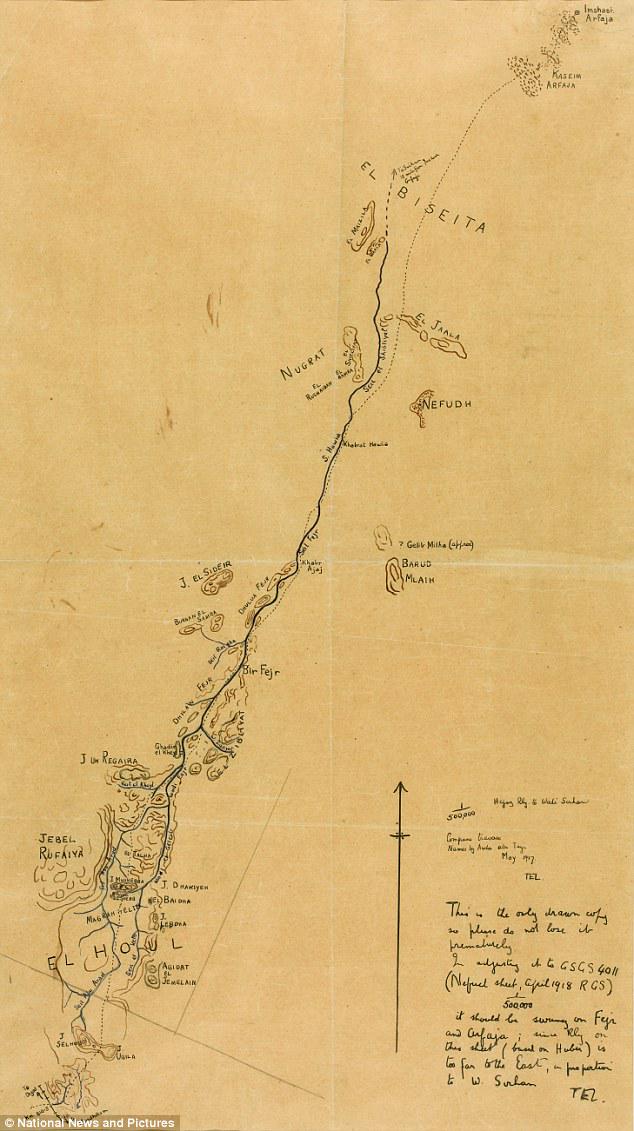
Map of Colonel TE Lawrence's Route in Hejaz

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This hand-drawn map by Colonel T.E. Lawrence, famously known as Lawrence of Arabia, outlines the proposed route taken by him and his Arab allies during a pivotal operation in the Hejaz region during World War I. Created for the guidance of Lawrence and his comrades on May 19, 1917, the map intricately details the path from the port of Al Wejh to Wadi Sirhan, emphasizing the strategic importance of this route in the context of the Arab Revolt against Ottoman rule.
As we delve into the specifics of this map, it's fascinating to consider the geographic and historical significance embedded within its lines. The Hejaz region, located in the northwest of present-day Saudi Arabia, is characterized by its rugged terrain, vast deserts, and critical trade routes that were instrumental during the war. This map is not just a piece of art; it encapsulates tactical planning and the spirit of collaboration among diverse forces fighting for autonomy.
Deep Dive into the Hejaz Region
The Hejaz is a historically significant area, not only for its role in the Arab Revolt but also as a cradle of ancient trade routes. Located along the Red Sea, the region features a mix of mountainous landscapes and arid deserts, making it both a challenging and strategic location for military operations. The map highlights key geographic features, including mountain ranges, valleys, and water sources that would have been crucial for sustaining troops during their journey.
One of the most notable aspects of the Hejaz is its climate, which can be described as arid to semi-arid. This climate has shaped the settlement patterns and lifestyle of its inhabitants. Interestingly, the map indicates various oases along the proposed route, which would have served as vital stops for water and provisions. These oases are not only geographical markers but also cultural hubs where trade and interactions occurred, enriching the social tapestry of the region.
Moreover, the terrain of the Hejaz is varied, with the Sarawat Mountains running parallel to the coastline. These mountains would have provided both challenges and opportunities for Lawrence and his forces. The elevations could serve as natural barriers against enemy forces, while also offering strategic vantage points. In terms of military tactics, understanding the geography of the region allowed Lawrence to engage in guerrilla warfare effectively, disrupting Ottoman supply lines and communications.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the Hejaz region as illustrated in Lawrence’s map, we can compare different areas along the proposed route. For instance, Al Wejh, the starting point, is a coastal town that has historically been a gateway for trade and military operations, serving as a logistical hub. From there, as one travels inland towards Wadi Sirhan, the landscape transitions from coastal plains to more rugged terrain, indicating a shift in both resources and challenges.
Wadi Sirhan, the destination, is situated in a valley that is known for its fertility compared to the surrounding desert. This area was not only strategically significant due to its natural resources but also because it was closer to the Arabian heartland, allowing for easier recruitment and mobilization of local forces. The juxtaposition of these two locations on the map illustrates the careful planning that went into the campaign, as Lawrence needed to consider both the physical geography and the socio-political landscape.
What’s fascinating is how the map reflects Lawrence's understanding of the terrain and the people. He collaborated closely with local tribes, recognizing their knowledge of the land was indispensable for success. This partnership was a crucial factor in the successful execution of the revolt, demonstrating a blend of military acumen and cultural sensitivity.
Significance and Impact
The significance of this map extends beyond the immediate military objectives of the Arab Revolt. It represents a turning point in the fight against Ottoman control and highlights the role of geographic understanding in warfare. Lawrence's ability to navigate the complex terrains of the Hejaz was instrumental in rallying support from various factions and coordinating their efforts against a common enemy.
In a broader context, the map serves as a historical artifact, illustrating the interplay between geography and politics during a transformative period in the Middle East. The strategic routes highlighted on the map continue to be relevant today, as they reflect the ongoing complexities of regional dynamics and the importance of understanding geography in international relations.
As we look at current trends in the region, it’s important to consider how historical maps like Lawrence’s inform our understanding of contemporary geopolitical issues. The legacy of the Arab Revolt and the subsequent formation of nation-states in the region is deeply rooted in the geography that Lawrence so carefully mapped out.
In conclusion, this hand-drawn map is not merely a depiction of a route; it encapsulates a significant moment in history where geography played a crucial role in shaping the destiny of nations. Lawrence's understanding of the land and its people remains a testament to the power of geography in conflict and cooperation.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 4, 2025
- Views
- 38
Comments
Loading comments...