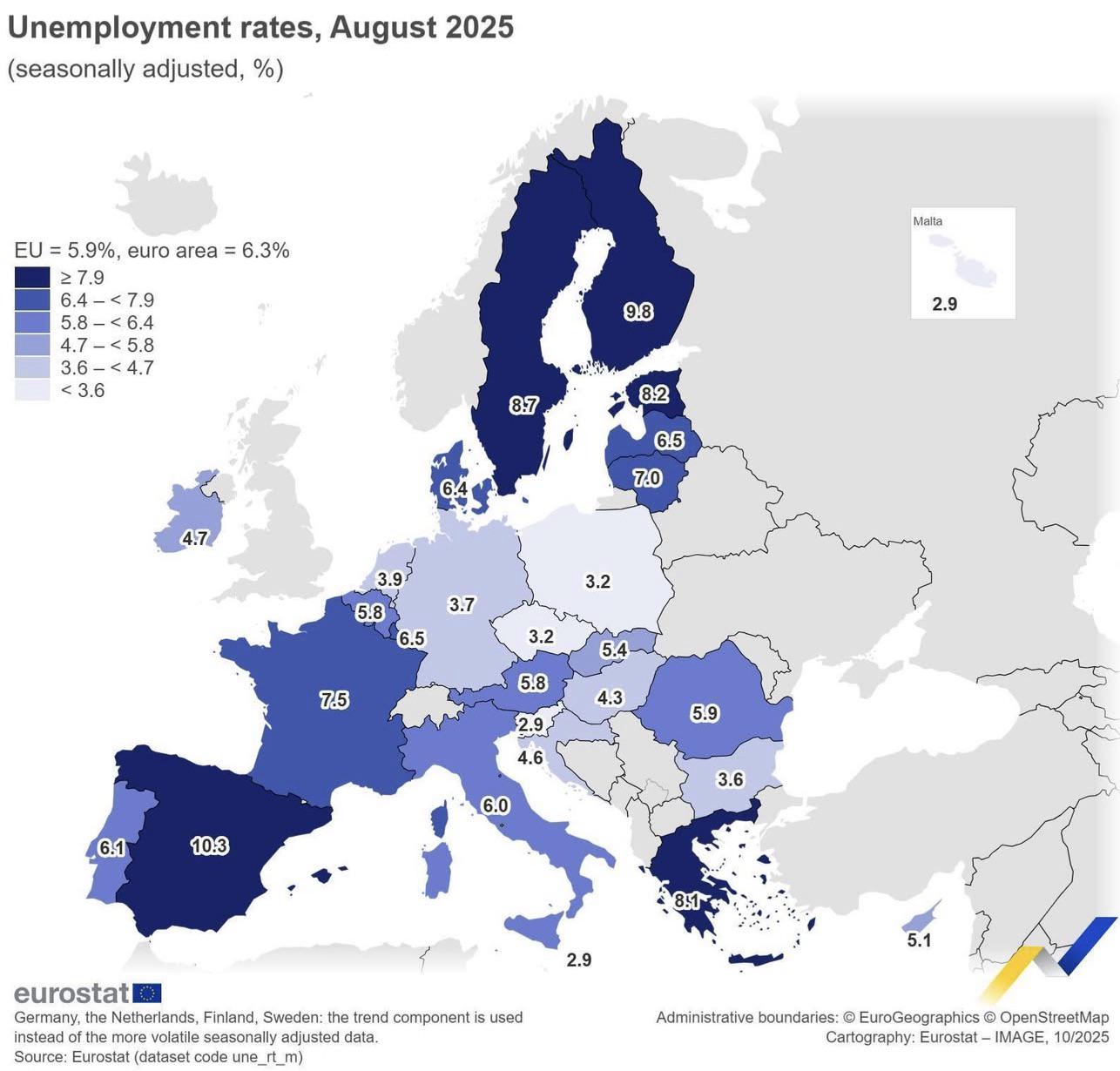
Unemployment Rates in the EU Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Unemployment Rates in the EU, August 2025" map provides a comprehensive visualization of the unemployment landscape across Europe. By illustrating the percentage of unemployed individuals within various EU member states, this map allows us to identify trends, disparities, and areas of concern regarding employment. As we delve deeper into the topic, it's essential to understand the socio-economic factors contributing to these varying unemployment rates.
Deep Dive into Unemployment Rates in the EU
Unemployment is a significant indicator of economic health, reflecting the ability of an economy to provide jobs for its population. In August 2025, the unemployment rates across the EU member states displayed considerable variation, highlighting the complex interplay of economic conditions, labor market policies, and social dynamics. Interestingly, while the EU has made strides towards economic recovery post-pandemic, the shadow of unemployment still looms over certain regions.
As of August 2025, the overall unemployment rate across the EU stood at approximately 6.5%. However, this figure belies the stark differences between member states. For instance, countries like Germany and the Netherlands boasted unemployment rates below 4%, a testament to their robust economic frameworks and effective labor market policies. Conversely, nations such as Greece and Spain faced unemployment rates exceeding 12%, revealing ongoing economic challenges and structural issues that have persisted for years.
One of the critical factors influencing these rates is the variation in economic recovery post-COVID-19. Countries with diversified economies and strong export sectors have rebounded more quickly, leading to job creation. For example, Ireland's tech sector has flourished, reducing unemployment significantly. In contrast, countries heavily reliant on tourism, like Spain, have struggled to regain pre-pandemic employment levels.
Additionally, youth unemployment remains a pressing issue throughout the EU. The overall youth unemployment rate in August 2025 was around 14.5%, with some countries reporting rates as high as 25%. This is particularly alarming as high youth unemployment can lead to long-term economic and social problems, including increased poverty and social unrest. Have you noticed how youth unemployment often reflects broader systemic issues within education and vocational training systems?
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can see how unemployment rates differ regionally across the EU. Northern Europe, particularly the Scandinavian countries, tends to have lower unemployment rates, often attributed to comprehensive welfare systems and active labor market policies that support job seekers. For instance, Sweden and Denmark report unemployment rates hovering around 4%, bolstered by strong social safety nets and an emphasis on continuous education and training.
In contrast, Southern Europe continues to grapple with higher unemployment rates. Countries like Greece, Italy, and Spain are still recovering from the economic fallout of the financial crisis and the subsequent COVID-19 pandemic. Greece's unemployment rate stands at approximately 13%, while Spain hovers around 12%. These figures are indicative of deeper-rooted economic issues, including high youth unemployment and a reliance on sectors that are vulnerable to economic fluctuations, such as tourism and agriculture. Interestingly, regions within these countries showcase stark differences; for example, urban areas may have lower unemployment rates compared to rural regions, which often face higher levels of joblessness.
Eastern European countries like Poland and Hungary have shown resilience with unemployment rates around 3-5%. Their economies have benefited from foreign investments and a growing manufacturing sector. However, challenges remain, particularly concerning labor shortages and the need for skilled workers to meet the demands of evolving industries.
Significance and Impact
Understanding unemployment trends in the EU is crucial not just for policymakers but for society as a whole. High unemployment can have far-reaching consequences, including increased poverty rates, social exclusion, and economic stagnation. As we look ahead, the implications of these unemployment rates may play a significant role in shaping policies and the socio-economic landscape of Europe.
Current trends indicate that countries with proactive labor market policies, such as job retraining programs and support for small businesses, are likely to fare better in the coming years. Furthermore, the ongoing digital transformation and green transition are expected to create new job opportunities, but only if there is adequate preparation and training for the workforce. What’s fascinating is how the future of work will demand a rethinking of education, skills training, and social safety nets to adapt to these changes.
In summary, the "Unemployment Rates in the EU, August 2025" map serves as a critical tool for understanding not just where jobs are lacking but also the broader economic forces at play. As we continue to monitor these developments, it is essential to advocate for policies that address these disparities and support those affected by unemployment across Europe.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 2, 2025
- Views
- 32
Comments
Loading comments...