Visigothic Kingdom Map 586-711 AD

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
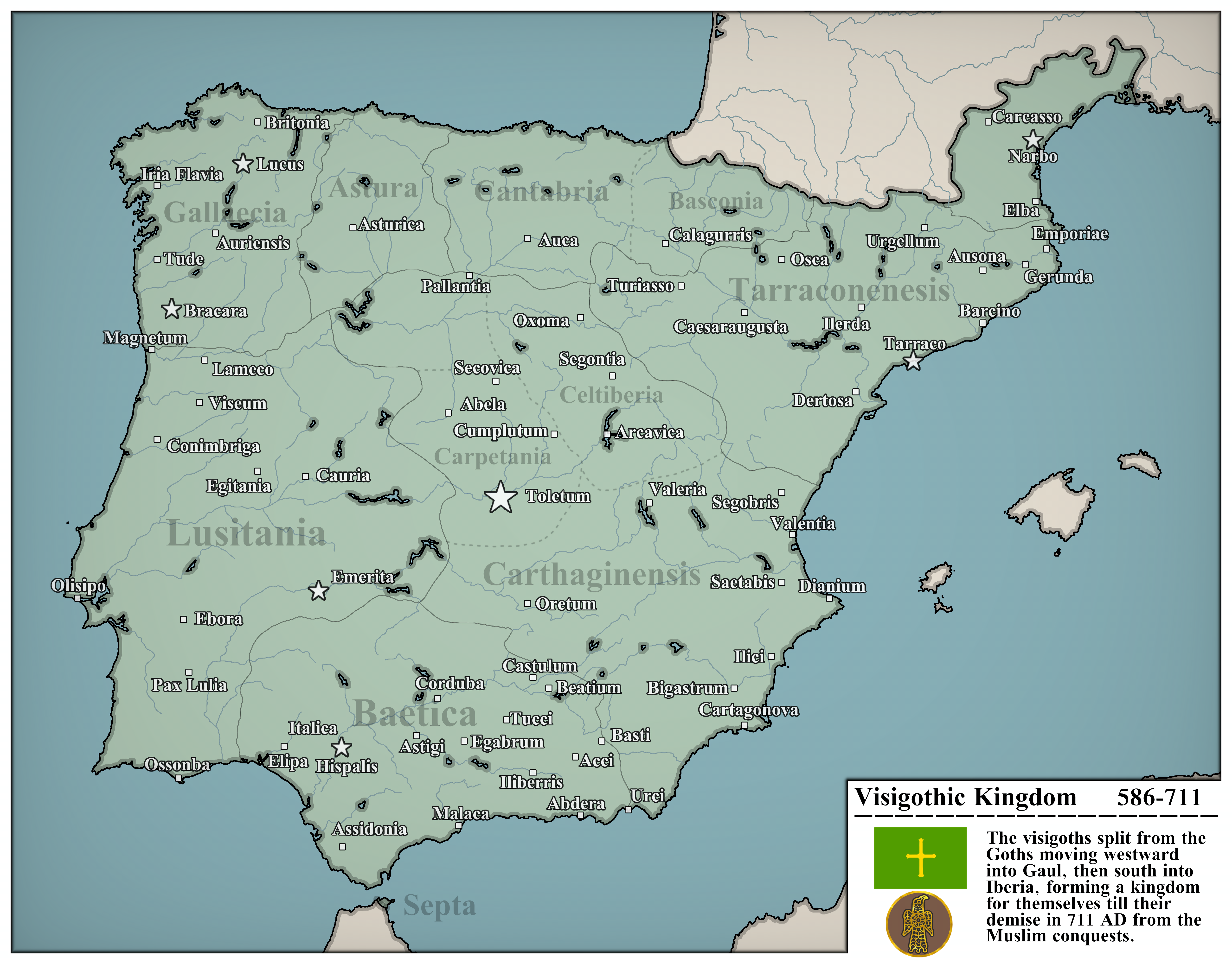
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "Visigothic Kingdom 586-711 AD" illustrates the territorial extent and influence of the Visigothic Kingdom during a pivotal period in Iberian history. Covering a substantial portion of modern-day Spain and Portugal, this map highlights the regions ruled by the Visigoths in the aftermath of the Roman Empire's decline. The map serves as a historical snapshot, showcasing the geographical boundaries that defined the Visigothic realm, as well as key cities, military outposts, and tribal territories that were significant during this era.
Deep Dive into the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigoths were one of the many Germanic tribes that played a critical role in the transformation of Europe following the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Originating from the regions of modern-day Sweden, they migrated southward, eventually settling in the Iberian Peninsula around the late 5th century. The Visigothic Kingdom established its prominence in 586 AD when King Reccared I converted to Christianity, leading to the consolidation of power and the unification of various tribes under a single crown.
Interestingly, the Visigoths were not just conquerors; they were also assimilators. They adapted to the existing Roman culture and governance structures, which allowed them to rule effectively over a diverse population. The capital of the kingdom was initially in Toledo, which became a significant cultural and political center. The Visigoths enacted legal reforms known as the "Code of Euric," which laid the groundwork for medieval legal systems in Spain.
During the 7th century, the Visigothic Kingdom reached its zenith, stretching from the northern regions around the Pyrenees to southern territories near the Strait of Gibraltar. This expansion facilitated trade routes across the Mediterranean, fostering economic growth and cultural exchanges with the Byzantine Empire and North Africa. However, the kingdom was not without its challenges. Internal strife, succession crises, and conflicts with other tribes created political instability.
A significant aspect of the Visigothic rule was their relationship with the local population, which was predominantly Romanized. The Visigoths were known for their relatively tolerant approach to governance, allowing for a degree of religious freedom that included both Arian Christians and Trinitarians. This tolerance, however, would later become a point of contention as different factions vied for control.
Regional Analysis
The map highlights several key regions within the Visigothic Kingdom, including notable cities like Toledo, Seville, and Mérida. Toledo, as the capital, was the seat of power and a melting pot of cultures and ideologies. The city was a hub for scholars and a center for theological debates, particularly concerning Arianism.
In contrast, areas such as the southern region near Seville were vital for trade and military defense due to their proximity to the coast. The port cities facilitated maritime commerce, connecting the Visigoths with other Mediterranean civilizations. Interestingly, the northern territories, which were more mountainous, often faced challenges in agricultural productivity, leading to a more pastoral lifestyle compared to their southern counterparts.
The complexity of the Visigothic Kingdom is further illustrated by the varying degrees of Roman influence in different regions. For instance, the eastern parts of the kingdom retained more Roman architectural and cultural legacies, while the western areas showed a blend of Visigothic and local traditions. This regional disparity highlights the adaptability of the Visigoths and their ability to integrate into the existing social fabric of the Iberian Peninsula.
Significance and Impact
The Visigothic Kingdom's legacy is profound, shaping the future of Spain and influencing the Iberian culture that would emerge in the Middle Ages. The legal reforms implemented during this period laid the foundation for the Spanish legal system, and the cultural fusion that took place contributed to the rich tapestry of languages, customs, and traditions found in Spain today.
However, the kingdom's decline in the early 8th century, primarily due to the Muslim conquests, marked a significant turning point in European history. The fall of the Visigothic Kingdom not only reshaped the political landscape of the Iberian Peninsula but also initiated a period of cultural transformation that would lead to centuries of Islamic influence in the region.
As we consider the modern implications, the Visigothic period serves as a reminder of the complexities of cultural integration and governance. The historical interactions between the Visigoths and the Romanized population set a precedent for the multicultural society that characterizes Spain today. Ever wondered how these early migrations and integrations have influenced contemporary Spanish identity? The answer lies in the rich history captured in maps like this one, reminding us of the layers of civilization that exist beneath the surface of modern nations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 14, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...