Genetic Legacy of Slavic Expansion Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
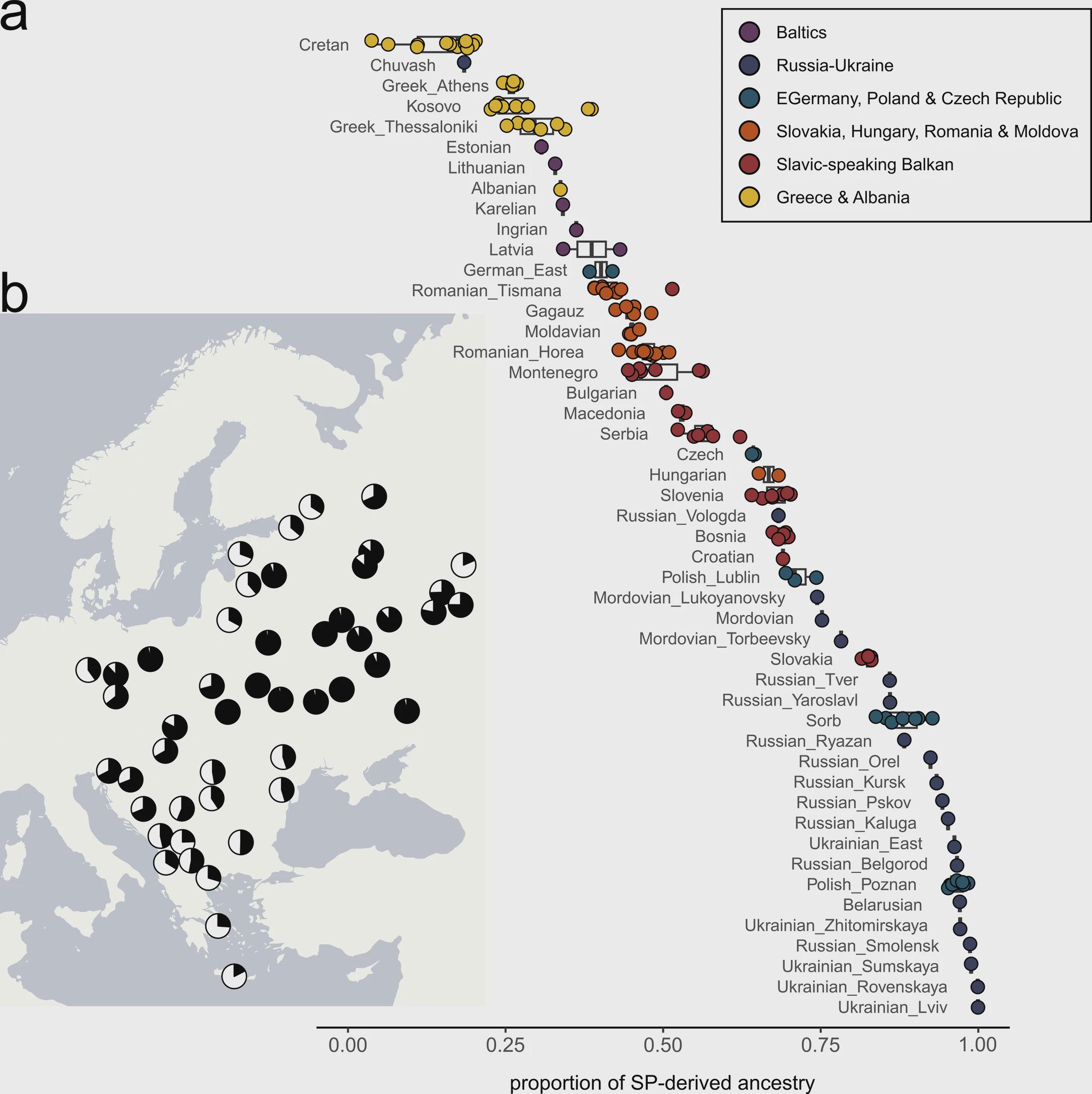
The map titled "The Genetic Legacy of the Slavic Expansion" by Gretzinger et al. (2025) visually represents the distribution of Slavic heritage across various regions of Europe. The black areas within the circles indicate regions with significant Slavic genetic lineage. This intriguing visualization provides insights into how Slavic populations have spread over time and their genetic contributions to the contemporary demographic landscape of Europe.
Transitioning from the map's visual elements, it's essential to delve deeper into the historical and genetic context of the Slavic expansion, a phenomenon that has shaped the cultural and genetic tapestry of Eastern Europe and beyond.
Deep Dive into the Slavic Expansion
The Slavic expansion, which began around the 6th century AD, was a significant movement that saw Slavic tribes migrate from their original homeland in Eastern Europe into vast territories that now encompass parts of Central Europe, the Balkans, and even into the Eastern reaches of Europe. This expansion was not merely a physical movement; it also involved cultural exchange and intermingling with various peoples.
Interestingly, the Slavs were not one homogenous group. Instead, they comprised multiple tribes, including the West Slavs, East Slavs, and South Slavs, each with its own unique characteristics and languages. The West Slavs settled in areas that are now Poland, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia, while the East Slavs primarily took root in what is now Russia and Ukraine. Meanwhile, the South Slavs moved into the Balkans, influencing the region's culture and language significantly.
Genetic studies have revealed fascinating insights into this expansion. For instance, research indicates that modern populations in areas where Slavic tribes settled show a mix of genetic markers from both Slavic and indigenous populations. This blend highlights the complex nature of migration and the lasting impact of these historical movements on contemporary genetic profiles.
Furthermore, the map illustrates how Slavic genetic markers are distributed unevenly across Europe. Regions with high concentrations of Slavic heritage tend to be located in Eastern Europe, reflecting the historical heartland of Slavic tribes. However, the influence of Slavic expansion can also be detected in Central Europe, where Slavic languages and cultural practices have intermingled with those of other ethnic groups.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can identify specific regions where Slavic heritage is most pronounced. For instance, Poland, with its considerable population of West Slavs, exhibits a strong genetic signature, which is reflected in both historical records and modern demographics. Interestingly, the Polish gene pool shows significant similarities with neighboring Czech and Slovak populations, demonstrating the interconnectedness of these regions.
In contrast, the Balkans present a more complex picture. Countries like Serbia and Bulgaria not only show Slavic genetic markers but also reflect the influence of earlier inhabitants such as the Thracians and Illyrians. This blending of genetic heritage creates a rich cultural mosaic, where Slavic traditions coexist alongside older, indigenous customs. The map's dark circles in these areas highlight the significant impact of Slavic migration on the genetic landscape.
Meanwhile, in Eastern Europe, particularly in Russia and Ukraine, the East Slavs dominate. Here, the genetic legacy is robust, with a clear lineage traceable to the early Slavic tribes. The map showcases how these genetic markers have remained relatively stable over the centuries, despite the tumultuous history of the region, including invasions, wars, and political upheaval.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the genetic legacy of the Slavic expansion is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it sheds light on the historical migrations that shaped modern Europe. By studying these patterns, researchers can gain insights into how cultural and genetic identities have been formed over centuries.
Moreover, this topic is relevant in contemporary discussions about nationalism and ethnic identity in Eastern Europe. As countries navigate their unique historical narratives, the understanding of shared genetic heritage can play a significant role in fostering regional cooperation and unity.
Current trends indicate an increasing interest in genetic studies that explore ancestry and heritage. This growing field not only helps individuals understand their roots but also encourages a broader appreciation of the interconnectedness of ethnic groups across Europe. As we move forward, the genetic legacy illustrated in this map will continue to inform both academic research and public discourse regarding identity, migration, and cultural heritage in an ever-evolving European landscape.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 6, 2025
- Views
- 112
Comments
Loading comments...