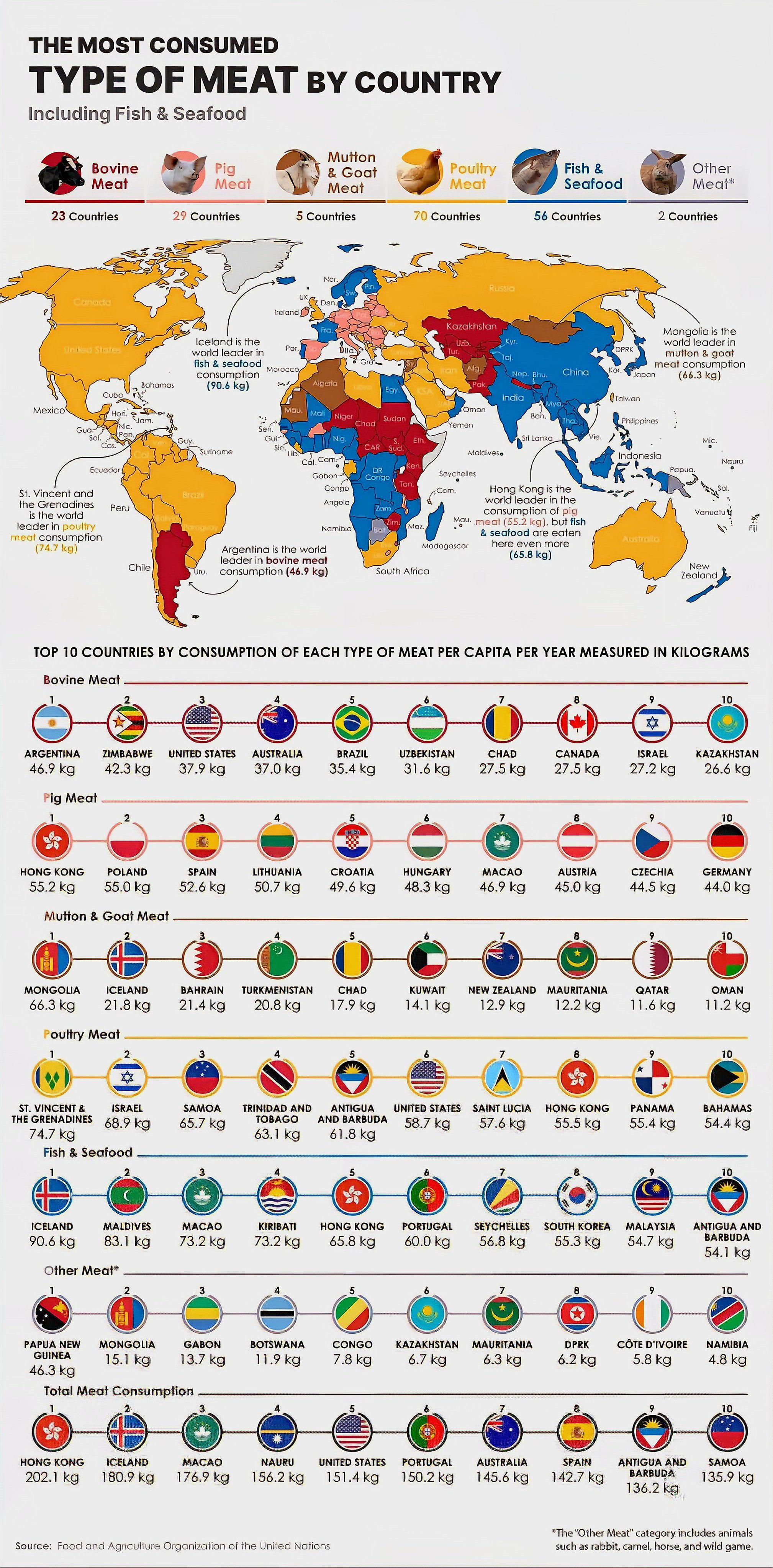
Most Consumed Meat by Country Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map provides a compelling visualization of the most consumed type of meat in various countries around the world. By highlighting the dominant meat choices, it offers insights into cultural preferences, dietary habits, and agricultural practices. From the beef-loving nations of North America to the pork-centric diets of East Asia, this map serves as a window into how meat consumption varies globally.
Deep Dive into Meat Consumption Trends
Meat consumption has been a significant aspect of human diets for centuries, but it varies dramatically from one region to another. The type of meat that predominates in a country often reflects not only culinary traditions but also environmental factors, economic conditions, and religious beliefs.
For instance, pork is the most consumed meat globally, with China being the largest consumer, accounting for nearly half of the world's pork intake. This preference is tied to cultural practices and the adaptability of pigs to various agricultural systems. Interestingly, in predominantly Muslim countries, such as Saudi Arabia and Turkey, pork is notably absent from the diet due to religious prohibitions, which shifts the focus to other meats like chicken and lamb.
Meanwhile, beef consumption is particularly high in countries like the United States and Argentina, where cattle farming is a major part of the agricultural economy. In the U.S., the beef industry is not only a cultural staple but also a significant economic driver, contributing billions to the GDP. What's fascinating is the American barbecue culture, where beef ribs and brisket are celebrated, showcasing how meat can intertwine with national identity and traditions.
On the other hand, poultry, especially chicken, has seen a meteoric rise in popularity worldwide due to its affordability and versatility. In many countries, chicken is considered a staple protein source. For example, Brazil has emerged as one of the largest producers and exporters of chicken meat, driven by both domestic consumption and international demand. This shift towards poultry can be attributed to health trends, as consumers become more conscious about the impacts of red meat on health.
The rise of vegetarianism and veganism also reflects changing attitudes toward meat consumption, especially in Western countries. However, despite these trends, meat consumption continues to rise globally, driven by population growth and increasing incomes in developing countries. As people become wealthier, they tend to incorporate more meat into their diets, leading to higher overall consumption rates.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map, several regional patterns emerge. In Asia, particularly in countries like China and Vietnam, pork is the clear favorite, whereas in Southeast Asia, chicken dominates due to its economic viability and cultural significance. Interestingly, countries such as India show a diverse picture where beef consumption is low due to religious beliefs, and chicken and goat meat are more prevalent.
In Europe, the consumption patterns shift as well; for instance, Spain and Portugal have a strong tradition of consuming pork, while Scandinavia leans more towards beef and lamb. In contrast, countries like Germany and Poland have significant pork consumption rates, showcasing how history and tradition shape these preferences.
Africa presents a mixed scenario. In regions like North Africa, lamb and goat are favored, reflecting pastoral lifestyles, while in sub-Saharan Africa, chicken is increasingly popular as urbanization grows and economic conditions improve.
Significance and Impact
Understanding meat consumption patterns is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the intricate link between culture, economy, and agriculture. Countries that prioritize certain meats often have agricultural practices tailored to support those industries, which in turn affects food security and trade dynamics.
Moreover, as the world faces challenges related to climate change and sustainability, the implications of meat consumption cannot be overlooked. The livestock sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, and as global demand rises, so does the urgency for sustainable farming practices.
Current trends suggest that while meat consumption will likely continue to grow in developing regions, there might be a shift in developed countries towards more plant-based diets. The intersection of health, environmental concerns, and ethical considerations is likely to shape future meat consumption patterns. How will this influence global agriculture? Will we see innovations in lab-grown meats and alternatives gain more traction? Only time will tell, but the map of meat consumption is just one piece of a much larger puzzle in our ever-evolving relationship with food.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 21, 2025
- Views
- 66
Comments
Loading comments...