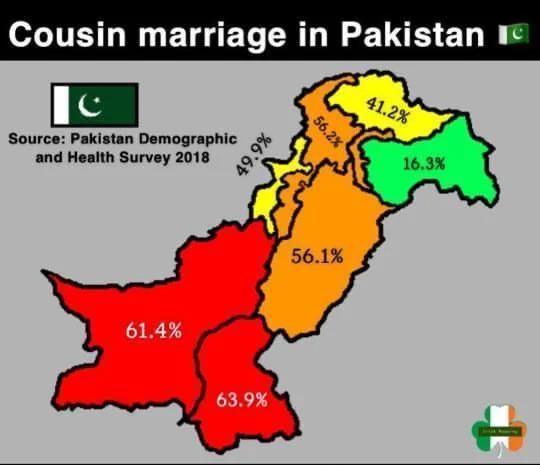
Rates of Consanguinity in Pakistan Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Rates of Consanguinity in Pakistan Map" provides a compelling visual representation of the prevalence of consanguineous marriages across various regions of Pakistan. Consanguinity refers to the practice of marrying within close familial relations, such as cousins, which can have significant implications for genetic diversity, public health, and social structure. By analyzing this map, we can observe how cultural, social, and economic factors influence the rates of such marriages throughout the country.
Deep Dive into Consanguinity in Pakistan
Have you ever wondered why certain regions exhibit higher rates of consanguinity than others? In Pakistan, this practice is not merely a personal choice but is deeply rooted in cultural traditions and social norms. In many communities, marrying within the family is seen as a way to strengthen familial ties, maintain property within the family, and ensure that cultural values are preserved. Interestingly, the rates of consanguinity can vary dramatically even within the same province, as different ethnic groups have distinct marriage customs.
According to research, approximately 60% of marriages in Pakistan are consanguineous, which places the country among those with the highest rates of cousin marriages in the world. A significant aspect of this phenomenon is the preference for first cousin unions, which are prevalent among many communities. The factors contributing to this trend include social pressure, economic considerations, and the desire to keep wealth within the family.
Health implications of consanguinity cannot be overlooked. Studies have shown that children born from consanguineous unions may face an increased risk of genetic disorders. This is primarily due to the likelihood of inheriting recessive genetic traits, which can lead to serious health issues. In regions where consanguinity is common, healthcare systems are often stressed by the prevalence of these inherited conditions. For instance, areas with high rates of consanguinity, such as parts of Sindh and Punjab, report a higher incidence of congenital disabilities and other health complications.
Moreover, the implications extend beyond individual health risks to broader public health considerations. Public health officials and genetic counselors in Pakistan are increasingly raising awareness about the potential risks of consanguineous marriages, promoting genetic testing and counseling for families considering such unions. However, changing deeply entrenched cultural practices is a slow process, often met with resistance.
Regional Analysis
When we take a closer look at the map, distinct regional patterns emerge. In the northern areas, such as Gilgit-Baltistan, the rates of consanguinity are relatively lower compared to central Punjab or Sindh. This difference can be attributed to the varied ethnic compositions and social structures across these regions. In Punjab, for instance, the practice is more prevalent among certain groups, whereas in the remote northern areas, geographical isolation and diverse ethnicities contribute to a more varied marital landscape.
Interestingly, urban areas like Karachi show a contrast in consanguinity rates compared to rural settings. As urbanization increases, there is often a trend towards more diverse marital choices, although certain communities still adhere to traditional practices. This creates a complex social tapestry where modern influences intersect with longstanding traditions.
In Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, the rates of consanguinity can also vary significantly among different tribes and communities. Some tribal groups have a strong preference for cousin marriages, while others are more open to external unions. This regional variation highlights the importance of understanding local customs and societal norms when discussing consanguinity in Pakistan.
Significance and Impact
The implications of consanguinity in Pakistan are profound, affecting everything from public health to social dynamics. Understanding the rates and reasons for consanguineous marriages is essential for public health planning and genetic counseling initiatives. As Pakistan continues to develop, addressing the challenges associated with high rates of consanguinity will be crucial in improving public health outcomes.
Moreover, as societal attitudes shift, especially among younger generations who may be more exposed to education and global perspectives, we may see changes in marriage patterns. Interestingly, some researchers speculate that increased awareness of genetic risks and health education could lead to a gradual decline in consanguinity rates in the coming decades. However, this will require sustained efforts from both the government and non-governmental organizations to promote healthy marriage practices while respecting cultural values.
Ultimately, the "Rates of Consanguinity in Pakistan Map" serves as a critical tool for understanding how cultural practices shape social structures and health outcomes. By examining these rates closely, we can glean insights that help inform policies aimed at fostering healthier communities across Pakistan.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 4, 2025
- Views
- 70
Comments
Loading comments...