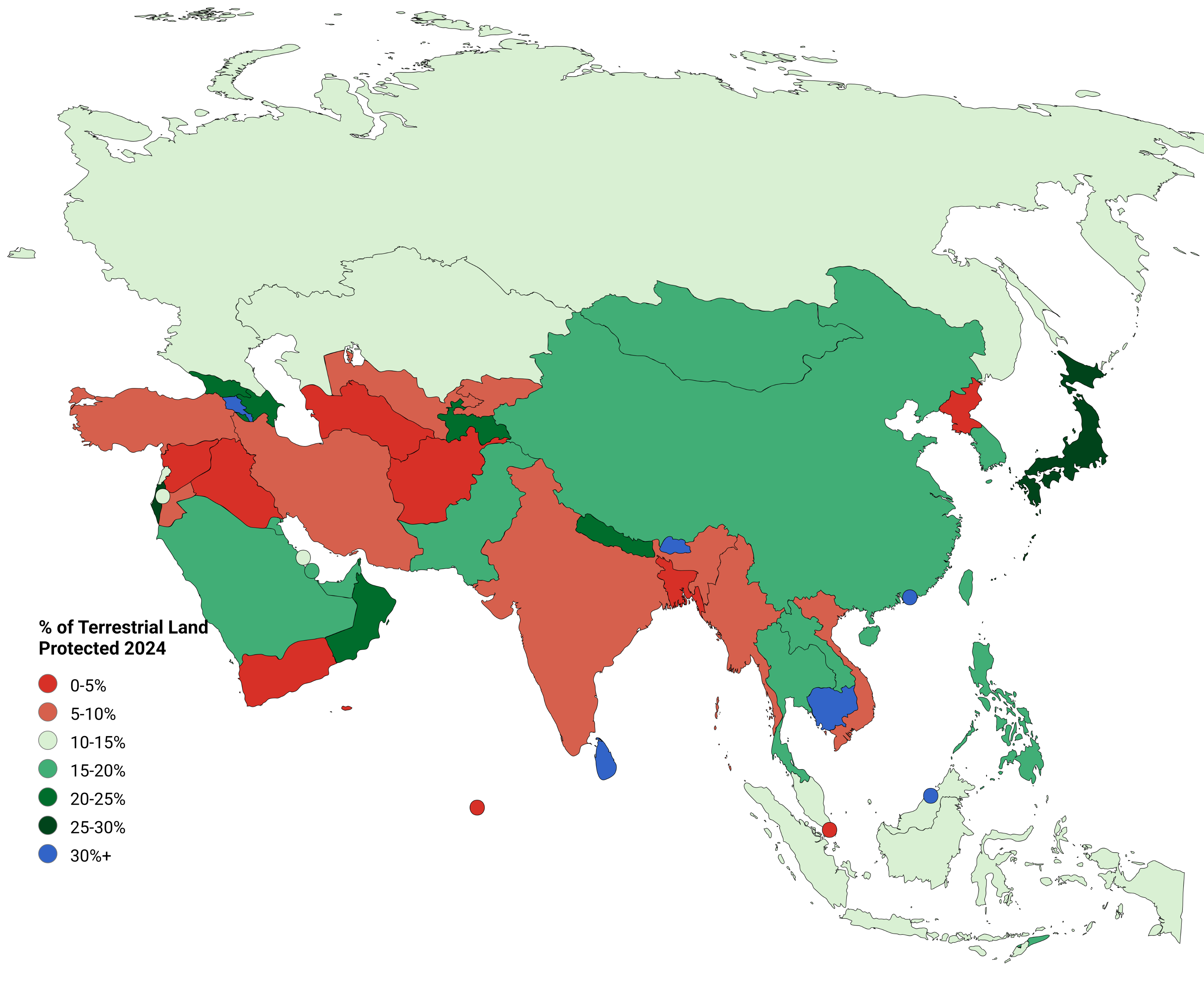
Asian Countries Percentage of Land Area Protected for Wildlife Map

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Asian Countries Percentage of Land Area Protected for Wildlife" provides a visual representation of how much land in various Asian countries is designated for wildlife protection. This visualization highlights the commitment of different nations to conserving natural habitats and protecting biodiversity. Understanding these designations is crucial, as they play a significant role in the preservation of ecosystems and the species that inhabit them.
Deep Dive into Land Protection for Wildlife
Wildlife protection encompasses a range of initiatives aimed at conserving natural habitats and the myriad species that rely on them. The percentage of land area protected varies greatly across Asia, reflecting differing national priorities, levels of economic development, and environmental policies. For instance, countries like Bhutan, with over 50% of its land designated as protected areas, showcase a strong commitment to preserving their unique ecosystems. Interestingly, Bhutan's constitution mandates that at least 60% of the country’s area remains under forest cover, which further aids in wildlife conservation efforts.
On the other hand, countries like Afghanistan have significantly lower percentages of protected land, often below 2%. This stark contrast raises important questions about the implications of land protection. Areas with higher protection levels usually boast richer biodiversity, healthier ecosystems, and more robust tourism sectors driven by wildlife enthusiasts. Moreover, protected areas can help mitigate climate change impacts by preserving carbon sinks, such as forests and wetlands.
The establishment of national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas are critical components of wildlife conservation strategies. In Southeast Asia, for instance, the creation of the Coral Triangle Initiative has led to increased protection of marine biodiversity, which is vital not only for wildlife but also for the livelihoods of millions of people in coastal communities.
Wildlife corridors also play a significant role in ensuring genetic diversity and the survival of species. These corridors connect protected areas, allowing animals to migrate safely between habitats. Countries like India have made efforts to create such corridors, particularly for big cats like tigers, which require large territories to thrive. However, balancing human development with wildlife needs remains a challenge in many regions.
Despite the progress made in some areas, challenges persist. Deforestation, urban expansion, and climate change threaten existing protected areas and the species that inhabit them. The impact of poaching and illegal wildlife trade cannot be underestimated either; these issues jeopardize the gains made in conservation efforts across the continent.
Regional Analysis
When looking at the map, we can identify distinct patterns across various regions in Asia. For instance, countries in Central Asia like Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan typically have lower percentages of protected land, often below 10%. This can be attributed to extensive agricultural practices and resource extraction that prioritize economic growth over conservation.
Conversely, Southeast Asian nations, such as Malaysia and Indonesia, have made significant strides in establishing protected areas, largely due to their rich biodiversity, which includes unique species found nowhere else on Earth. However, even these countries face tremendous pressure from logging and palm oil plantations, which threaten the integrity of their protected areas.
In South Asia, countries like Nepal and India stand out with their efforts to protect wildlife. Nepal, for example, has over 23% of its land designated as national parks and conservation areas, showcasing a strong commitment to environmental stewardship. This is particularly significant given the pressures from rising populations and urbanization in the region.
Significance and Impact
The significance of wildlife protection cannot be overstated. Protecting land for wildlife is not just about conserving nature; it has profound implications for human health, economic stability, and cultural heritage. Ecosystems provide critical services such as clean air, water purification, and climate regulation. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for these services will escalate, making the preservation of natural habitats even more urgent.
Interestingly, there's also a growing global awareness regarding the importance of biodiversity. The UN’s Convention on Biological Diversity has highlighted the need for countries to increase their protected areas as part of international agreements on climate change and sustainable development. As we look to the future, the challenge will be to balance human development with the necessity of conserving our planet's wildlife. The map serves as a reminder of the progress made and the work still needed in the quest for sustainable coexistence between humanity and nature.
Visualization Details
- Published
- September 3, 2025
- Views
- 72
Comments
Loading comments...