EU Attitude Map by Member States 2025

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
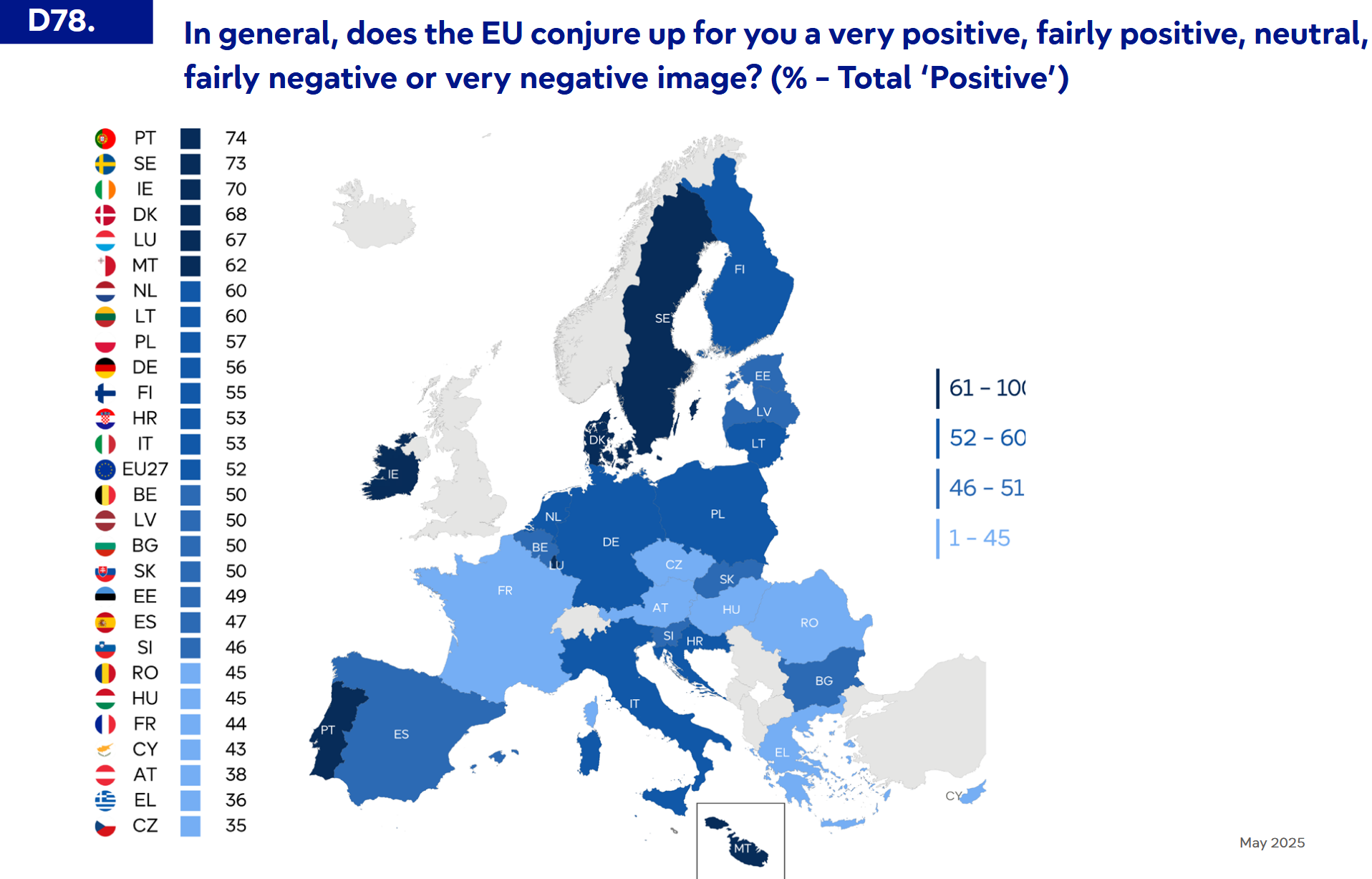
What This Map Shows
The recently released Eurobarometer 2025 visualization outlines the attitudes towards the European Union across its member states. This map provides a clear snapshot of how citizens in various countries perceive the EU, ranging from strong support to notable skepticism. The data highlights public sentiment, revealing the complexities of national perspectives within the broader EU framework. Understanding these attitudes is crucial, as they can shape policy, influence elections, and affect the EU's future direction.
Deep Dive into Attitudes Towards the EU
Examining attitudes towards the European Union is not just a matter of political interest; it reflects deeply rooted cultural, economic, and historical contexts. The EU was established to promote peace, stability, and economic cooperation among European nations after decades of conflict. However, these ideals can be challenged by national interests, economic disparities, and differing cultural identities. Interestingly, the Eurobarometer shows that support for the EU can vary significantly based on economic conditions, historical ties, and recent political developments. For instance, countries like Luxembourg and Ireland often report high levels of EU support, largely due to their economic benefits from EU membership. They enjoy access to a larger market, funding for infrastructure, and increased foreign investment, which has fostered a positive view of the EU. Conversely, newer member states from Eastern Europe, such as Hungary and Poland, have displayed more ambivalent or even negative attitudes towards the EU in recent years. Factors contributing to this skepticism include perceived encroachments on national sovereignty and dissatisfaction with how the EU handles migration and economic policies. Have you ever wondered why public sentiment can shift so dramatically? Events such as the migrant crisis, economic downturns, and political scandals can rapidly alter perceptions, leading to fluctuating support levels. Moreover, the economic landscape plays a pivotal role in shaping attitudes. Countries experiencing economic hardship often express more anti-EU sentiments. For example, Greece's financial crisis in the 2010s led to a surge in Euroscepticism, as citizens blamed the EU for imposing harsh austerity measures. Such economic strains can overshadow the EU's benefits, highlighting the delicate balance between national priorities and European unity. As we delve deeper, it’s essential to recognize the generational differences in attitudes toward the EU. Younger generations generally tend to be more pro-EU, viewing it as a platform for opportunities such as study abroad programs and job mobility. In contrast, older populations may harbor nostalgia for national sovereignty, often leading to harsher criticisms of the EU. These demographic factors further complicate the EU's image across member states, creating a mosaic of opinions influenced by age, economic status, and historical experiences.
Regional Analysis
The map reveals notable regional patterns in attitudes towards the EU. In Western Europe, countries such as France and Germany typically display robust support for the EU, seeing it as a cornerstone of stability and peace. However, even within these countries, there are pockets of skepticism. For instance, in France, rising populist sentiments have led to increased criticism of EU policies, particularly regarding immigration and economic governance. In Southern Europe, nations like Spain and Italy have historically supported the EU, but recent economic struggles have led to a shift in public opinion. The rise of political parties that challenge the EU's authority reflects this growing skepticism. On the other hand, Northern European countries, including the Netherlands and Denmark, maintain a strong pro-EU stance, driven by a focus on environmental policies and economic cooperation. However, they also express concerns about the EU's regulatory frameworks and their impact on national interests. Interestingly, Eastern European states show a mixed bag of attitudes. While countries like Estonia and Lithuania exhibit strong EU support, Hungary and Poland are more critical, often voicing concerns about migration policies and perceived overreach by EU institutions. This division underscores the diverse political landscapes across Europe, influenced by national histories and contemporary challenges.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the attitudes toward the EU is vital for several reasons. First, it influences policy-making at both national and EU levels. Public opinion can sway governments to adopt more EU-friendly policies or, conversely, to pull back from EU commitments. Furthermore, these attitudes can impact elections, as parties that advocate for a stronger or weaker EU presence often gain or lose support based on prevailing public sentiments. Moreover, this data is crucial for predicting future trends. As the EU faces significant challenges, including climate change, economic inequalities, and geopolitical tensions, understanding public attitudes can help shape effective responses. The rise of Euroscepticism in certain regions may lead to calls for reform within the EU, pushing for a more flexible and responsive organization. In conclusion, the Eurobarometer 2025 map serves as a window into the complex landscape of public opinion within the EU. By analyzing these attitudes, we can better understand the future of European integration and the challenges it faces in an ever-changing world. Will citizens embrace a stronger EU, or will national interests take precedence? Only time will tell, but the data clearly shows that public sentiment will play a crucial role in shaping the EU’s path forward.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 3, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...