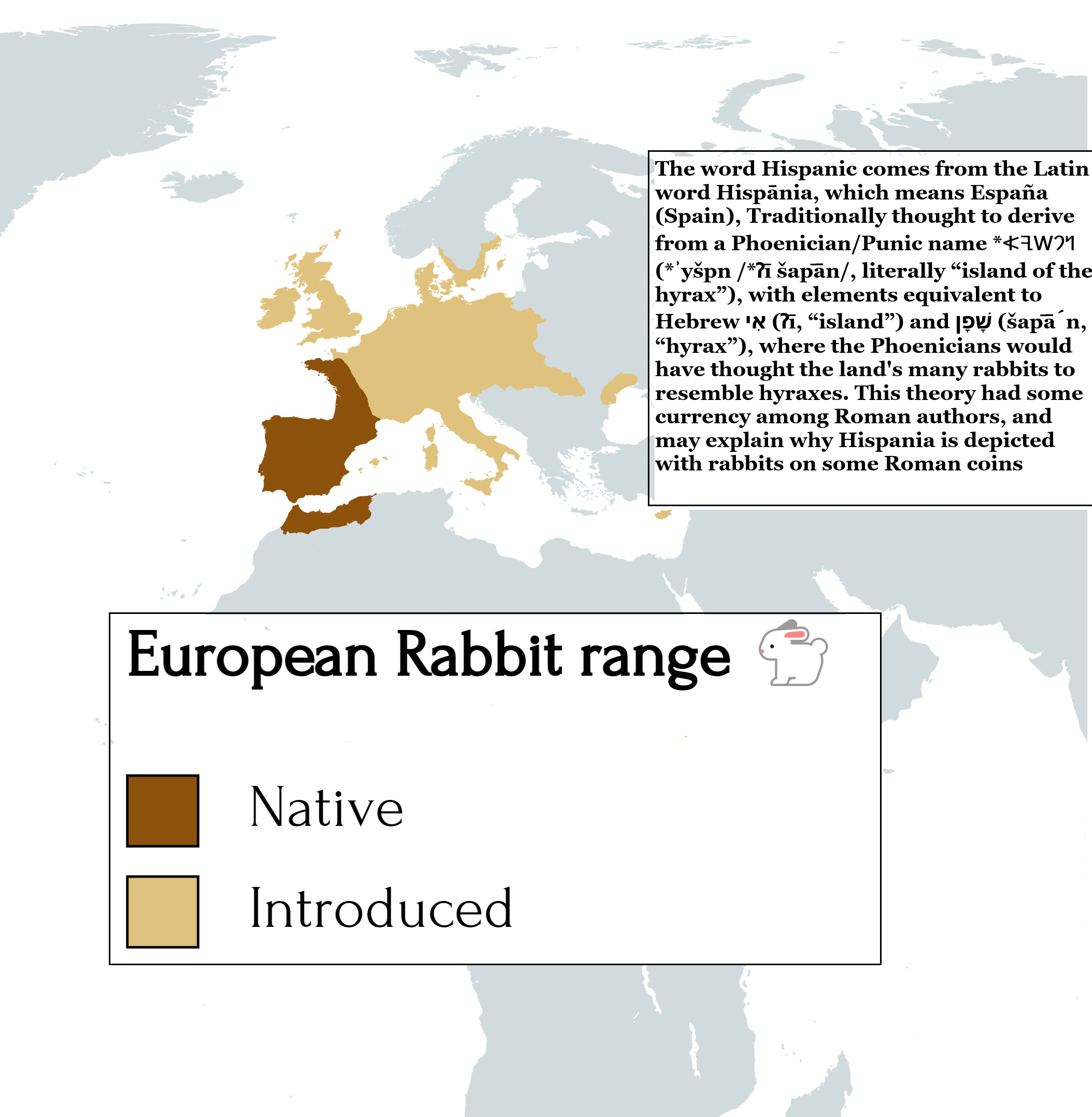
European Rabbit Range Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "European Rabbit Range Map" provides a detailed visualization of the geographical distribution of European rabbits across Europe. This map highlights the areas where these rabbits thrive, illustrating their natural habitat and the regions where they are most commonly found. Understanding this distribution is crucial for conservation efforts, wildlife management, and studying the ecological impact of this species.
Deep Dive into European Rabbits
European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) are fascinating creatures known for their social behavior and significant ecological role. Originally native to the Iberian Peninsula, these rabbits have adapted to various environments across Europe, from lush meadows to arid regions. Interestingly, they have also been introduced to other parts of the world, including Australia and New Zealand, where they have become invasive species, much to the detriment of local ecosystems.
Rabbits are herbivores, primarily feeding on grass, forbs, and leafy weeds. Their diet can significantly impact the vegetation in their habitats, leading to both positive and negative consequences. For instance, while they help maintain grassland ecosystems by grazing, overpopulation can lead to overgrazing, which can degrade habitats and displace native species.
The European rabbit's social structure is another intriguing aspect. They live in complex burrow systems called warrens, where they form large colonies. This social behavior not only aids in their survival but also influences the broader ecological community. The presence of rabbits can attract predators such as foxes and birds of prey, creating a balanced ecosystem that supports various species.
From a conservation perspective, understanding the range of European rabbits is vital. In some areas, they face threats from habitat loss, hunting, and disease outbreaks like rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD). Recent studies have shown that while their populations thrive in certain regions, others are declining rapidly. For instance, in the UK, conservationists are actively working to restore rabbit populations in specific areas to boost local biodiversity. The map serves as a helpful tool in identifying these critical habitats and planning conservation efforts accordingly.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can see that the European rabbit's range is most concentrated in southern and western Europe, with significant populations in countries like Spain, France, and Portugal. In these regions, the climate and landscape are conducive to their survival, with abundant food sources and suitable shelter.
Interestingly, northern Europe presents a different scenario. Countries such as Sweden and Finland have much lower rabbit populations. The colder climate and less favorable habitat conditions limit their distribution, demonstrating a clear correlation between climate and habitat suitability for these animals. In contrast, the Mediterranean regions provide ideal conditions for rabbits due to warmer temperatures and diverse vegetation.
In addition to climate, human activities play a significant role in rabbit distribution. Urbanization and agriculture have led to habitat fragmentation, affecting rabbit populations. In parts of Italy, for instance, traditional farming practices have allowed rabbits to thrive, while in other areas, industrial development has significantly reduced their habitats. Understanding these regional nuances is essential for effective wildlife management and conservation strategies.
Significance and Impact
The distribution and range of European rabbits are not just a matter of ecological interest; they have real-world implications for biodiversity, agriculture, and conservation. As mentioned earlier, rabbits play a crucial role in their ecosystems, influencing plant communities and serving as prey for various predators. Their decline in certain areas can lead to unforeseen consequences, such as an overabundance of specific plant species or a decrease in predator populations.
Moreover, rabbits are significant in agricultural contexts. While they can be pests in some crops, they also contribute to soil health through their burrowing behavior, which aerates the soil and promotes nutrient cycling. Balancing the ecological benefits and agricultural challenges presented by rabbits is a critical task for land managers and farmers alike.
Looking ahead, tracking the range of European rabbits will be crucial as climate change continues to alter habitats. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns may force rabbits into new areas, leading to potential conflicts with existing wildlife and human populations. Thus, ongoing research and updated mapping efforts are essential to ensure the sustainable management of this iconic species in Europe. The European Rabbit Range Map not only serves as a visual representation of their current distribution but also as a vital tool for future conservation efforts and ecological studies.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 19, 2025
- Views
- 54
Comments
Loading comments...