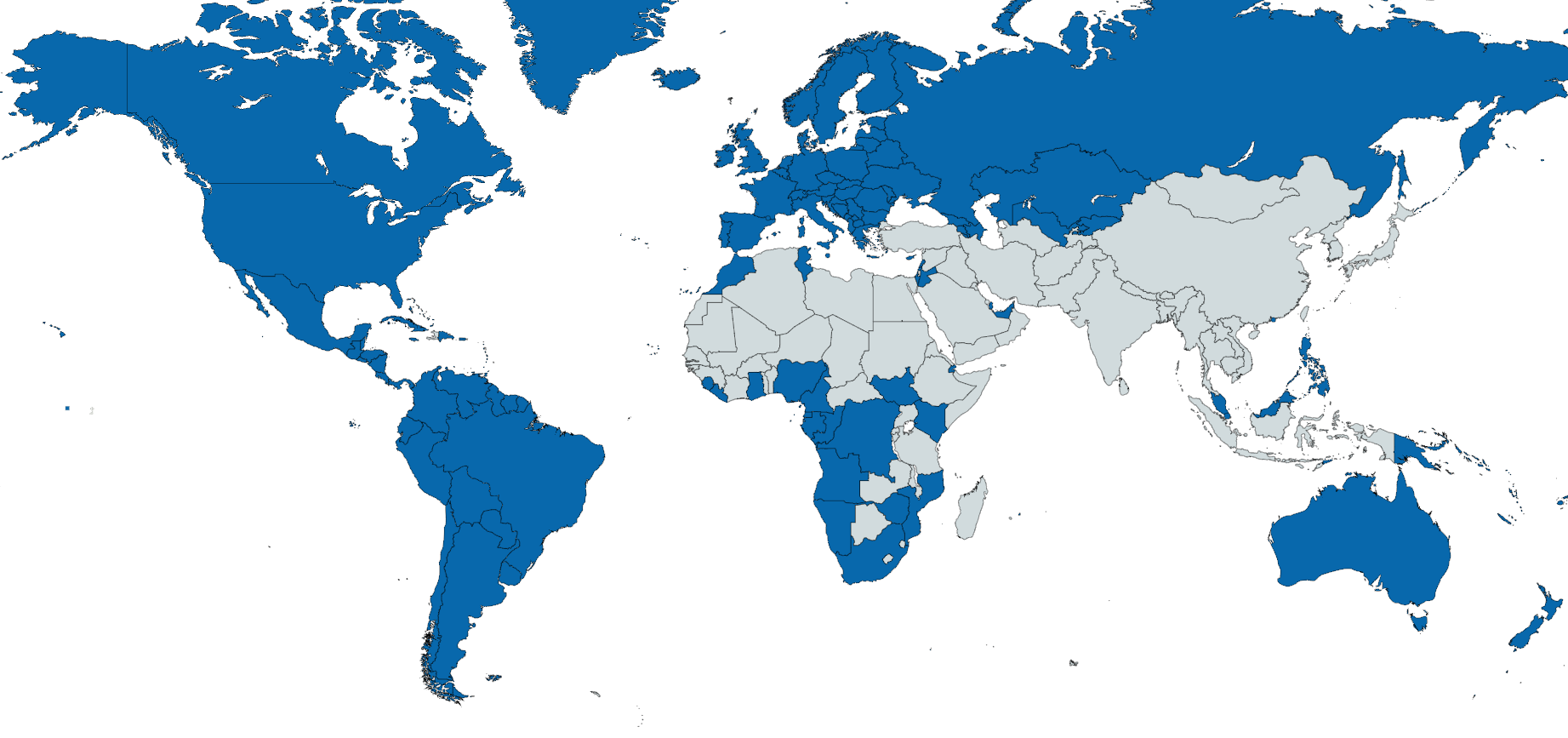
Map of Countries Speaking European Languages

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows\nThis map illustrates the countries where the majority of the population can speak a language that originated in Europe. It’s a fascinating visualization that highlights the linguistic diversity and cultural ties among nations. These languages include widely spoken ones such as English, Spanish, French, and German, among others. What’s interesting is that while many countries have adopted a variety of languages due to globalization and migration, a significant portion of the world's population still identifies primarily with a European-origin language as their mother tongue.
Deep Dive into European Languages\nEuropean languages are part of several major language families, including Indo-European, Uralic, and Turkic. The Indo-European family is the most widely spoken, encompassing languages like English, Spanish, French, Portuguese, German, and Russian. In fact, English alone is a global lingua franca, with millions speaking it as a second language alongside native speakers primarily concentrated in countries like the United States, the UK, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
Interestingly, Spanish is the second most spoken language globally, with significant populations in Latin America and parts of the United States. It traces its roots to the Iberian Peninsula and has evolved into various dialects throughout the world. French, once the lingua franca of diplomacy, remains a major language across parts of Europe, Africa, and parts of North America.
While examining these languages, it’s essential to consider the historical contexts that shaped their spread. Colonialism played a significant role in dispersing European languages across continents. For instance, Spanish and Portuguese colonizers brought their languages to Latin America, while the British Empire's reach facilitated the rise of English as a global language.
Moreover, the presence of languages like German is prominent in Central Europe and is recognized for its rich contributions to art, philosophy, and science. In addition, languages such as Italian and Dutch have maintained their relevance primarily within their respective countries, contributing to the cultural richness of Europe.
Regional Analysis\nIn Europe, the distribution of languages can vary significantly from one country to another. For example, Scandinavian countries like Sweden, Norway, and Denmark primarily speak languages derived from North Germanic roots, while Southern European countries like Italy and Spain showcase Romance languages. Interestingly, the linguistic map reveals that countries such as Belgium and Switzerland are multilingual, with populations speaking Dutch, French, and German.
In Eastern Europe, Slavic languages such as Polish, Czech, and Russian dominate, with Russian being a significant language in several former Soviet states. Countries like Ukraine and Belarus showcase a blend of Ukrainian and Russian, reflecting historical and political influences.
When we look at language prevalence in Africa, we can see the impact of European colonization. Countries like Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia have a significant number of French speakers due to historical ties with France. Similarly, in many parts of Asia, English is widely spoken as a result of British colonial influence, particularly in countries like India and Pakistan.
Significance and Impact\nUnderstanding the linguistic landscape is crucial for various reasons. Language shapes cultural identity, influences social interactions, and plays a vital role in international relations. The prominence of European languages in global contexts underscores issues of cultural imperialism and globalization. Moreover, the dominance of certain languages can affect educational policies, economic opportunities, and social mobility.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of multilingualism cannot be overstated. Countries with a high proficiency in European languages tend to have better access to global markets and international diplomacy. Current trends show a growing interest in learning these languages for business and travel, reflecting the interconnectedness of today’s world.
Looking forward, we can anticipate shifts in language prevalence as migration patterns evolve and technology influences communication. The rise of digital platforms is fostering new forms of linguistic expression, blending traditional languages with modern vernaculars. Ever wondered how these changes will shape future generations’ linguistic identities? The answers lie in our ongoing interactions across cultures and languages, highlighting the dynamic nature of human communication.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 5, 2025
- Views
- 38
Comments
Loading comments...