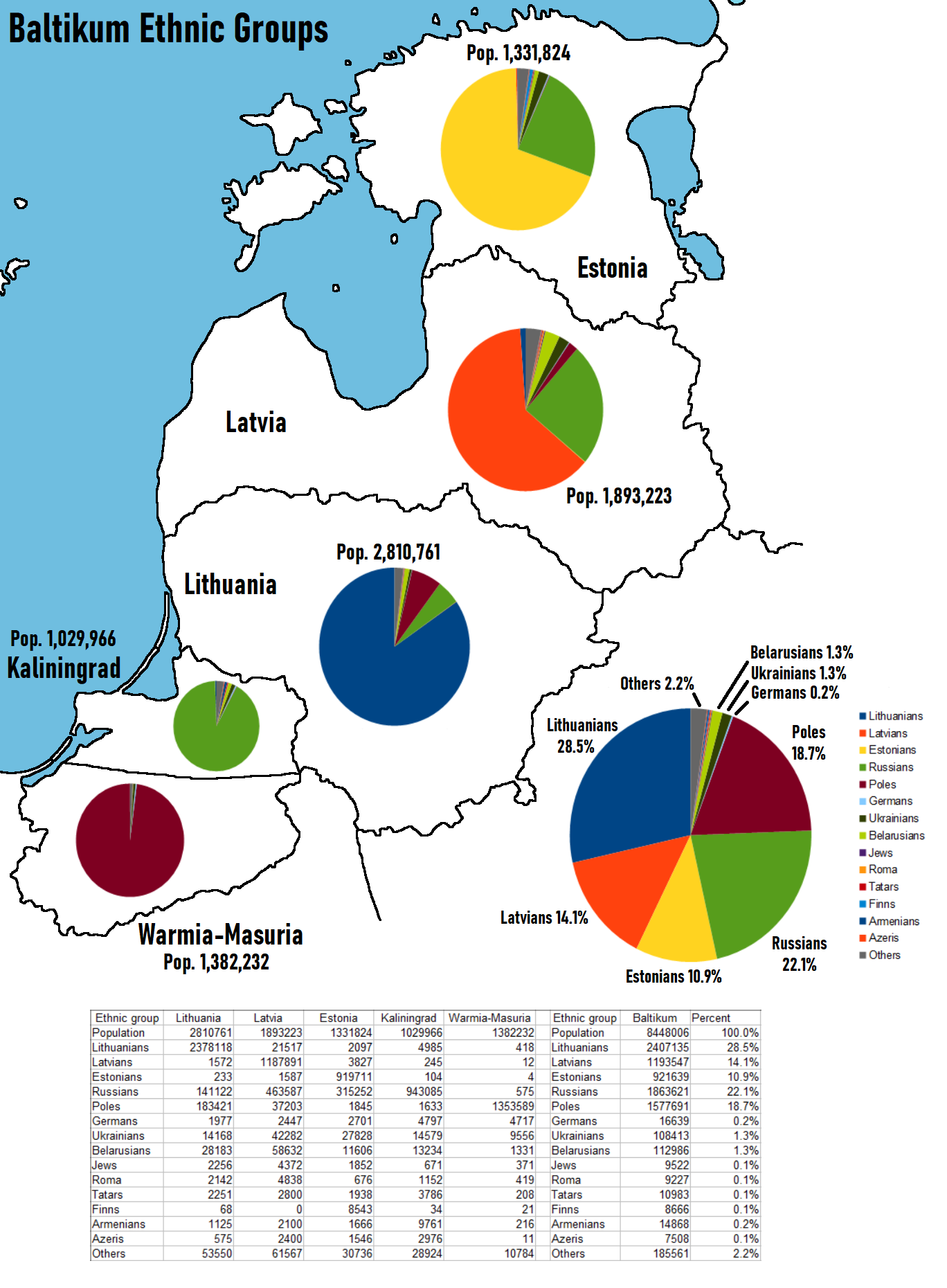
Ethnic Groups of Baltikum Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Ethnic Groups of Baltikum Map" provides a comprehensive visualization of the diverse ethnic compositions across the Baltic region, specifically focusing on areas such as Kaliningrad and Warmia-Masuria. This map highlights the distinct ethnic groups that inhabit these territories, showcasing the rich cultural tapestry that has developed over centuries.
Transitioning into the core topic, we see that the Baltic region is a fascinating case study in ethnic diversity, with historical influences shaped by centuries of migration, trade, and political shifts.
Deep Dive into Ethnic Diversity in the Baltic Region
The Baltic region, comprising countries like Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia, along with parts of Poland and Russia, has a unique ethnic landscape. This area is home to a variety of ethnic groups, including Lithuanians, Latvians, Estonians, Poles, Russians, and the remnants of the Old Prussians, whose legacy is notably present in Warmia-Masuria and Kaliningrad.
Interestingly, the Old Prussians were Baltic-speaking tribes who inhabited the area before the arrival of German settlers in the 13th century. While the Old Prussian language has largely disappeared, historical ties remain strong, influencing the cultural practices and identity of the region's inhabitants.
As of recent data, the largest ethnic group in Latvia is Latvians, making up about 62% of the population, followed closely by Russians at around 25%. In Estonia, Estonians represent roughly 69% of the population, with Russians again being a significant minority, accounting for about 25%. Lithuania, on the other hand, is predominantly Lithuanian at around 85%, with Poles and Russians forming smaller communities.
In Kaliningrad, formerly part of East Prussia, the population is predominantly Russian, a result of significant demographic changes post-World War II. This shift provides a unique lens through which to examine the historical migration patterns and the impact of geopolitical changes on ethnic identities. The region also reflects a blend of cultural influences, showcasing how historical events have shaped modern demographics.
What's fascinating is that this diversity is not just a relic of the past. Current trends indicate a growing interest in preserving local cultures and languages. For instance, initiatives in Latvia and Lithuania aim to revitalize the languages and traditions of their respective minorities, highlighting the ongoing negotiation of identity in the face of globalization.
Regional Analysis
When we break down the map regionally, we can observe significant variations in ethnic compositions across different areas. In Warmia-Masuria, for example, there is a notable presence of both Polish and Russian communities, reflecting the historical complexities of the region. This area, rich in lakes and forests, has been a crossroads for various cultures, leading to a unique blend of traditions and languages.
Kaliningrad stands out due to its predominance of Russian culture, which is a direct result of the post-war resettlement policies that displaced the native German-speaking population. This has created a distinct cultural environment, where Russian customs and practices dominate daily life, despite the region's historical ties to the Baltic and Germanic cultures.
In contrast, the Baltic states exhibit a more balanced ethnic composition, where national identities are often intertwined with the presence of significant minority populations. For instance, the coexistence of Latvians and Russians in Latvia raises intriguing questions about national identity, language rights, and cultural preservation. The Latvian government has implemented various policies to promote the Latvian language and culture while ensuring that minority rights are respected, reflecting a delicate balance between unity and diversity.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the ethnic groups of the Baltikum is crucial for several reasons. First, it provides insights into the cultural richness of the region and the historical narratives that have shaped contemporary identities. Moreover, examining these demographics can reveal underlying tensions, as seen in places where ethnic minorities seek greater representation and rights within national frameworks.
Additionally, the ethnic diversity in the Baltikum has real-world implications for political stability and social cohesion. As globalization continues to influence migration patterns, the region's ability to navigate its complex ethnic landscape will be vital for fostering peaceful coexistence. Trends show that younger generations are increasingly embracing multicultural identities, which could lead to more inclusive societies in the future.
In conclusion, the "Ethnic Groups of Baltikum Map" not only provides a visual representation of the region's demographics but also serves as a starting point for deeper conversations about identity, culture, and the ongoing evolution of ethnic relationships in the Baltic region. As we continue to explore these themes, we gain valuable perspectives on how history and culture shape the societies we live in today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 14, 2025
- Views
- 78
Comments
Loading comments...