Identified Settlements in 16th Century Palestine Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
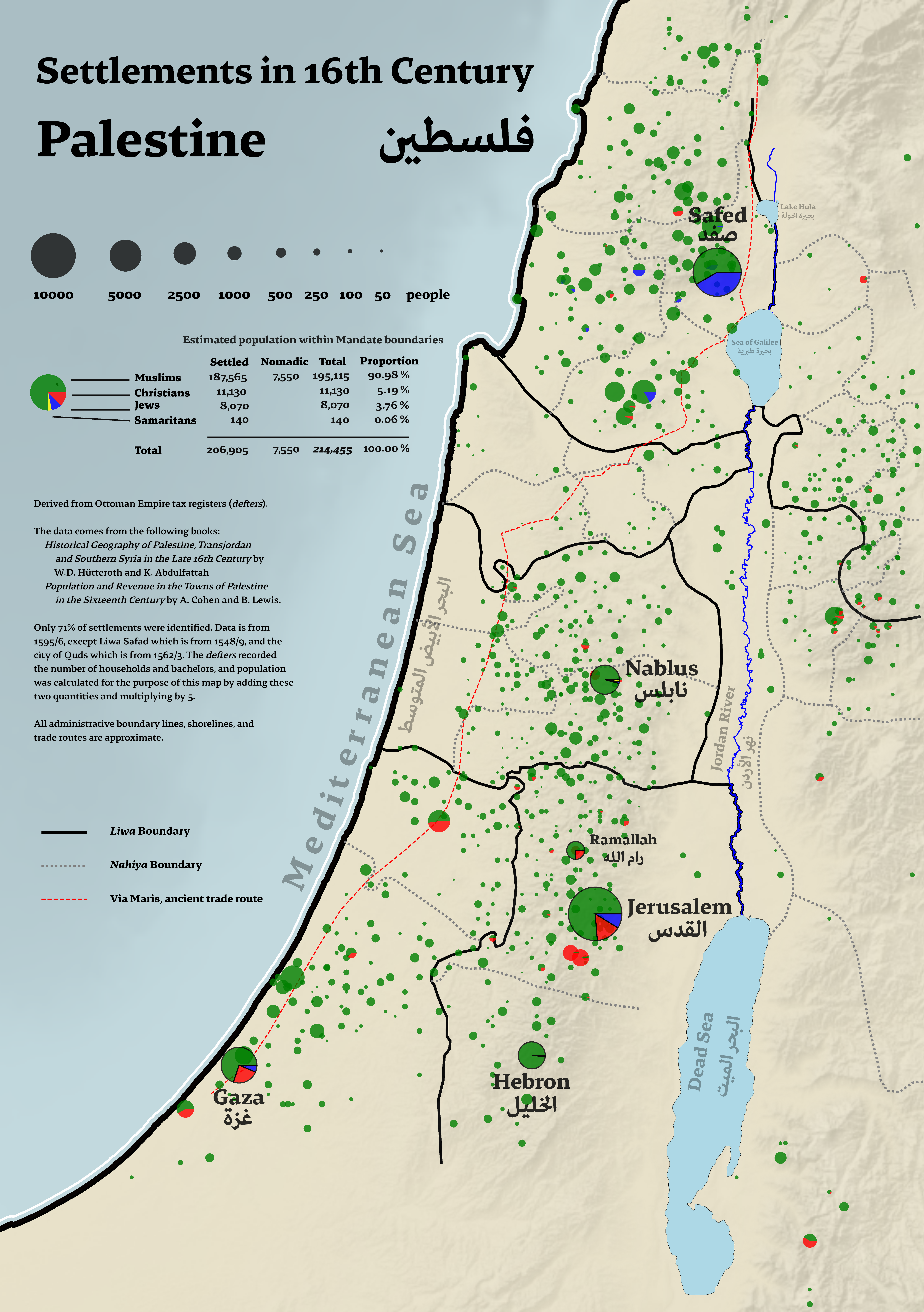
What This Map Shows
The "Identified Settlements in 16th Century Palestine Map" provides a detailed look at the various settlements that existed in Palestine during the 16th century. It highlights key cities, towns, and villages across the region, offering insights into the demographics, trade routes, and cultural hubs of that era. This historical visualization serves as a foundation for understanding the geographic and socio-political landscape of Palestine in a time of significant transition, particularly under Ottoman rule.
Deep Dive into 16th Century Settlements
The 16th century was a pivotal period for Palestine, characterized by the establishment and development of numerous settlements. The Ottoman Empire, which ruled the region from 1517, implemented administrative changes that influenced urban planning and settlement patterns. Urban centers like Jerusalem, Hebron, and Nablus thrived, serving as major hubs of trade, religion, and culture.
Interestingly, the 16th century saw the flourishing of Jerusalem, which was not only a spiritual epicenter for Jews, Christians, and Muslims but also a bustling trade city. The Ottoman authorities invested in the city's infrastructure, enhancing its appeal as a pilgrimage destination. The city's walls were reconstructed, and new religious structures were built, which attracted inhabitants and visitors alike. Have you noticed that many of the significant historical sites today, such as the Dome of the Rock and Al-Aqsa Mosque, date back to this period?
Moreover, smaller settlements like Safed became prominent due to the Kabbalistic movement, drawing scholars and mystics, which contributed to the town's growth. On the other hand, towns like Tiberias were pivotal due to their proximity to the Sea of Galilee, which supported fishing and trade. The map showcases how geography influenced settlement patterns, with many towns strategically located near water sources or trade routes.
The demographic distribution was diverse, with various ethnic and religious communities cohabiting in these settlements. This diversity is reflected in the architecture and cultural practices seen in the area today, as many structures from that time still stand. The settlements were not just places of residence but also centers for agriculture, craftsmanship, and scholarship. The economic activities of these settlements were closely tied to the land, with agriculture being a primary livelihood for many, especially in regions with fertile soil.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map regionally reveals fascinating contrasts in settlement patterns. For instance, in the northern parts of Palestine, settlements such as Nazareth and Acre show a blend of agricultural and maritime economies. Interestingly, Acre, with its significant port, became a critical trade point connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. The map indicates that these northern settlements were more influenced by Mediterranean trade routes compared to the inland areas.
Conversely, the central region, featuring Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and Hebron, was deeply influenced by religious significance and pilgrimage. This area attracted a different demographic, with many settlers drawn to the spiritual allure of these cities. The population density in these areas was higher, partly due to the influx of pilgrims and traders.
In contrast, the southern regions, including Gaza, faced different challenges. While Gaza was an important settlement with rich agricultural land, it struggled with geopolitical instability, which affected population growth and economic development. What's fascinating is how the map illustrates these variances vividly, showing how geography and politics shaped the lives of the inhabitants.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the identified settlements in 16th century Palestine is crucial for grasping the historical narrative of the region. These settlements set the stage for the socio-political dynamics that would unfold in the following centuries, particularly during conflicts in the 20th century. The cultural and religious landscapes established during this time continue to influence the region today.
Furthermore, as contemporary scholars and historians dive deeper into this era, they reveal patterns that resonate with current demographic and political realities in Palestine. The legacy of these settlements can be seen in today’s urban centers, where the echoes of history are palpable in architecture, cultural practices, and social structures. Ever wondered how the past informs the present? This map provides a tangible link between the historical and modern-day realities of Palestine, reminding us of the complex tapestry that is the region's heritage.
In conclusion, the "Identified Settlements in 16th Century Palestine Map" serves not just as a historical artifact, but as a tool for understanding the intricate layers of cultural identity and social dynamics that define Palestine. As we look at this map, we gain insights into how geography, culture, and history intertwine, shaping the world we live in today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 15, 2025
- Views
- 60
Comments
Loading comments...