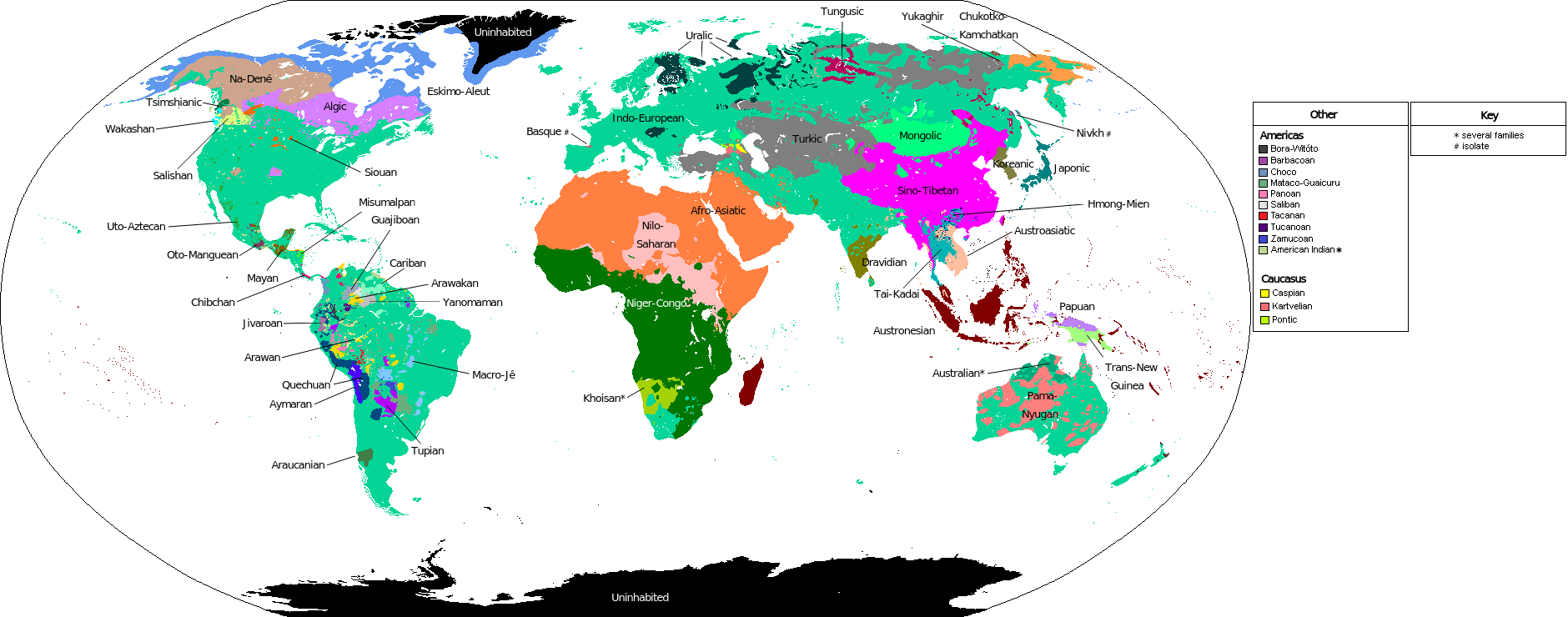
The "Map of the Main Language Families of the World" provides a comprehensive visual representation of the linguistic diversity across the globe. It categorizes languages into families based on their historical and structural relationships, illustrating how languages are interrelated and how they have evolved over time. This visualization not only highlights the geographical distribution of these language families but also offers insights into cultural and historical connections among different peoples.
Language is a fundamental aspect of human identity and communication, and understanding the different families that exist around the world can deepen our appreciation for the diversity of human expression.
Deep Dive into Language Families
Language families are groups of languages that share a common ancestral language. For example, the Indo-European family includes many languages spoken in Europe and parts of Asia, such as English, Spanish, Hindi, and Russian. There are several major language families that dominate the linguistic landscape of the world, each with unique characteristics and historical significance.
Major Language Families
1. **Indo-European**: This is the largest language family and includes languages spoken by nearly half of the world's population. It is divided into several branches, including Germanic, Romance, Slavic, and Indo-Iranian. The spread of Indo-European languages is closely tied to historical migrations and conquests, with English becoming a global lingua franca in recent centuries.
2. **Sino-Tibetan**: Primarily found in East Asia, the Sino-Tibetan family includes Chinese languages such as Mandarin and Cantonese, as well as Tibetan and Burmese. Interestingly, the Chinese writing system is one of the oldest continuously used writing systems in the world, reflecting the deep cultural history of the region.
3. **Afro-Asiatic**: This family encompasses languages spoken in parts of North Africa and the Middle East, including Arabic, Hebrew, and Amharic. Arabic, in particular, has significant cultural and religious importance, serving as the liturgical language of Islam.
4. **Niger-Congo**: Predominantly found in Sub-Saharan Africa, this family contains over 1,500 languages, including Swahili, Yoruba, and Zulu. The sheer number of languages and dialects within this family speaks to the rich cultural tapestry of the African continent.
5. **Austronesian**: Covering a vast area from Madagascar to the Pacific Islands, the Austronesian family includes languages like Tagalog, Hawaiian, and Malagasy. What's fascinating is how these languages reflect the maritime history of the peoples who speak them, as many have words related to navigation and the sea.
The study of language families offers insights into migration patterns, historical interactions, and cultural exchanges. For instance, the spread of the Indo-European languages is often linked to the expansion of agriculture and the domestication of animals, which facilitated the movement of people across different regions.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can see distinct patterns in language distribution. In Europe, the Indo-European family dominates, with languages such as English, French, and German being widely spoken. Interestingly, linguistic boundaries often align with historical borders, showcasing how events like wars and treaties have influenced language spread.
In Asia, the Sino-Tibetan family is predominant, particularly in China, where Mandarin is the most spoken language. However, within the country, there are numerous dialects that can be so different that they are almost mutually unintelligible. In contrast, the diverse languages of the Niger-Congo family in Africa reflect the continent's complex ethnic and cultural landscape. For example, Nigeria alone is home to over 500 languages, underscoring the rich linguistic diversity that characterizes the region.
Significance and Impact
Understanding language families is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the interconnectedness of cultures and the historical journeys that have shaped human societies. Language is not just a tool for communication; it is also a vessel for culture, tradition, and identity. The preservation of languages is vital for maintaining cultural heritage, especially for indigenous languages that are at risk of extinction.
Moreover, as globalization continues to influence the way we communicate, the dynamics of language use are shifting. Languages like English are gaining prominence, often at the expense of local languages. This raises important questions about linguistic diversity and the potential loss of cultural identity.
In conclusion, the "Map of the Main Language Families of the World" serves as a reminder of the rich tapestry of human communication. By understanding the relationships between languages, we can appreciate the cultural narratives that accompany them and recognize the importance of preserving linguistic diversity in an increasingly globalized world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 5, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...