Uranium Resources Around the World Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
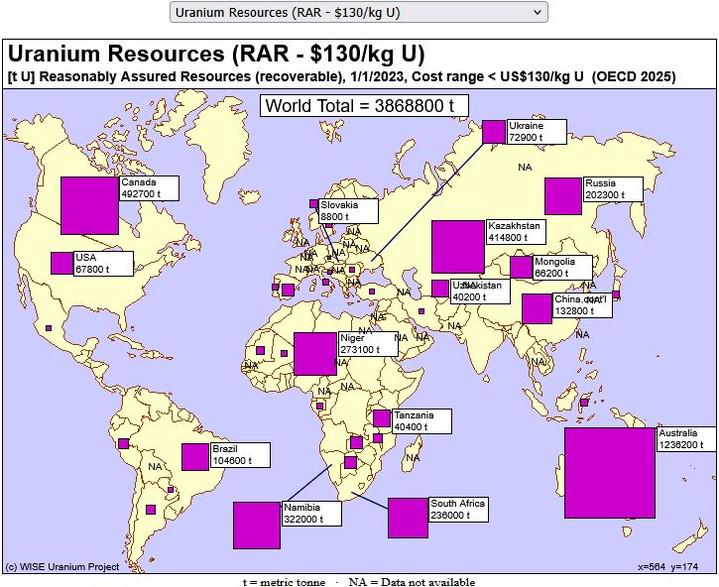
What This Map Shows
The "Uranium Resources Around the World Map" provides a comprehensive visualization of the global distribution of uranium resources, highlighting key regions where uranium deposits are found. This essential mineral, primarily used as fuel for nuclear power plants, plays a significant role in the energy landscape, particularly as countries look for alternatives to fossil fuels. The map visually represents not only the locations of these resources but also their estimated quantities, offering a clear picture of where the world's uranium is concentrated.
Deep Dive into Uranium Resources
Uranium is a heavy metal that is a critical component in the generation of nuclear energy. Its isotopes, particularly U-235, are capable of sustaining nuclear fission reactions, which release a tremendous amount of energy. Interestingly, the abundance of uranium in the Earth's crust is about 2 to 4 parts per million, which is relatively low compared to other minerals. However, what makes uranium particularly valuable is its concentrated deposits, which can be extracted and refined for use in nuclear reactors.
The largest reserves of uranium are found in countries with significant mining operations, such as Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia. Kazakhstan has emerged as the world's leading producer, accounting for over 40% of global uranium production in recent years. The country employs in-situ recovery methods, which are less intrusive and more environmentally friendly than traditional mining techniques. In contrast, Canada is home to some of the richest uranium mines globally, such as the Cigar Lake and McArthur River mines, which have some of the highest grades of uranium ore.
Interestingly, Australia holds the largest identified uranium resources globally, predominantly located in the Olympic Dam and Ranger mines. These mines not only contribute significantly to Australia's economy but also position the country as a key player in the global uranium market. The future of uranium mining in Australia, however, faces challenges, including regulatory hurdles and public opposition to nuclear energy.
In the context of global energy needs, the significance of uranium cannot be overstated. As countries strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, nuclear energy presents a viable alternative. In fact, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) predicts that nuclear power could provide a substantial portion of the world’s energy needs by 2050, making the exploration and responsible extraction of uranium more crucial than ever.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map, it's clear that uranium resources are not evenly distributed across the globe. For instance, North America, particularly the United States and Canada, has historically been a major player in uranium mining, although production has fluctuated due to market conditions and regulatory changes. The U.S. has significant reserves, but domestic production has decreased in recent years, leading to increased imports.
In contrast, Africa also plays a critical role in the global uranium market. Countries like Namibia and Niger are significant contributors, with large-scale mining operations that export uranium to nuclear power plants worldwide. Namibia, in particular, is known for its Rossing and Husab mines, which have been pivotal in supplying uranium to meet international demand.
Additionally, Russia is another key player in the uranium sector, with extensive resources and a robust mining industry. The country's geopolitical influence means that its uranium resources are not just important for energy production but also for international relations, especially with countries looking to secure energy independence.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of uranium resources is vital for several reasons. First, as the world shifts towards cleaner energy sources, the demand for nuclear power is likely to rise, meaning that countries with abundant uranium reserves could see economic benefits. Moreover, the geopolitical landscape could shift as nations vie for control over these essential resources, leading to new alliances and tensions.
What’s fascinating is that the conversation around uranium is not just about energy; it also connects to environmental and safety concerns. Nuclear energy is often seen as a clean alternative to fossil fuels, but the mining, processing, and disposal of nuclear waste raise significant environmental questions. Furthermore, the potential for nuclear proliferation remains a concern for many governments and international organizations.
As we look towards the future, the role of uranium in our energy systems will continue to evolve. Innovations in nuclear technology, such as small modular reactors and advancements in fuel recycling, could change the dynamics of uranium demand and supply. The global approach to uranium mining will need to balance economic interests with environmental and social responsibilities, making this an essential topic for policymakers, environmentalists, and industry leaders alike.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 2, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...