Apostasy Punishable by Death Countries Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
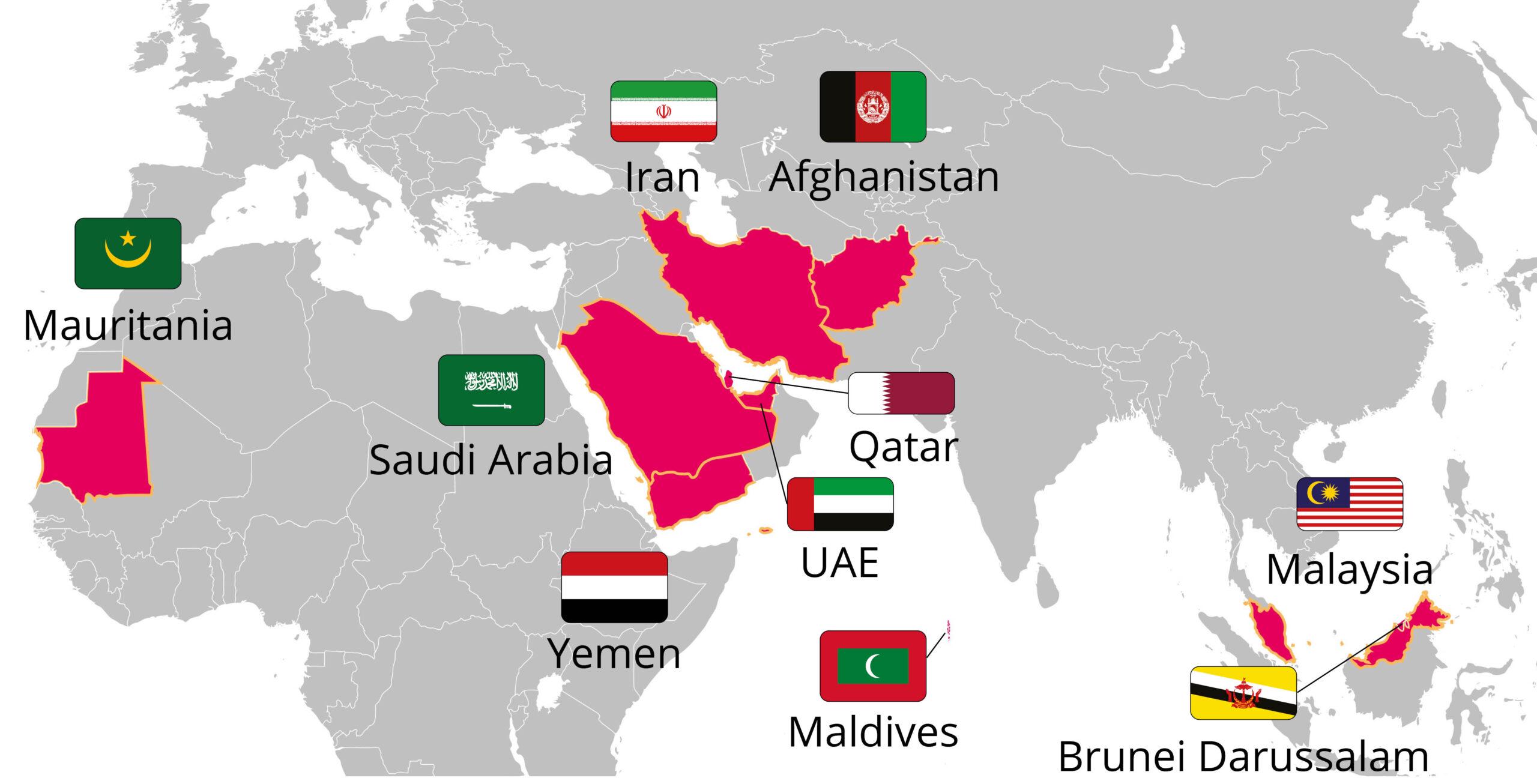
This map visually represents countries where apostasy, the act of leaving one’s religion, is punishable by death. It highlights the legal and societal repercussions faced by individuals who choose to change their religious beliefs in these nations. In many cases, the implications of such laws extend beyond the legal framework, influencing societal attitudes and personal safety for those contemplating a shift in faith.
Deep Dive into Apostasy Laws
Apostasy laws are rooted in religious doctrines and cultural traditions, often reflecting a society's view on faith and identity. What's fascinating is that the concept of apostasy varies significantly across different religions and regions. In some countries, leaving a faith may not only lead to social ostracism but also to severe penalties, including imprisonment or even death.
As of 2023, there are at least ten countries where the death penalty remains an option for those accused of apostasy. Among these, nations like Afghanistan, Iran, and Saudi Arabia are often highlighted due to their strict interpretations of Islamic law. It’s essential to understand that these laws are not merely theoretical; they can lead to real-life consequences, affecting countless individuals’ lives.
Interestingly, the implementation of apostasy laws can vary widely even within the same country. For example, while Saudi Arabia enforces strict adherence to Sharia law, the application of apostasy laws may differ based on regional interpretations and the political climate at any given time. In countries like Sudan, recent legal reforms have attempted to soften these laws, showcasing a shift towards more liberal approaches, although challenges remain.
In contrast, countries such as Pakistan enforce blasphemy laws that can indirectly affect apostasy cases, leading to mob violence or pressure from extremist groups against those perceived to have renounced their faith. This creates an atmosphere of fear, stifling personal freedom and religious expression.
The impact of these laws extends beyond the individual; they affect families, communities, and even international relations. Countries that impose such harsh penalties often face criticism from human rights organizations and foreign governments, leading to diplomatic tensions. In some instances, this can result in sanctions or other forms of international pressure aimed at encouraging reform.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map by region reveals fascinating contrasts. In the Middle East, countries like Iran and Yemen are significant for their stringent laws against apostasy. Iran, for instance, has a long history of enforcing such penalties, which is closely tied to its theocratic governance. Conversely, in African nations like Somalia and Mauritania, apostasy laws are also rooted in Islamic jurisprudence but can be influenced by local customs and governance structures.
In South Asia, Pakistan stands out due to its blasphemy laws that heavily influence perceptions and treatment of apostasy. The government's approach can lead to extreme societal repercussions, including vigilantism against those accused of leaving Islam. Meanwhile, in the more secularized regions of Asia and Europe, apostasy is generally not criminalized, reflecting broader trends towards religious tolerance and personal freedoms.
Interestingly, the variation in apostasy laws can also be seen within the same religious context. For instance, while Islamic countries may share a common theological framework, the socio-political landscape can result in vastly different implementations and consequences of apostasy laws. This highlights the complexity of the relationship between religion, law, and culture.
Significance and Impact
The significance of this topic cannot be overstated. Apostasy laws not only infringe on basic human rights but also serve as a barometer for the level of tolerance and freedom within a society. The implications are profound; they can lead to international condemnation and affect diplomatic relations, especially as global movements advocate for human rights and religious freedom.
Additionally, the rise of global connectivity and the influence of social media have made it increasingly challenging for oppressive regimes to control narratives surrounding religion and belief. Young people, in particular, are questioning traditional norms and seeking greater personal freedom, leading to a potential clash between established religious authorities and a new generation advocating for change.
As we look to the future, it’s essential to consider how these laws might evolve. With ongoing debates about human rights, religious freedom, and societal change, there is hope that more nations will reconsider their stance on apostasy. Ultimately, the desire for personal belief and freedom of conscience is a fundamental aspect of the human experience, and addressing apostasy laws is a crucial step towards achieving a more just and equitable world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 5, 2025
- Views
- 286
Comments
Loading comments...