Indo-Aryan Languages Map of India

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
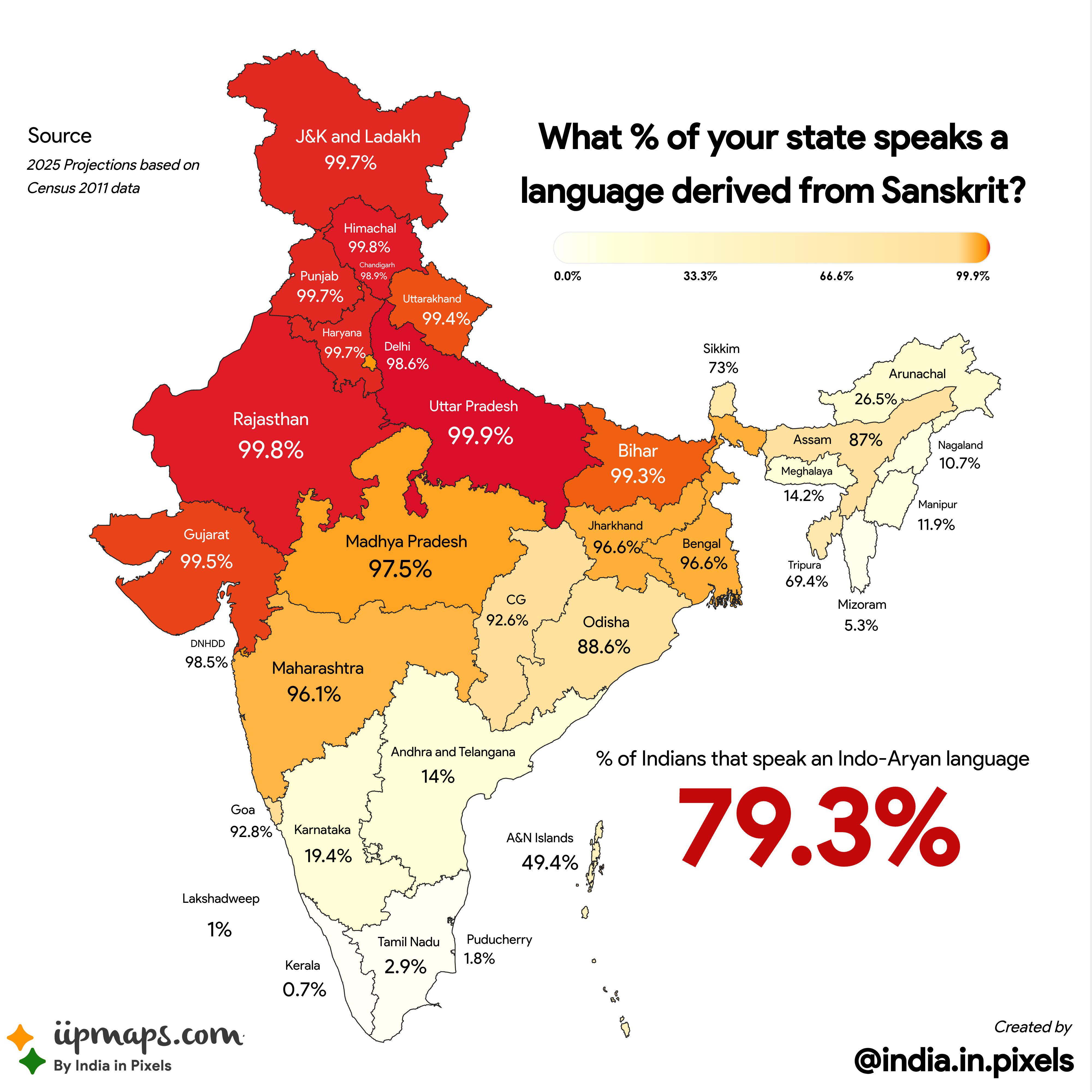
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "The Sanskrit Footprint: A Map of Indo-Aryan Languages Across India" provides a detailed look at the linguistic landscape of India, specifically highlighting the prevalence of languages derived from Sanskrit as projected for 2025. It visually represents the percentage of speakers of these languages across various Indian states and union territories, revealing a distinct regional pattern. States in North, West, and Central India are shaded in darker colors, indicating a higher percentage of speakers, while southern and northeastern states show lighter shades, suggesting a lower prevalence of Indo-Aryan languages.
Deep Dive into Indo-Aryan Languages
Indo-Aryan languages, a major branch of the Indo-European family, are primarily spoken in the Indian subcontinent. These languages have evolved from Sanskrit, an ancient language of India that holds immense cultural and historical significance. Linguists categorize Indo-Aryan languages into various groups, with Hindi, Bengali, Punjabi, and Marathi being some of the most prominent examples.
Interestingly, the linguistic diversity in India is a reflection of its rich cultural tapestry. According to the 2011 Census, around 78% of the population speaks an Indo-Aryan language. As we project into 2025, this percentage is expected to remain relatively stable, although regional variations will continue to emerge.
Most Indo-Aryan languages share a common grammatical structure, which often makes them mutually intelligible. Moreover, many of these languages have absorbed elements from local dialects and languages, resulting in unique variations. For instance, Hindi speakers in Delhi may use different vocabulary and expressions compared to those in rural Uttar Pradesh.
The influence of Sanskrit on these languages extends beyond mere vocabulary; it affects syntax, phonetics, and even cultural expressions embedded in literature, poetry, and religious texts. The resurgence of interest in Sanskrit, particularly in educational institutions, is indicative of a broader trend towards cultural revivalism. Interestingly, many modern Indian languages have also adopted words and phrases from Sanskrit to enrich their lexicon, showcasing the language's lasting influence.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, it is clear that Northern and Central India, which includes states like Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Punjab, exhibit high percentages of Sanskrit-derived language speakers. For instance, Uttar Pradesh, with its rich literary history in Hindi and Urdu, shows over 90% of its population speaking these languages. This region is considered the heartland of Indo-Aryan languages, where dialects like Awadhi and Braj continue to thrive alongside standard Hindi.
In contrast, the Southern states, such as Tamil Nadu and Kerala, display a lower prevalence of Indo-Aryan languages, with Dravidian languages like Tamil and Malayalam dominating. This linguistic divide can be attributed to historical migrations and the development of distinct cultural identities over centuries. Interestingly, while these states may not have a high percentage of Sanskrit-derived languages, they have significantly contributed to India's cultural diversity through their unique linguistic heritage.
The Northeastern states, including Assam and Nagaland, present a fascinating case. The map indicates a low percentage of Sanskrit-derived language speakers, as many local languages belong to the Tibeto-Burman family. However, Hindi is commonly used as a lingua franca in urban areas, showcasing a blend of linguistic influences.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of Indo-Aryan languages across India is vital for several reasons. First, it highlights the cultural and historical connections among different regions. Language is a powerful tool for communication, and its preservation is essential for maintaining cultural heritage.
Moreover, the prominence of these languages has implications for education, media, and policy-making. As India continues to modernize, the demand for proficiency in both regional languages and Hindi or English is growing. This linguistic landscape affects everything from job opportunities to access to information.
Future projections suggest that the influence of Indo-Aryan languages will continue to remain strong, particularly in the context of globalization. As younger generations engage with technology and social media, they are likely to incorporate elements from traditional languages into contemporary usage, creating a dynamic linguistic evolution. Have you noticed how regional dialects are increasingly finding their way into popular media? This phenomenon reflects an ongoing conversation about identity and cultural expression in India.
In conclusion, the map not only visualizes the current status of Indo-Aryan languages in India but also offers a window into the complex interplay between language, culture, and identity. As we move toward 2025, it will be interesting to see how these dynamics evolve and what new trends emerge in the linguistic landscape of this diverse nation.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 9, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...