Raw Material Sources for Batteries Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
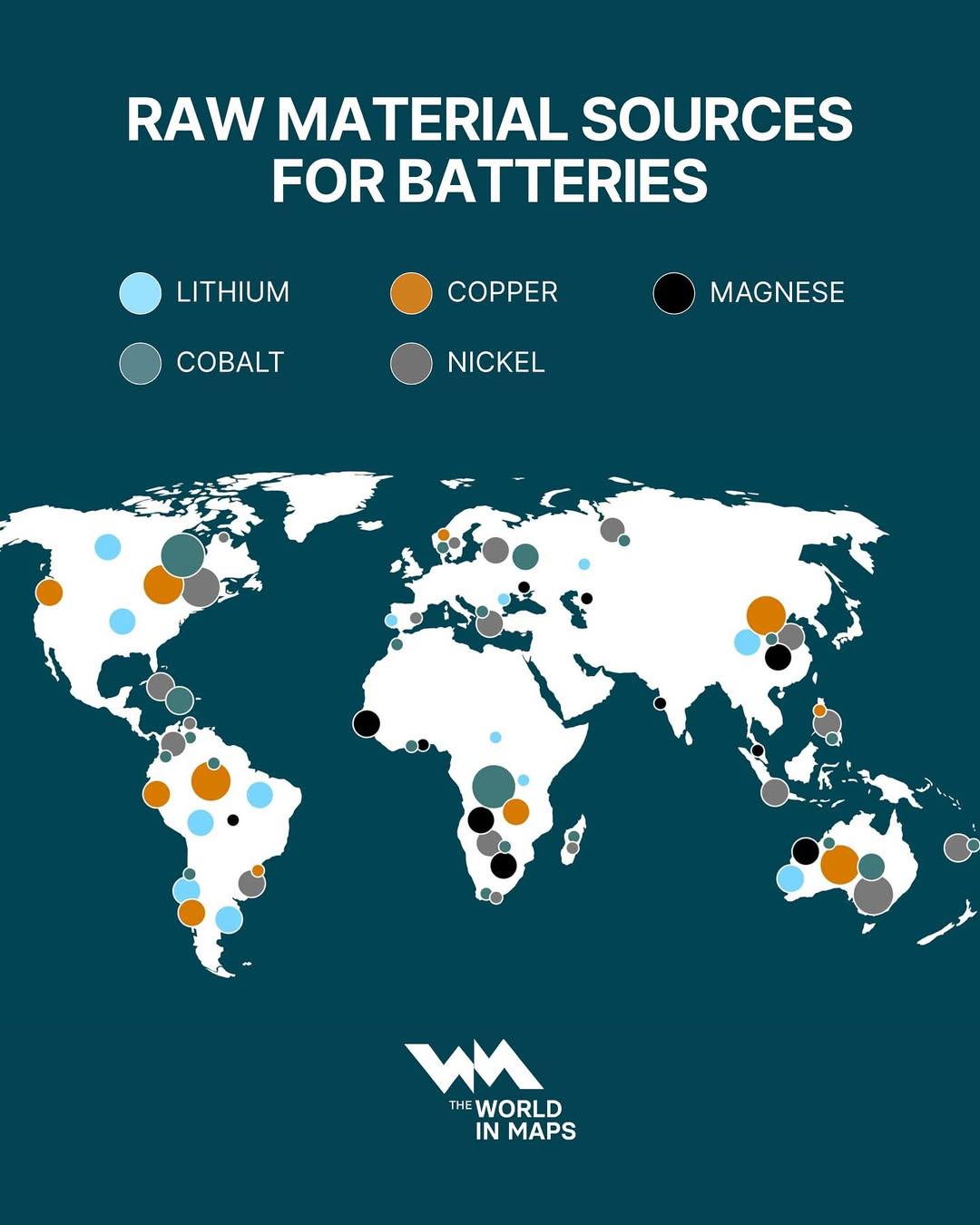
What This Map Shows
The "Raw Material Sources for Batteries Map" provides a comprehensive overview of the geographic distribution of key raw materials essential for battery production. Specifically, it highlights the locations of vital minerals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite, which are fundamental components in modern battery technologies, particularly those used in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage systems. This visualization not only pinpoints where these resources are extracted globally but also emphasizes the geopolitical significance of these deposits in the context of the rising demand for sustainable energy solutions.
Deep Dive into Raw Materials for Batteries
The growing shift towards electrification and renewable energy has made the extraction and processing of battery raw materials increasingly crucial. Lithium, often referred to as 'white gold,' is a primary ingredient in lithium-ion batteries, which power everything from smartphones to electric cars. Countries such as Australia, Chile, and Argentina are significant players in the lithium market, with vast reserves located in the so-called "Lithium Triangle" of South America. Interestingly, Australia leads the world in lithium production, primarily through hard rock mining methods.
Cobalt, another essential component, is predominantly sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), which accounts for over 60% of the world’s supply. However, cobalt mining has faced scrutiny due to ethical concerns surrounding labor practices and environmental impacts. As a result, companies are exploring alternative sourcing strategies and investing in recycling technologies to mitigate these issues.
Nickel is crucial for enhancing battery energy density and is primarily extracted from Indonesia and the Philippines. The global demand for nickel is expected to surge as manufacturers strive to produce batteries with higher capacity and longer life cycles. Interestingly, Indonesia has become a dominant player in the nickel market, with initiatives to expand its processing capabilities, thus moving up the value chain.
Graphite, used in battery anodes, is another critical material. China currently dominates the natural graphite supply chain, accounting for nearly 70% of global production. However, concerns about over-reliance on Chinese sources have prompted other countries to explore domestic mining opportunities, particularly in North America and Europe.
What’s fascinating is the interplay between these materials and the broader sustainability goals of nations worldwide. As the demand for EVs increases, so does the urgency to secure these raw materials responsibly, leading to a complex web of international trade agreements and environmental regulations.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can see distinct regional clusters of these raw materials. In South America, the lithium-rich countries are strategically positioned along the Andes, where evaporation from salt flats facilitates lithium extraction. Conversely, cobalt mining is concentrated in Central Africa, where political instability and regulatory challenges can complicate supply chains.
In Asia, both China and Indonesia play pivotal roles in the battery materials landscape. China’s dominance in graphite processing and its investments in battery technology have positioned it as a global leader, while Indonesia's nickel reserves are increasingly attracting foreign investment aimed at battery production. The comparative analysis shows that while some regions are rich in specific materials, others are beginning to develop their resources to diversify supply sources and reduce dependency on single countries.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geographic distribution of battery raw materials is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for global energy policies and economic strategies. As countries commit to reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to electric mobility, the demand for these materials is projected to escalate. According to recent reports, the global demand for lithium alone could increase by over 400% by 2030.
Moreover, the geopolitical landscape is shifting as nations vie for control over these essential resources. This competition could lead to increased investment in mining operations, technology development for sustainable extraction, and innovations in battery recycling. Interestingly, international collaborations and treaties may also emerge, focusing on responsible sourcing and environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, the "Raw Material Sources for Batteries Map" serves as a vital tool for understanding the complex and interconnected nature of resource extraction in the age of electrification. As we move forward, it will be crucial to balance the demand for these materials with the need for ethical practices and environmental conservation, shaping the future of energy storage and consumption worldwide.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 13, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...