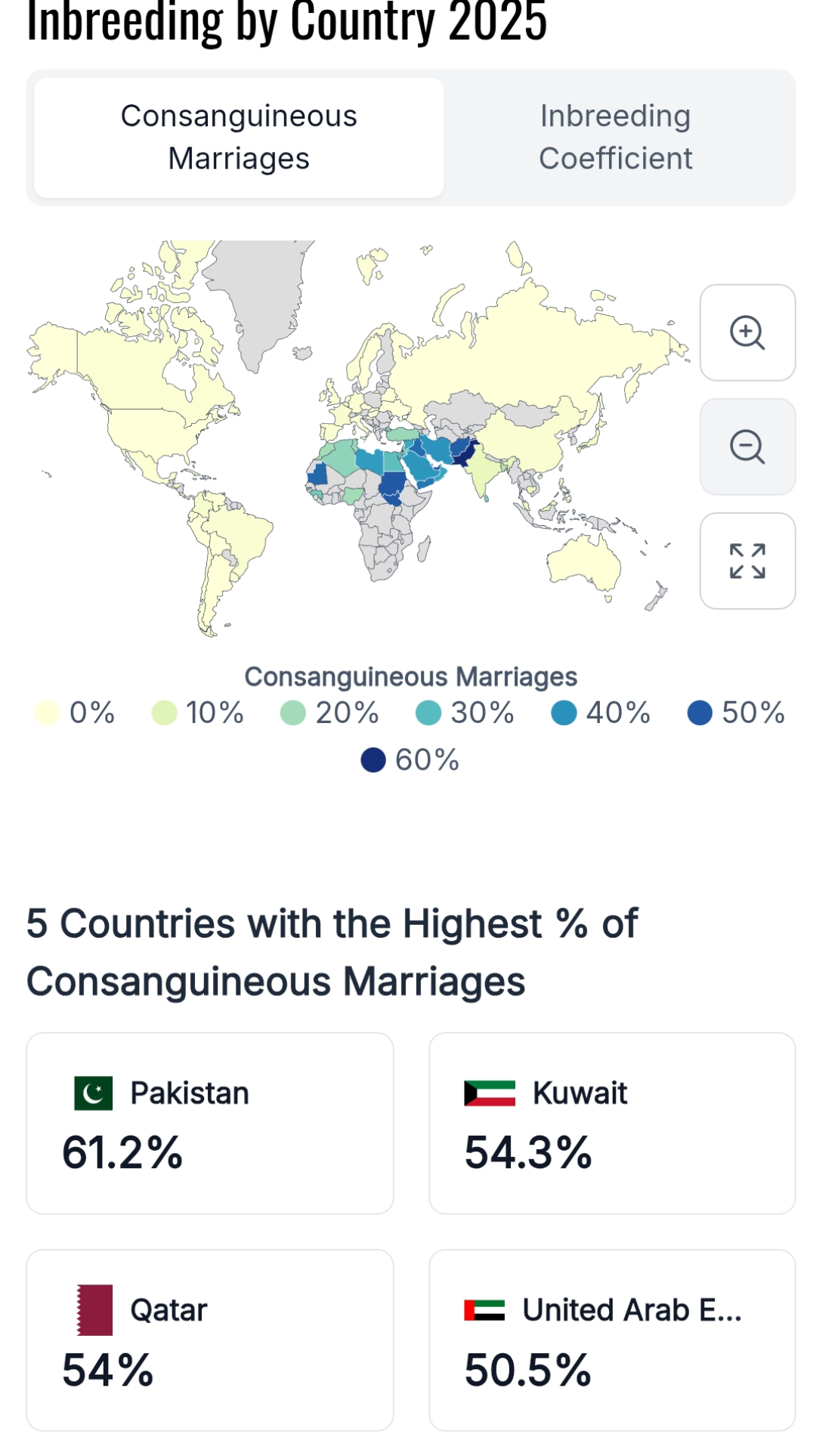
Consanguinity Rates by Country Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map presents an estimated percentage of children globally who are born to consanguineous parents, defined as parents who share a close blood relationship, such as cousins or other close relatives. The visualization highlights the varying prevalence of this practice in different regions of the world, illustrating the cultural and social factors that influence family structures and reproductive choices.
Deep Dive into Consanguinity
Consanguinity, the practice of marrying within one's own family, has deep historical and cultural roots. It is often seen in societies where family ties and lineage are of paramount importance. Have you ever wondered why certain areas have higher rates of consanguinity? Factors such as geographic isolation, cultural traditions, and even socio-economic conditions play significant roles in these patterns.
In many Middle Eastern and South Asian countries, for instance, it's estimated that up to 40% of marriages may be consanguineous. Interestingly, these regions often emphasize extended family networks, which can lead to a higher prevalence of cousin marriages. Studies have shown that such unions can increase the risk of genetic disorders, as they may lead to a higher likelihood of inheriting recessive genetic conditions.
On the other hand, in many Western nations, the rates of consanguinity are markedly lower, often below 2%. This decline can be attributed to increased mobility, changing social norms, and a greater emphasis on genetic health awareness. In these societies, marrying outside one’s immediate familial or ethnic group is more common, thereby reducing the chances of genetic complications.
Globally, it’s estimated that 8-12% of children are born to consanguineous parents. This figure can vary widely depending on local customs and laws. For instance, in countries like Egypt, where approximately 30% of marriages are consanguineous, there is a notable prevalence of genetic conditions such as thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Conversely, regions such as Scandinavia report much lower rates of consanguineous births, with more focus on genetic counseling and education.
The implications of consanguineous unions extend beyond genetics. They often influence social structures, inheritance laws, and even healthcare policies. For example, in cultures where consanguinity is common, there may be a tendency to prioritize kinship ties over individual merit, affecting social mobility and access to resources.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can identify distinct patterns of consanguinity across various regions. In the Middle East, countries like Saudi Arabia and Pakistan stand out with the highest estimated rates, often attributed to cultural traditions that favor cousin marriages. In contrast, regions such as North America and Western Europe show significantly lower percentages, reflecting not only cultural diversity but also the impact of modern medical practices and increased public awareness regarding genetic health.
In Africa, consanguinity rates vary widely. Northern African countries often mirror Middle Eastern trends, while sub-Saharan nations display a broader range of practices influenced by local customs and tribal affiliations. For example, in Nigeria, where ethnic diversity is high, consanguinity is less common among certain groups, whereas others still practice cousin marriages, highlighting the complex interplay of culture and genetics.
Interestingly, in East Asia, particularly in countries like Japan and South Korea, consanguinity is also low due to social stigma and legal restrictions against cousin marriages. This reflects a societal shift towards valuing genetic health and diversity, with awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about potential genetic risks.
Significance and Impact
Understanding consanguinity is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it has significant health implications. Genetic disorders can arise more frequently in populations with high rates of consanguineous marriages. This raises public health concerns and necessitates the need for genetic counseling and education, particularly in regions where such practices are prevalent.
Moreover, the topic of consanguinity connects to broader discussions about cultural identity, social structure, and public health. As societies evolve, the dynamics of marriage and family are also changing. Current trends suggest a gradual decline in consanguinity rates in many parts of the world, driven by globalization, urbanization, and shifts in societal values. Looking ahead, it will be fascinating to see how these changes impact genetic diversity and public health initiatives globally.
In conclusion, the consanguinity rates map serves as a vital tool for understanding not just the genetic implications but also the cultural narratives that shape human relationships across the globe. As we continue to explore these patterns, we gain deeper insights into the intricate fabric of human society and health.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 18, 2025
- Views
- 106
Comments
Loading comments...