Zones of Occupation Map of France 1815-1818

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
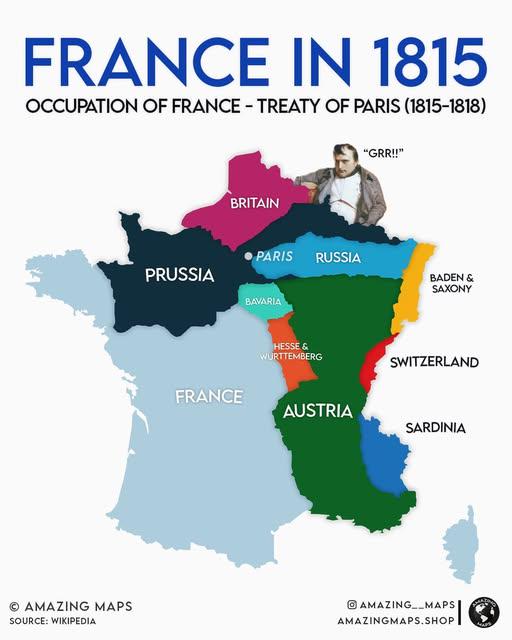
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "Zones of Occupation of France From June 1815 to November 1818 Following Napoleon’s Defeat" provides a detailed overview of the territorial divisions established in France after the fall of Napoleon Bonaparte. Following his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo in June 1815, a coalition of European powers occupied France, leading to a complex arrangement of military zones. The map illustrates how France was divided among the Allied forces—primarily the British, Prussian, Dutch, and Austrian armies—each controlling distinct regions. This occupation lasted until the eventual withdrawal of foreign troops, which culminated in November 1818.
Deep Dive into Zones of Occupation in France
The zones of occupation were not merely arbitrary divisions; they reflected the geopolitical tensions and power dynamics of post-Napoleonic Europe. The New European order was solidified at the Congress of Vienna, where representatives from various nations negotiated to restore stability and balance of power. In this context, the occupation zones were established to prevent a resurgence of French militarism and to ensure reparations were paid for the war.
Interestingly, the occupation was marked by a significant military presence, with thousands of soldiers stationed across France. The British, for instance, primarily occupied the northern regions, including Paris, the capital. This strategic placement allowed them to maintain a stronghold over the most influential part of the country, ensuring that any potential uprisings could be swiftly quelled. Meanwhile, the Prussians occupied the eastern zones, where their military influence helped to counteract any French ambitions toward eastern Europe.
The occupation wasn’t just a straightforward military endeavor; it had profound cultural and economic implications as well. The presence of foreign troops led to an influx of different ideas, customs, and practices, contributing to a unique cultural exchange. However, it also bred resentment among the French populace, who were often subjected to strict regulations and economic burdens imposed by their occupiers. This duality of influence is a fascinating aspect of the occupation period.
Demographically, the occupation had varying impacts across different regions. In urban areas, like Paris, the presence of foreign soldiers often led to increased tensions, while in rural regions, life continued with less disruption. However, the economic policies enacted by occupiers often had long-lasting effects, altering trade patterns and agricultural practices for years to come.
Regional Analysis
The map clearly delineates the different zones occupied by the Allied forces, allowing us to analyze the impacts of occupation regionally. For example, in the northern zone, controlled primarily by the British, there was a significant focus on maintaining order and rebuilding infrastructure. This area saw investments in roads and bridges to facilitate trade and military movement, which would pay dividends in the long run.
Conversely, the Prussian zone in the east was characterized by a more militarized environment. The presence of Prussian troops was heavily felt, and local governance was often directly influenced by military leaders. This created a stark contrast in administrative styles between the British and Prussian zones, which can be observed in the local responses to foreign rule.
Interestingly, the southern regions, where the Austrians had a considerable presence, exhibited a different dynamic altogether. The Austrians tended to adopt a more conciliatory approach, focusing on negotiation and collaboration with local leaders. This led to a relatively smoother coexistence compared to the tensions experienced in the north and east, illustrating how the nature of occupation varied across France.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the zones of occupation in France from 1815 to 1818 is crucial for appreciating the broader implications of this period in European history. The occupation served as a critical juncture that shaped France's political landscape for decades. The presence of foreign troops not only helped to stabilize the region post-Napoleon but also laid the groundwork for the eventual rise of nationalist sentiments and the push for self-determination in the years that followed.
Moreover, the repercussions of the occupation can still be felt today. The complex relationship between France and its European neighbors was heavily influenced by this period of foreign control, which contributed to a legacy of mistrust and rivalry that would play out in subsequent conflicts, including World War I.
In conclusion, the map of zones of occupation in France during this pivotal time highlights more than just military logistics; it showcases the intricate web of power, culture, and economy that defined post-Napoleonic France. As we reflect on this historical moment, it’s essential to consider how such events continue to shape our understanding of European history and international relations today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 8, 2025
- Views
- 72
Comments
Loading comments...