Gravity Map of the Moon

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
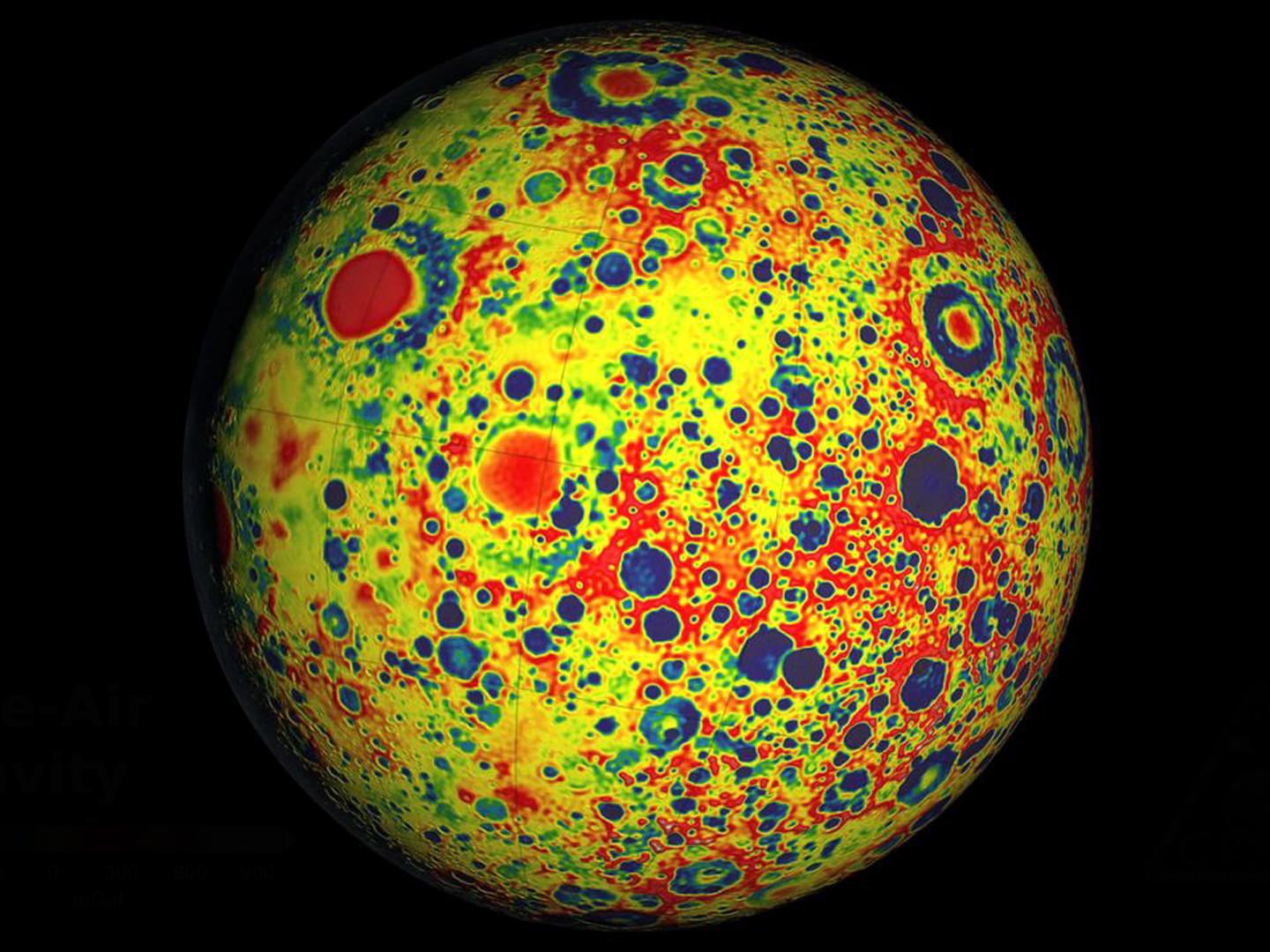
The Gravity Map of the Moon, created through NASA's GRAIL (Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory) mission, provides a detailed visualization of the Moon's gravitational field. This gravity map employs a color-coding system where red indicates areas of mass excess, while blue signifies regions of mass deficiency. This innovative mapping allows scientists and enthusiasts alike to understand the Moon's geological features and internal structure better than ever before.
Deep Dive into Lunar Gravity
Gravity on the Moon varies significantly due to its uneven distribution of mass. Unlike Earth, the Moon lacks a significant atmosphere, and its lower gravity (about one-sixth that of Earth) plays a crucial role in how we perceive its surface features. The gravity field reflects the Moon's complex geological history, including volcanic activity, impacts from asteroids, and the formation of its crust.
Interestingly, the Moon's gravitational anomalies are primarily attributed to its crust's thickness and the distribution of mass below the surface. For instance, the large, circular basins formed by ancient meteorite impacts, such as the Imbrium and Serenitatis basins, show a mass excess due to the dense materials that were ejected during the impacts. These areas are often depicted in red on the gravity map, indicating where scientists may find denser rock formations and potential mineral deposits.
Additionally, the blue regions on the map indicate areas where the Moon's mass is less than expected. These could be attributed to variations in crust thickness or potentially underlying voids created by volcanic activity. An example of this can be seen in the areas surrounding the Oceanus Procellarum, which reveals intriguing insights into the Moon's volcanic past and its geological evolution over billions of years.
Regional Analysis
The GRAIL gravity map allows for a regional analysis of the Moon's surface. For instance, the eastern hemisphere, particularly the South Pole-Aitken basin, shows significant mass deficiency, suggesting that this ancient impact site has less dense material than surrounding areas. This contrasts sharply with the western hemisphere, where the Imbrium basin exhibits a pronounced mass excess, making it one of the Moon's most geologically dynamic regions.
Furthermore, the Mare regions, including Mare Tranquillitatis and Mare Crisium, are notable for their relatively low gravitational anomalies. These regions are primarily composed of basaltic lava flows, which contribute to their density characteristics and impact the overall gravity field. In contrast, the highland areas, with their heavily cratered terrain, tend to show greater gravitational anomalies due to their thicker crust and elevated topography.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the Moon's gravity field is vital for several reasons. First, it provides insights into the Moon's internal structure, including its crust and mantle composition. This knowledge is crucial for future lunar exploration missions, especially those aiming to establish a permanent human presence on the Moon. The data gleaned from the gravity map can inform where to land spacecraft, how to gather resources, and where to set up lunar bases.
Moreover, studying the Moon's gravity helps scientists draw parallels with Earth and other celestial bodies. By understanding the Moon's geological history and processes, researchers can gain insight into planetary formation and evolution across the solar system. Current trends suggest that as we prepare for missions to Mars and beyond, the Moon will serve as an essential stepping-stone in our quest to explore the cosmos further.
In conclusion, the Gravity Map of the Moon is more than just a colorful representation of gravitational data; it is a window into understanding our celestial neighbor's history, composition, and future exploration potential. As we continue to advance in space exploration, the insights gained from this remarkable map will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the Moon and beyond.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 16, 2025
- Views
- 70
Comments
Loading comments...