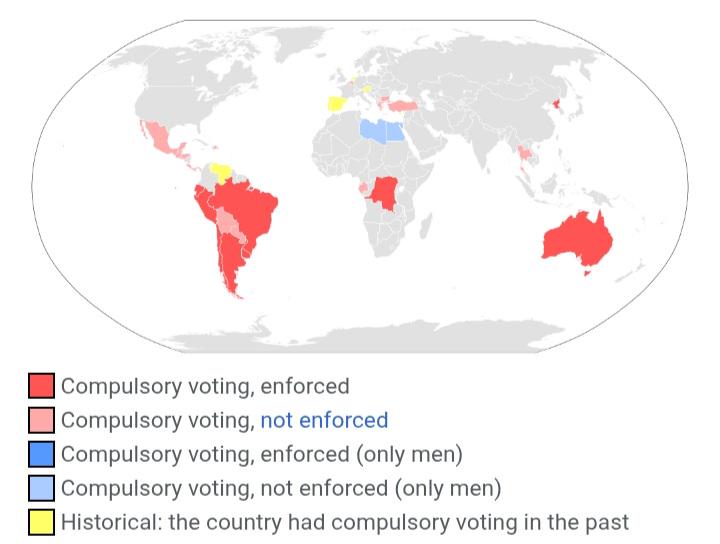
Mandatory Voting Countries Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This visualization highlights countries where voting is mandatory, providing a clear representation of global electoral participation norms. Mandatory voting laws require citizens to participate in elections, often under the threat of penalties for non-compliance. As you explore the map, you’ll notice a mix of countries from various continents, each with its own approach to enforcing civic duty. Interestingly, this practice is relatively rare, with only a select number of nations adopting such laws.
Deep Dive into Mandatory Voting
Mandatory voting is a fascinating topic that touches upon the intersection of democracy, civic duty, and social responsibility. The concept is rooted in the belief that voting is not just a right, but an obligation. Countries that enforce mandatory voting generally aim to increase electoral participation and ensure that the political landscape reflects the will of a larger segment of society.
Take Australia, for example. One of the most well-known examples of mandatory voting, Australia requires eligible citizens to vote and imposes a fine for those who neglect to do so without a valid excuse. Since the introduction of this law in 1924, voting participation rates have consistently hovered around 90%. This high level of engagement ensures that elections are more representative of the populace, leading to a more balanced political climate.
On the other hand, countries like Belgium and Brazil also enforce mandatory voting, with similar results in terms of turnout. Belgium has had mandatory voting since 1893, and the country regularly sees participation rates exceeding 80%. Brazil’s laws date back to 1932, and the country also engages the electorate heavily, with turnout rates that often exceed 75%.
However, the effectiveness and ethics of mandatory voting can be debated. Critics argue that forcing individuals to vote may lead to uninformed choices, as some may simply choose to cast any ballot rather than engage with the candidates and issues at stake. However, supporters contend that the benefits of higher participation outweigh these concerns, as it fosters a sense of civic engagement and responsibility.
Interestingly, some countries, while not enforcing mandatory voting, have implemented measures to encourage participation. For instance, in countries like Canada and the United States, various initiatives, including voter registration drives and educational campaigns, aim to boost turnout without imposing mandatory laws. However, these nations often face challenges with turnout rates, which can dip below 60% in some elections, highlighting the complexities of electoral engagement.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, we can see that mandatory voting is most prevalent in South America and parts of Europe. Countries like Argentina and Uruguay have established mandatory voting systems, reflecting a cultural emphasis on civic duty. In South America, the rationale often ties back to historical contexts where political engagement was seen as a pathway to consolidate democracy, especially post-dictatorship.
Conversely, in regions like North America and parts of Asia, the concept of mandatory voting is absent. The United States, for example, prides itself on the principle of voluntary participation, though it often grapples with lower voter engagement rates compared to its mandatory voting counterparts. This divergence in electoral practices raises questions about how different cultures view the role of government and individual responsibility in democratic processes.
In Europe, while many countries opt for voluntary voting, nations like Belgium and Switzerland stand out as exceptions, showcasing how historical and social factors shape voting laws. Interestingly, Switzerland provides a unique case where voting is not mandatory, yet citizens engage in frequent referendums and votes, demonstrating a different model of civic engagement that still yields high participation.
Significance and Impact
Understanding mandatory voting is crucial as it brings to light the broader implications for democratic participation. Countries that implement such laws often see increased voter turnout, which can lead to more representative governance. High participation rates can also empower marginalized groups, ensuring their voices are heard in the political arena.
However, the challenges of mandatory voting, such as ensuring informed voting, cannot be overlooked. As we move towards the future, the debate surrounding mandatory versus voluntary voting continues to evolve. With the rise of digital engagement and changing societal values, how will countries adapt their electoral systems to meet the needs of modern citizens? Will we see a shift towards more inclusive voting practices, or will mandatory voting gain traction in new regions? These questions highlight the ever-changing landscape of democracy and civic engagement as we navigate the complexities of the 21st century.
Ultimately, the topic of mandatory voting is not just about laws and regulations; it reflects a society's values and commitment to democratic principles. By understanding where and why these laws exist, we gain insight into the functioning of democracy worldwide, shedding light on the various paths nations take to engage their citizens.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 24, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...