Electricity Consumption for Bitcoin Mining Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
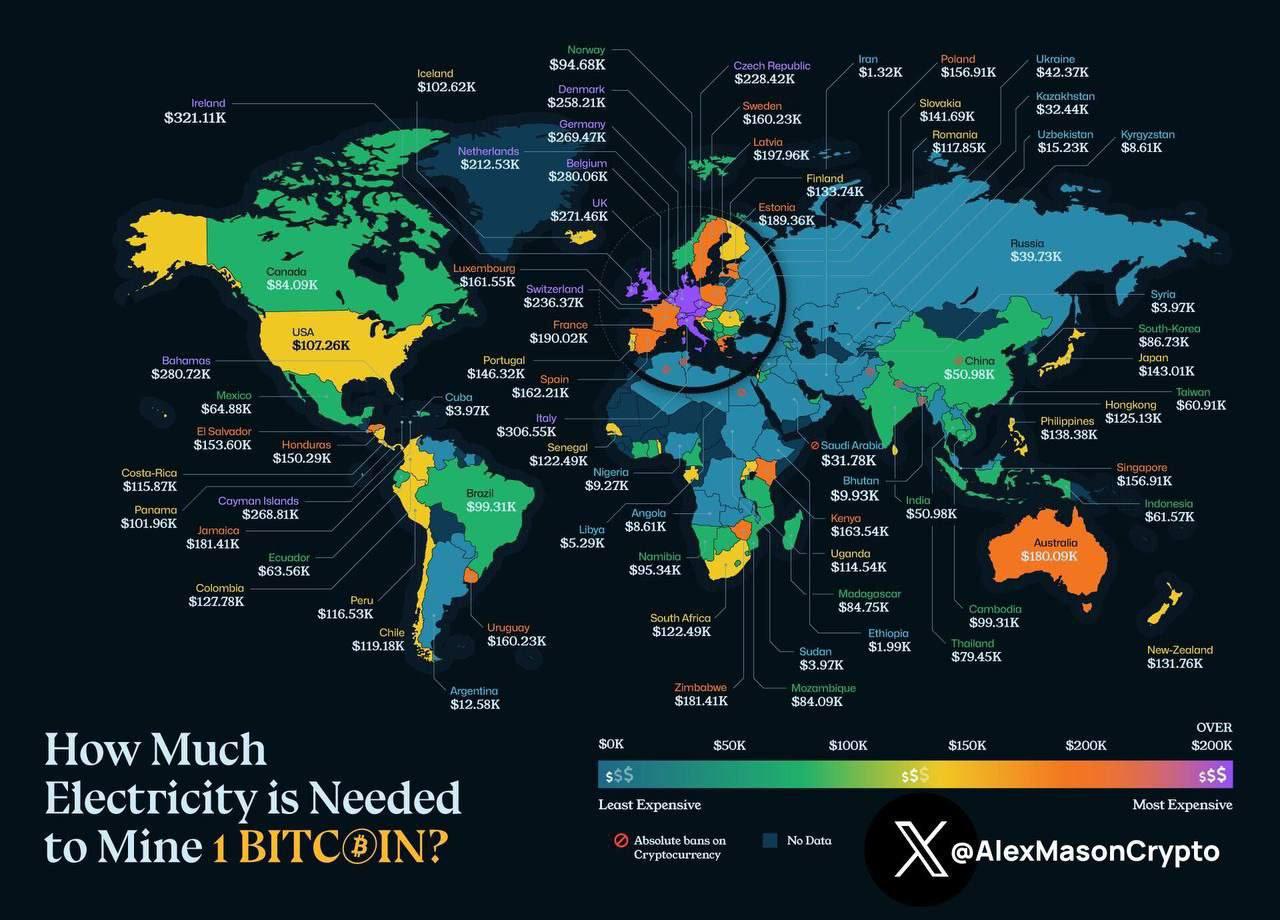
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "How Much Electricity is Needed to Mine 1 BITCOIN?" provides a striking portrayal of the electricity consumption associated with Bitcoin mining across different countries. Each region depicted on the map highlights the estimated amount of energy required to mine a single Bitcoin, with varying shades and colors to indicate the levels of electricity use. This visualization is not just about numbers; it reflects the environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining, an issue that has become increasingly pertinent in discussions about energy consumption and sustainability.
Deep Dive into Bitcoin Mining and Electricity Consumption
Bitcoin mining is a complex process that requires significant computational power, which in turn demands vast amounts of electricity. To understand why this is the case, we need to delve into how Bitcoin operates. Bitcoin, a decentralized digital currency, relies on a network of miners who validate transactions and secure the network through a process called proof-of-work. This process involves solving complex mathematical puzzles, which requires high-performance computers running continuously.
Interestingly, the electricity consumption of Bitcoin mining has become a hot topic in recent years. According to estimates by the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, Bitcoin mining consumes about 120 terawatt-hours (TWh) annually, roughly equivalent to the energy consumption of entire countries like Argentina or the Netherlands. This staggering figure raises important questions about the sustainability of cryptocurrencies and their environmental footprint.
What's fascinating is the disparity in electricity consumption across different regions. For instance, some areas benefit from renewable energy sources, like hydroelectric power in regions such as Sichuan, China, or the Pacific Northwest in the United States. In these regions, the energy costs are lower, making mining operations more economically viable. In contrast, regions that rely heavily on fossil fuels, such as coal-based energy in parts of Eastern Europe and the U.S. Midwest, exhibit much higher carbon footprints for the same mining activities.
Moreover, the source of electricity plays a crucial role in determining the overall environmental impact. When Bitcoin is mined using renewable energy, it has a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to mining operations powered by coal or natural gas. This fact is vital as the world grapples with climate change and the urgent need to transition to sustainable energy sources.
Regional Analysis
Turning our attention to the regional breakdown presented in the map, we see stark contrasts in electricity consumption for Bitcoin mining. For example, in countries like Iceland and Norway, the use of geothermal and hydroelectric energy means that mining operations have a relatively low environmental impact. In Iceland, a country known for its abundant geothermal resources, the electricity consumption for mining is much lower than in countries that depend on coal.
On the other hand, China, which has dominated Bitcoin mining for years, has seen a significant shift due to regulatory crackdowns on mining operations, especially in regions that rely on coal. The Sichuan province, which was once a hotspot for Bitcoin mining due to its cheap hydroelectric power, has now seen a decline in operations as miners are forced to relocate or adapt to new regulations. This shift underscores the dynamic nature of the cryptocurrency landscape and its dependence on energy policies and availability.
Interestingly, the United States has emerged as a new leader in Bitcoin mining, particularly in states like Texas and Wyoming, where energy costs are low, and there is a growing focus on renewable energy. These states are harnessing the potential of wind and solar power, allowing miners to operate more sustainably. As a result, the U.S. is expected to play a significant role in the future of Bitcoin mining, especially as environmental concerns continue to shape public discourse.
Significance and Impact
The significance of understanding electricity consumption in Bitcoin mining cannot be overstated. As cryptocurrencies gain popularity, the energy requirements associated with their production have sparked debates about their sustainability and environmental impact. With increasing awareness of climate change, many stakeholders are calling for greater transparency in how Bitcoin is mined and the energy sources used.
Furthermore, as more miners seek cost-effective solutions, the race to find sustainable energy sources is intensifying. This trend could lead to innovations in energy technology, including more efficient mining operations and the integration of renewable energy solutions. In the long run, the future of Bitcoin mining may hinge on its ability to adapt to these environmental challenges and the ongoing transition to a greener economy.
In conclusion, the map illustrating electricity consumption for Bitcoin mining is not just a reflection of energy use; it represents a broader conversation about the intersection of technology, economy, and environment. As we move forward, understanding these dynamics will be crucial in shaping a sustainable future for cryptocurrencies and our planet.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 5, 2025
- Views
- 88
Comments
Loading comments...