Male Median Income Vs Female Median Income Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
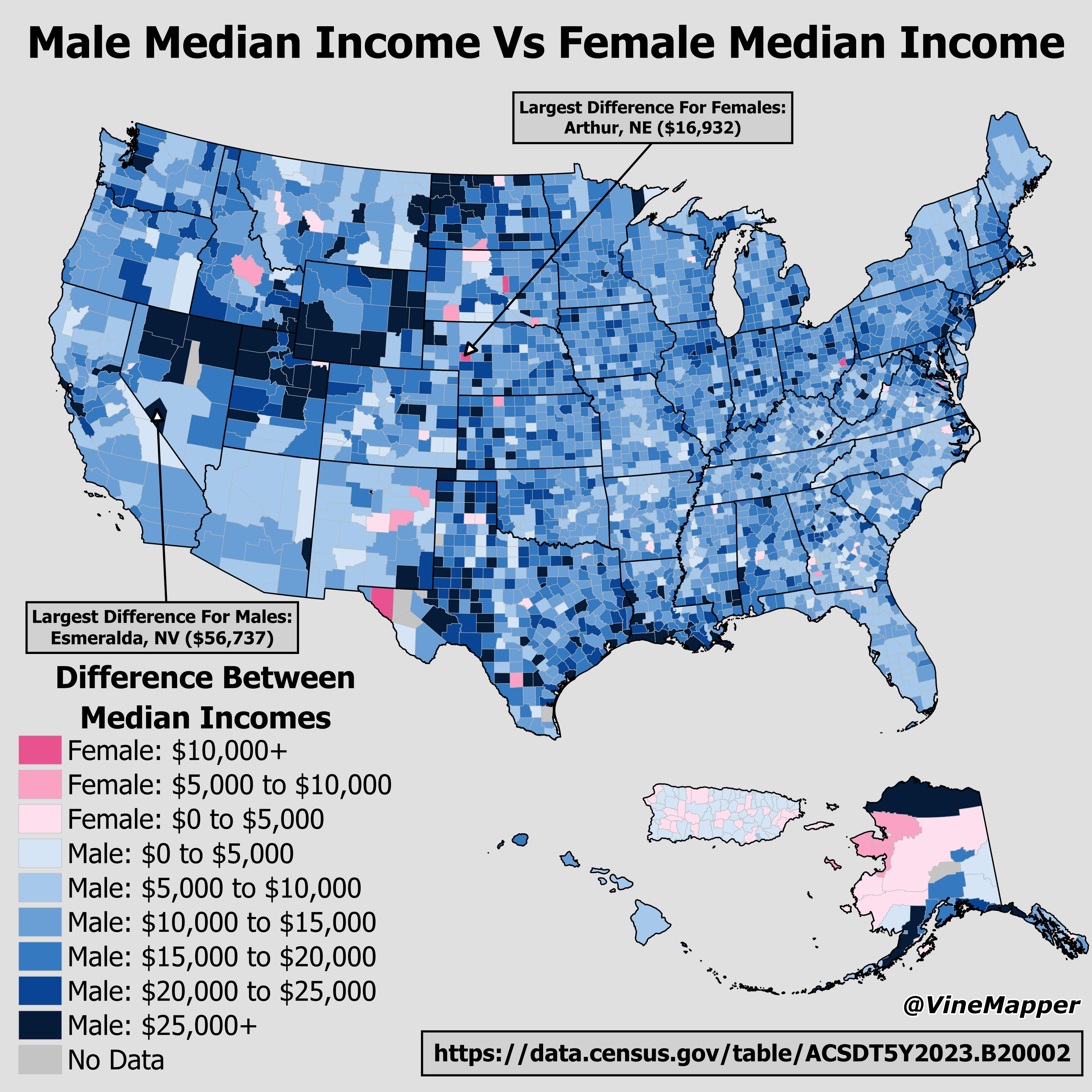
What This Map Shows
The "Male Median Income Vs Female Median Income" map provides a clear visual representation of the income disparities between men and women across different regions. This visualization highlights the median earnings of males compared to females, showcasing the persistent wage gap that exists in various areas. Understanding this data is crucial for recognizing economic inequalities and their implications on society.
Deep Dive into Income Disparities
Income disparity, particularly between genders, is a critical issue that has economic, social, and political ramifications. The concept of median income is essential for understanding how much individuals earn on average, providing a clearer picture than mean income, which can be skewed by extremely high earners. In many countries, the median income for males remains higher than that for females, reflecting systemic issues such as discrimination, occupational segregation, and differences in work experience.
Interestingly, the gender pay gap is not uniform across the globe; it varies significantly by region, industry, and even job roles. According to the World Economic Forum, as of 2022, women globally earned about 63% of what men earned when considering median income levels. In some regions, these disparities are even more pronounced, with women earning less than half of their male counterparts' income.
One of the contributing factors to this gap is the type of work men and women typically pursue. For instance, jobs that are traditionally dominated by women, such as caregiving and teaching, often pay less than male-dominated sectors like technology and engineering. This occupational segregation is a key driver of the income gap. Moreover, women are often underrepresented in leadership positions, which tend to offer higher wages and more opportunities for advancement.
Another important aspect to consider is the impact of education on income. While educational attainment has increased for women over the decades, which has allowed many to enter higher-paying fields, the wage gap persists. Studies indicate that even with equal qualifications, women still face negotiation challenges and biases in hiring practices, which can contribute to lower starting salaries compared to men.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals significant regional variations in the male-to-female income ratios. In Scandinavian countries, for example, the gender pay gap is notably smaller, with policies promoting gender equality and transparency in pay structures. Countries like Iceland consistently rank at the top for gender equality, showcasing a gap of less than 10%, thanks to proactive measures in workplace equality.
Conversely, in regions such as South Asia and parts of the Middle East, the disparities can be stark. For instance, in several countries, women earn less than 40% of what their male counterparts do, reflecting cultural norms and economic structures that limit women’s access to certain jobs and educational opportunities.
In the United States, the gender pay gap has narrowed over the years, yet it still remains a pressing issue, with women earning approximately 82 cents for every dollar earned by men as of 2022. The map indicates that urban areas may present different trends compared to rural regions, where traditional roles may still dominate, influencing income potential for women.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the nuances of male and female median income is essential for addressing broader societal issues, including economic inequality, social justice, and women's rights. The implications of the income gap extend beyond individual earnings; they affect families, communities, and even national economies. When women earn less, it limits their purchasing power and economic independence, impacting their ability to invest in education, healthcare, and housing.
Current trends suggest that while progress is being made, the path toward income equality is slow. Factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic have also exacerbated these disparities, as many women have faced job losses or reduced hours in sectors severely impacted by the crisis, such as hospitality and retail.
As we look towards the future, projections indicate that achieving full gender pay parity may take decades unless significant changes are implemented. This entails not only advocating for equal pay legislation but also fostering an environment where women can thrive in all sectors, breaking the barriers that have historically held them back.
The map serves as a vital tool for policymakers, educators, and advocates to identify where efforts need to be concentrated, making it clear that while some progress has been made, there is still a long way to go in achieving true income equality between genders.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 19, 2025
- Views
- 46
Comments
Loading comments...