Angel Mounds Lordship Map of 14th Century Kentucky

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
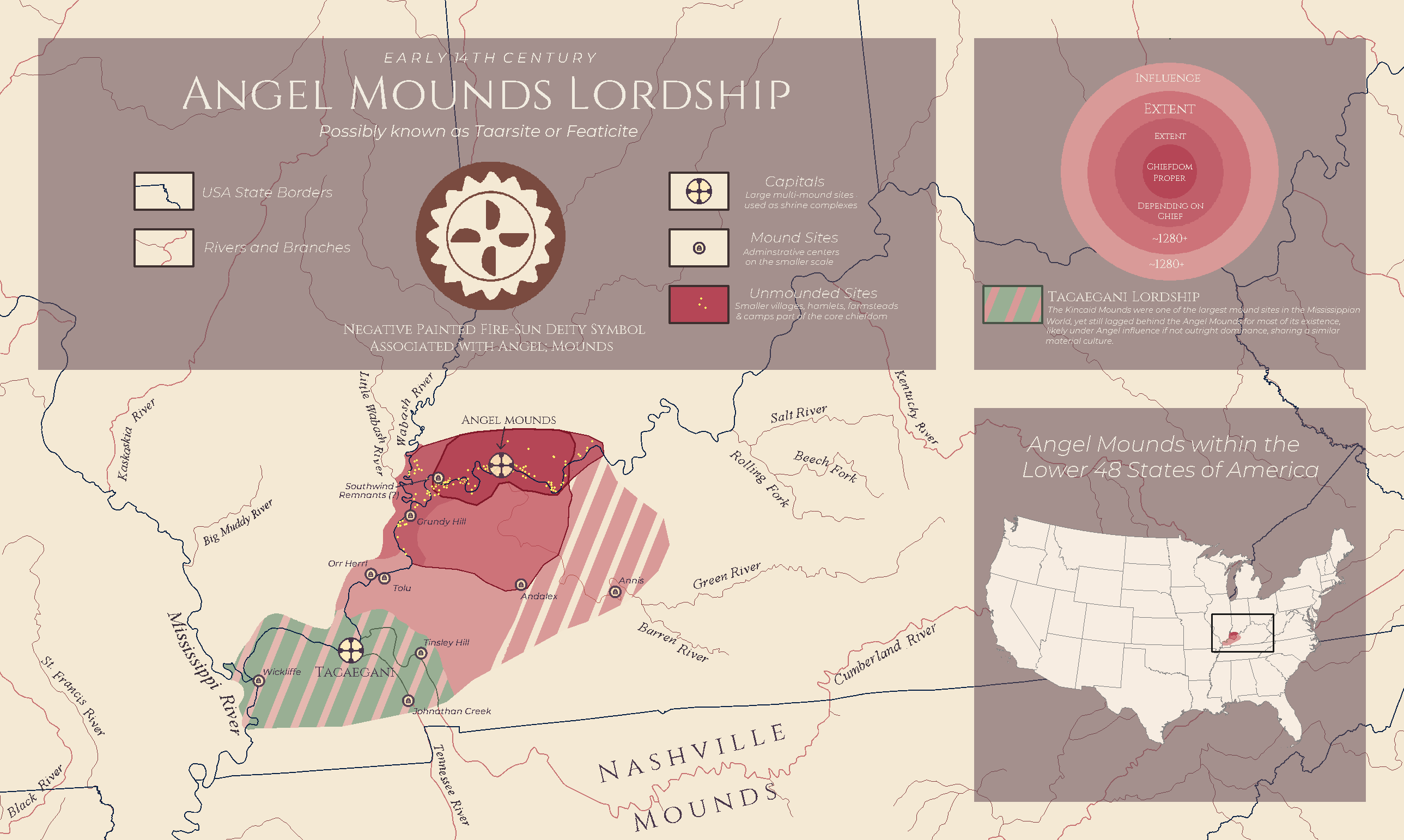
The "Angel Mounds Lordship: 14th Century Kentucky Map" provides a fascinating glimpse into the socio-political landscape of Kentucky during the 14th century. It highlights the locations and boundaries of the Angel Mounds, an important archaeological site that reflects the power dynamics and territorial claims of the indigenous peoples during that period. This map serves as a visual representation of the extent of the Angel Mounds lordship, showcasing the area’s geographical features, including rivers, forests, and settlement patterns. By examining this historical context, we can better understand the lives and governance of the Mississippian cultures that thrived in this region.
Deep Dive into Angel Mounds and Indigenous Governance
The Angel Mounds, located near present-day Evansville, Indiana, were among the most significant urban centers of the Mississippian culture, which flourished from around 800 CE to 1600 CE. This civilization was characterized by complex societies that engaged in extensive trade networks and had hierarchical political structures. The 14th century marked a pivotal time for these communities, as they navigated both internal dynamics and external pressures.
Interestingly, the map illustrates how the Angel Mounds served not only as a residential area but also as a ceremonial center. The large earthen mounds, which were constructed for religious and political purposes, acted as focal points for the community. These mounds were often used for burials, rituals, and gatherings, signifying their importance in reinforcing social cohesion and leadership.
At its peak, the Angel Mounds site likely had a population of several thousand, making it a bustling hub of activity. The governance structures at Angel Mounds were complex; leaders wielded considerable power, often linked to their lineage and religious authority. The map allows us to visualize the spatial organization of the settlements, with evidence suggesting a stratified society where elite classes lived closer to the mounds and access to resources was closely regulated.
An essential aspect of Mississippian culture was their agricultural practices, which were highly developed. The fertile floodplains surrounding the Ohio River provided rich soil for crops like maize, beans, and squash, staples that supported the population. The map's depiction of these agricultural zones helps us comprehend the land-use patterns and the importance of agriculture in sustaining the communities.
Regional Analysis
The geographical context of the Angel Mounds is crucial for understanding its influence over the surrounding areas. Kentucky, during the 14th century, was characterized by various ecological zones, which shaped the livelihoods of different groups. The regions to the north, characterized by forested areas, provided ample hunting grounds, while the southern areas, closer to the river, were more suited for agriculture.
Interestingly, the map suggests that the influence of the Angel Mounds extended into neighboring territories. This kind of regional dominance is evident in the trade networks that connected communities across the Ohio River Valley. For instance, artifacts found in the area, such as pottery and tools, indicate extensive trade relationships with tribes in what is now Illinois and Ohio. The map also highlights the interactions between different cultural groups, showcasing how trade routes and territorial boundaries were not static but evolved over time, influenced by alliances, conflicts, and environmental factors.
Moreover, the strategic positioning of the Angel Mounds near waterways facilitated transportation and communication, making it easier to maintain control over trade routes and resources. This geographical advantage helped solidify the power of the Angel Mounds lordship, enabling it to exert influence far beyond its immediate borders.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the dynamics of the Angel Mounds lordship is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it sheds light on the sophisticated governance systems developed by indigenous cultures long before European contact. The societal structures and political organization evident in the 14th-century Angel Mounds challenge the perspective that pre-colonial Americas were populated solely by nomadic tribes; instead, they reveal a tapestry of complex societies with rich histories.
Moreover, studying this map and its context allows us to appreciate the profound connections between geography and culture. The way indigenous peoples adapted to their environment, utilizing the land's resources sustainably, offers valuable lessons today as we grapple with issues of land use and environmental stewardship.
As we look ahead, the legacy of the Angel Mounds and similar sites continues to impact discussions around cultural preservation and indigenous rights. Current trends in archaeology and anthropology emphasize the importance of recognizing and honoring these historical sites, ensuring that they are preserved for future generations. The insights gained from maps like this one can inspire a deeper understanding of our shared history and the interconnectedness of human societies across time and space.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 18, 2025
- Views
- 64
Comments
Loading comments...