Antarctica Territorial Claims Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
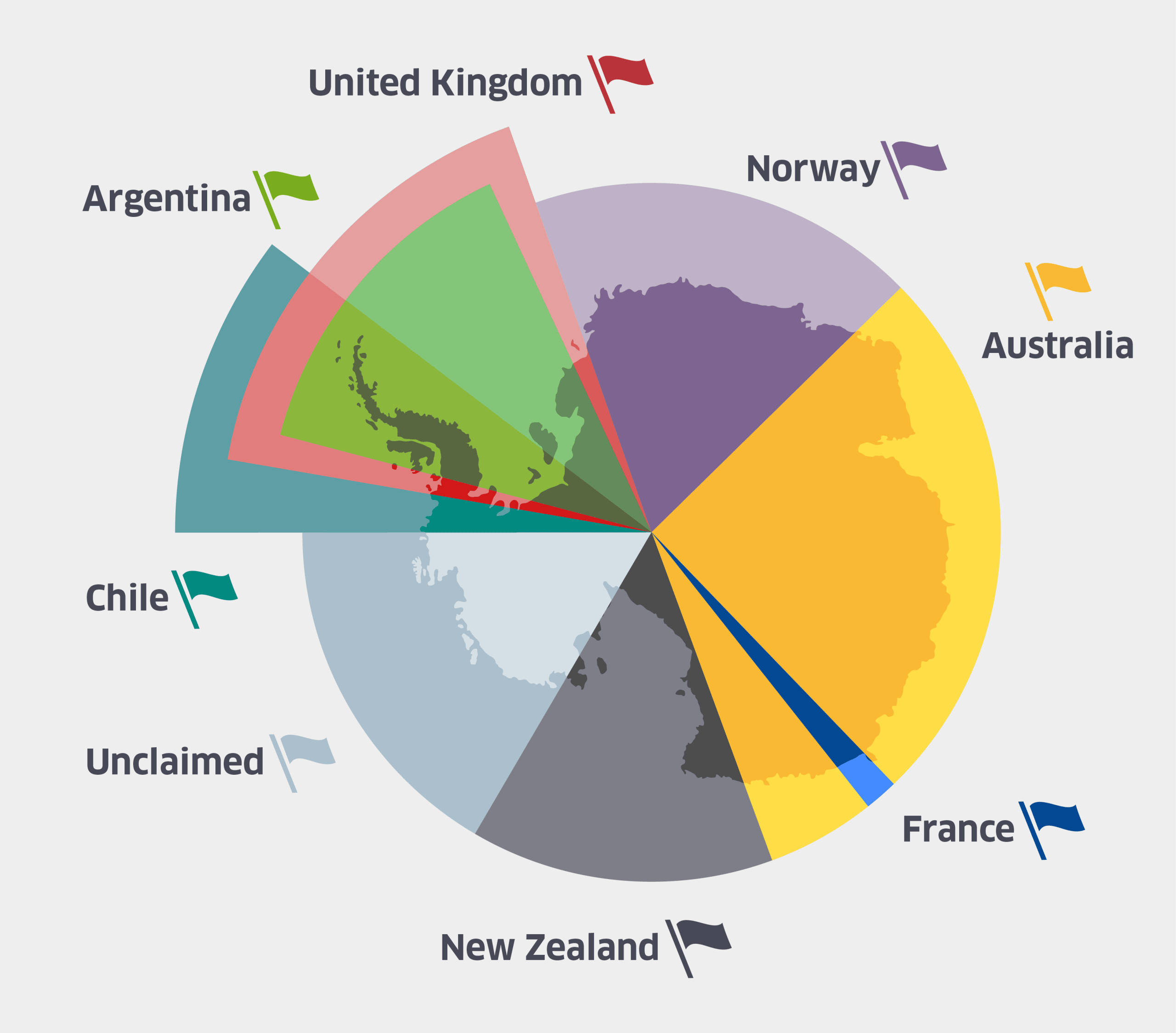
The "Parts of Antarctica Claimed by Countries" map illustrates the various territorial claims made by different nations over the Antarctic region. Unlike most other continents, Antarctica is governed by complex international treaties rather than traditional sovereignty. This visualization highlights the various claims, demarcating areas that are asserted by countries like Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom, among others. It effectively conveys the geopolitical landscape of one of the planet's most remote and least inhabited regions.
Deep Dive into Territorial Claims in Antarctica
Antarctica is unique in its governance and territorial claims. The Antarctic Treaty System, established in 1961, has played a crucial role in maintaining peace and cooperation among nations with interests in the region. However, this hasn't prevented individual countries from asserting claims over portions of the continent based on historical exploration and discovery.
Currently, seven countries have made territorial claims on parts of Antarctica: Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom. Interestingly, these claims overlap, giving rise to a complex web of international interests. For instance, Argentina and Chile both claim parts of the Antarctic Peninsula, leading to a contentious situation that underscores the need for diplomatic engagement.
Most of the claimed areas are vast, with Argentina claiming approximately 1.09 million square kilometers, which is about 42% of the continent. Chile asserts a claim that overlaps with Argentina's, covering around 1 million square kilometers, while the United Kingdom claims about 1.6 million square kilometers in the British Antarctic Territory.
One of the most significant aspects of these claims is the influence of natural resources. Antarctica is believed to be rich in minerals and oil, although the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty, signed in 1991, prohibits any mineral exploration or extraction. The potential for natural resource exploitation raises important questions about future governance and environmental protection in the region.
What's fascinating is how the lack of a definitive resolution on territorial claims has led to a unique situation where scientific research and environmental stewardship are prioritized. The international community largely agrees that Antarctica should be preserved for peaceful purposes, which has led to a cooperative atmosphere among countries.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map more closely reveals distinct regions with differing claims. The Antarctic Peninsula is perhaps the most contested area, with both Argentina and Chile asserting their rights. This region is experiencing significant environmental changes due to climate change, which may impact the stability of these claims. Interestingly, the warming climate is leading to increased accessibility, potentially heightening international interest in the area.
Beyond the Peninsula, East Antarctica is primarily claimed by Australia, which asserts its rights over a large portion known as the Australian Antarctic Territory. This vast area is less frequented than the Peninsula but is equally crucial for scientific research, particularly concerning climate studies and biodiversity.
In contrast, the region surrounding the Ross Sea, claimed by New Zealand and the United States (though the U.S. has not made a formal claim), exemplifies cooperation over competition. The U.S. operates several research stations in this area, focusing on climate change and its global impacts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the territorial claims in Antarctica is crucial not only for geopolitical reasons but also for environmental and scientific considerations. As countries continue to engage in research, the need for collaboration becomes increasingly important. The unique governance structure of Antarctica allows for various nations to work together, which is something we can all learn from.
Moreover, as climate change brings about significant shifts in the region, these territorial claims could become more contentious. The melting ice sheets and glaciers are revealing new landscapes and possibly untapped resources, leading to renewed interest from nations around the world.
In conclusion, the claims over Antarctica are not just about land; they intertwine with issues of environmental stewardship, international diplomacy, and scientific collaboration. As we move forward, it’s essential to navigate these complex dynamics carefully to preserve this unique and fragile continent for future generations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 10, 2025
- Views
- 136
Comments
Loading comments...