Apple vs Banana Consumption Map in Europe

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
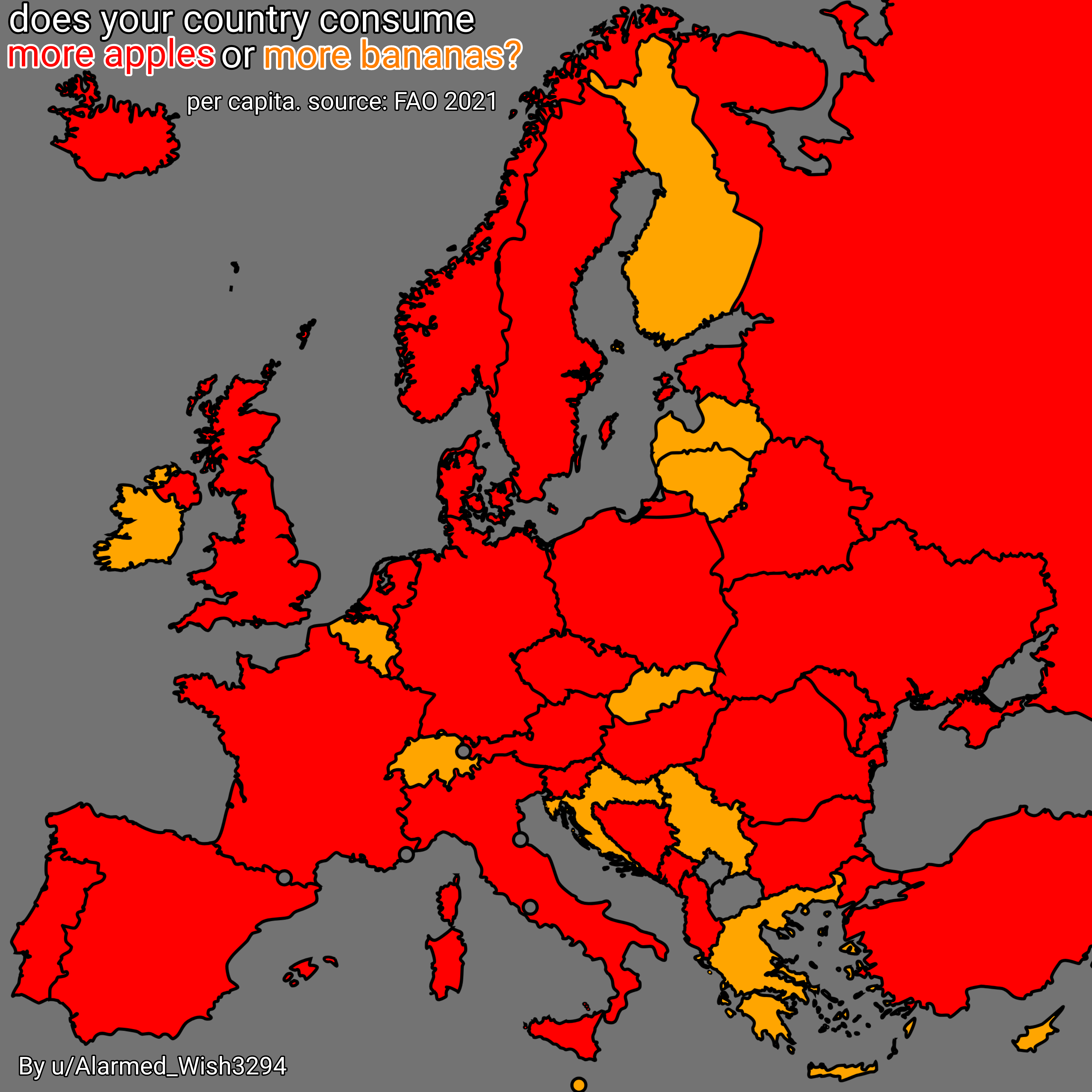
This map visually depicts the per capita consumption of apples and bananas across various European countries. It provides a fascinating look at fruit preferences in Europe, revealing which countries favor one fruit over the other. By analyzing these consumption patterns, we can gain insights into dietary habits, agricultural trends, and even cultural preferences linked to these two popular fruits.
Deep Dive into Apple and Banana Consumption
Apples and bananas are staples in many diets worldwide, but their consumption rates can tell us much about a region's agricultural practices, health trends, and cultural preferences. Apples, often synonymous with health and nutrition, have been consumed for centuries, originating from Central Asia. They are celebrated for their versatility, fitting seamlessly into both sweet and savory dishes. Interestingly, the European Union alone accounts for a significant share of global apple production, with countries like Poland and Germany leading the way.
On the other hand, bananas, which originated in Southeast Asia, have become the world's most popular fruit. Their appeal lies in their convenience, taste, and nutritional value, making them a preferred choice for many. In Europe, bananas have seen a steady rise in consumption, often surpassing apples in several countries. The factors influencing these trends are multifaceted, including availability, pricing, and marketing strategies. Interestingly, bananas thrive in tropical climates, which can limit local production in Europe, making imports essential. This reliance on imports might contribute to their growing popularity, as they offer a taste of the tropics irrespective of the season.
The nutritional comparison between the two fruits also plays a role. Apples are high in fiber and vitamin C but lower in calories, making them a favorite for health-conscious consumers. Bananas, while higher in calories, boast potassium, vitamin B6, and magnesium, appealing to those seeking energy and muscle recovery. This nutritional divergence can influence consumer choices based on personal health goals.
Regional Analysis
Looking at the map, we can identify distinct patterns in consumption across the continent. For instance, countries like Ireland and the United Kingdom showcase a strong preference for bananas, with per capita consumption rates considerably higher than those for apples. This trend might stem from the convenience of bananas as a quick snack and their year-round availability.
Conversely, Eastern European countries such as Poland and Romania exhibit a higher affinity for apples. This could be attributed to local agricultural practices, where apples are more readily available and often more affordable than imported bananas. What's fascinating is how these consumption trends reflect not just individual preferences but also broader agricultural policies and economic conditions.
Southern European nations, such as Spain and Italy, present a mixed picture. These countries enjoy a diverse fruit culture, often incorporating both apples and bananas into their diets. Interestingly, cultural dishes featuring apples, such as tarts and sauces, might elevate their consumption in regions where they are traditionally grown. Meanwhile, the warm climate allows for a variety of fruits, making it a culinary playground for both apples and bananas.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the consumption rates of apples versus bananas in Europe is more than just a matter of dietary preferences. It reflects deeper economic and agricultural implications. For instance, rising banana consumption may push countries to rethink import policies, logistics, and trade agreements, especially as climate change continues to affect agricultural productivity.
Moreover, this topic connects to larger discussions about health and nutrition. With increasing awareness about diet-related diseases, understanding fruit consumption patterns can help policymakers promote healthier eating habits. For example, promoting apple consumption in banana-loving countries could be a strategy to enhance fiber intake and reduce sugar consumption. Conversely, encouraging the consumption of bananas in regions where they lag might provide a convenient source of energy, particularly for active populations.
In conclusion, the per capita consumption of apples versus bananas in Europe provides a snapshot of dietary habits that are influenced by culture, availability, and health considerations. As consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware, tracking these trends will be crucial for both agricultural producers and policymakers moving forward. The conversation around fruit consumption is not just about taste; it’s about health, economy, and lifestyle choices that shape our world today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 8, 2025
- Views
- 70
Comments
Loading comments...