Cultural Boundaries Map of Southeast Europe and Asia

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
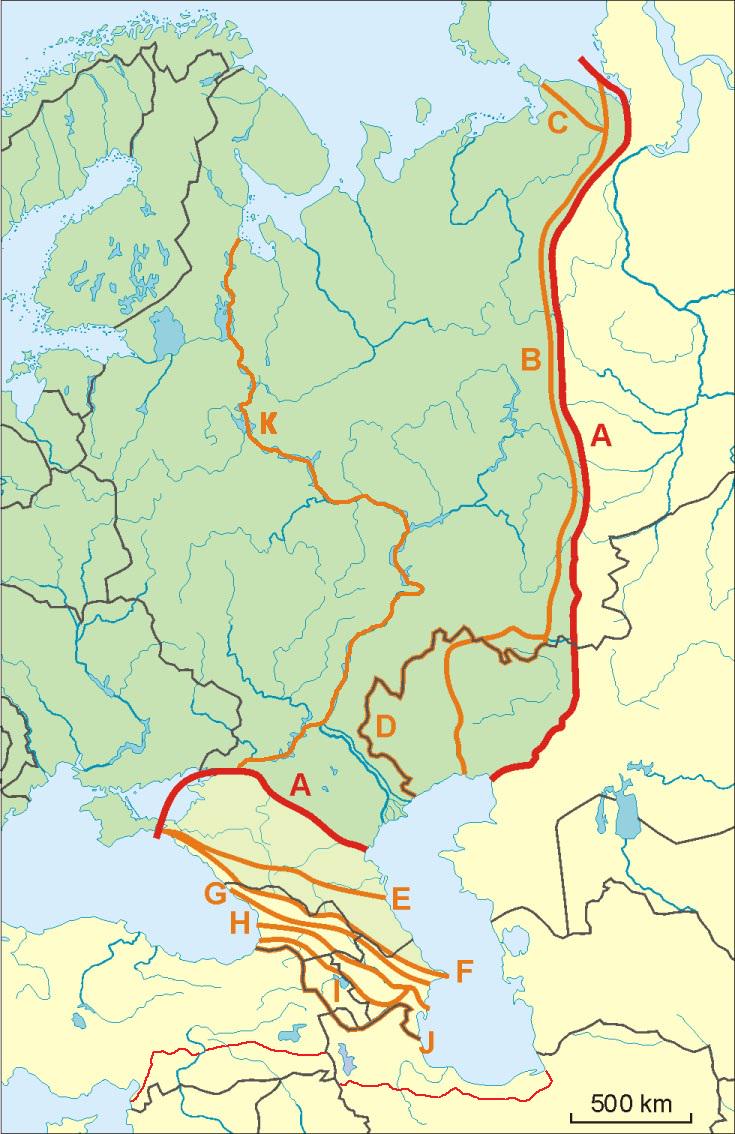
What This Map Shows
This map presents a compelling visualization of the geocultural opinions regarding the southeast land border of Europe, which also serves as the western land border of Asia. The boundaries are not merely lines drawn on a map; they are deeply influenced by geographical features, particularly mountain ranges, and cultural dynamics, especially in regions such as northwest Iran. Such a visual representation allows us to understand how natural barriers and cultural identities intertwine to shape perceptions of territory and belonging.
Deep Dive into Geocultural Boundaries
Geocultural boundaries reflect the complex interplay between natural landscapes and human societies. Mountains, for instance, are not just physical barriers; they often symbolize cultural divides that have evolved over centuries. The Zagros Mountains, which stretch through Iran and into parts of Iraq, serve as a significant geographical barrier that influences both migration patterns and cultural exchange. Interestingly, these mountains have historically delineated various cultural groups, impacting their languages, traditions, and even political affiliations.
Cultural identity in this region is multifaceted. The diverse ethnic groups residing near these borders—such as Persians, Kurds, and Armenians—contribute to a rich tapestry of cultural expressions. For example, have you noticed how the Kurdish culture, with its unique language and traditions, thrives in the mountainous terrains of this border? Meanwhile, Persian culture, which is more dominant in Iran, reflects a different historical narrative shaped by its long-standing empires and trade routes.
Moreover, this region has been a crossroads for various civilizations throughout history, leading to a unique blend of cultural influences. The Silk Road, for instance, passed through this area, fostering not only trade but also cultural exchanges that enriched the societies on both sides of the border. In contemporary times, the implications of these cultural boundaries can still be felt, as they influence everything from local governance to international relations.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can break down the cultural dynamics into several key regions. The northwest of Iran, characterized by its mountainous terrain, is home to a diverse array of ethnic groups. Here, the Kurdish regions exhibit distinct cultural practices, including traditional music and dance, which stand in contrast to the more Persian-influenced central and southern parts of Iran. Interestingly, the cultural expressions found in these areas often reflect the rugged landscape, with folklore and stories deeply rooted in the mountains.
Moving further west into Turkey, the border regions also reveal a complex interplay of cultures. The Turkish influence is prominent, yet there exists a significant Kurdish population that continues to assert its cultural identity. The socio-political dynamics in this area are fascinating; the cultural boundaries often lead to tensions, as different groups vie for recognition and rights.
In contrast, the eastern edges of Europe, such as parts of Armenia and Georgia, present their own unique cultural landscapes. The Caucasus Mountains act as a natural divide, yet they also foster a rich cultural mosaic. Here, traditions such as dance and cuisine reflect influences from both Europe and Asia, demonstrating how geographical boundaries can blur cultural lines.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the cultural boundaries depicted in this map is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the importance of geographical features in shaping human societies. Natural barriers like mountains can isolate communities, leading to the development of unique cultural identities. Conversely, these same barriers can facilitate the preservation of languages and traditions that might otherwise be lost in a more homogenized world.
Moreover, these cultural boundaries have real-world implications, especially in terms of political stability and conflict. Regions where cultural identities clash often become hotspots for tension and unrest. As we look to the future, current trends suggest that globalization may challenge these cultural boundaries, leading to a blend of traditions and increased intercultural dialogue. However, this can also result in backlash from communities striving to protect their unique identities against perceived encroachment.
In conclusion, the southeast land border of Europe and the west land border of Asia is more than just a geographical line; it is a reflection of the rich, intricate tapestry of human culture shaped by the natural environment. Understanding these geocultural opinions allows us to appreciate the complexities of identity, belonging, and the ongoing dialogue between nature and culture in this vibrant region.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 12, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...