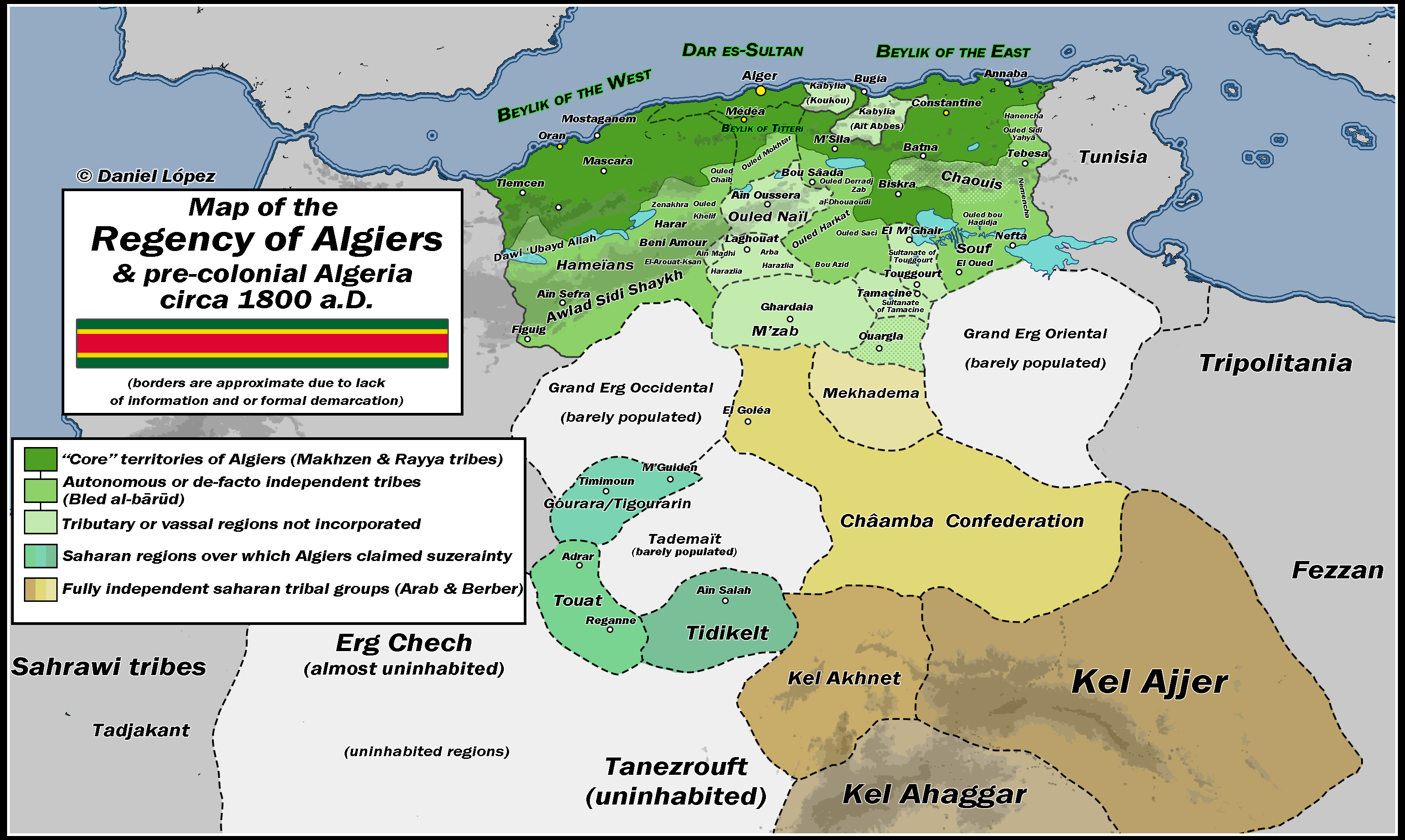
Map of the Regency of Algiers c.1800 A.D.

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Map of the Regency of Algiers c.1800 A.D." provides a detailed depiction of the geographical and political landscape of the Regency of Algiers during the early 19th century. This map illustrates not only the territorial boundaries but also key cities, trade routes, and topographical features of the region. It serves as a snapshot of a significant period in North African history, when the Regency was a powerful entity influenced by both indigenous and colonial forces.
Deep Dive into the Regency of Algiers' Geography
The Regency of Algiers, part of present-day Algeria, was a vital hub for trade and maritime activities in the Mediterranean. Interestingly, the geographical positioning of Algiers along the coast facilitated its role as a trade center. The region was characterized by its rugged terrain, including the Atlas Mountains, which not only shaped the settlement patterns but also influenced agricultural practices.
Have you ever wondered how the topography affects trade routes? In this case, the mountains created natural barriers while the coastal plains allowed for more accessible land for farming and trade. The fertile areas near the Tell Atlas were crucial for producing grains and olives, which were essential for both local consumption and export.
The Regency was dominated by the Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climatic condition significantly influenced the types of crops grown and the lifestyle of the inhabitants. Furthermore, the coastal proximity allowed for fishing to be a staple source of food, integrating into the local economy.
Population-wise, the Regency was a melting pot of cultures, primarily Berber, Arab, and European influences. The blend of these cultures created a unique demographic landscape, with cities like Algiers serving as cultural and administrative centers. By 1800, Algiers was bustling with a diverse population, reflective of its status as a trade nexus.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can identify several key regions within the Regency of Algiers that exhibit distinct characteristics. The coastal cities, including Algiers itself, Oran, and Constantine, were pivotal for maritime trade and served as gateways to Europe. In contrast, the mountainous regions, such as Kabylie, were less accessible and largely rural, leading to a different lifestyle focused on agriculture and pastoralism.
For instance, while Algiers thrived as a commercial hub with a population engaged in trade and diplomacy, the Kabylie region maintained a more traditional, subsistence-based economy. The contrast between these areas is evident not just in lifestyle but also in the architectural styles and cultural practices found there.
Interestingly, the map also highlights the presence of various forts and military installations, which were critical during this period of conflict and piracy in the Mediterranean. These fortifications indicate the strategic importance of the Regency in protecting trade routes, as well as its engagements with European powers, particularly during the era of the Barbary Wars.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the geography of the Regency of Algiers is essential for grasping the broader historical context of North Africa in the 19th century. The Regency was not just a local power; it played a significant role in Mediterranean geopolitics, influencing trade, military strategy, and cultural exchanges.
Fast forward to today, and the legacy of the Regency can still be felt in Algeria’s cultural and social structures. The historical interactions between the Berber, Arab, and European populations laid the groundwork for modern Algerian society. As global trade continues to evolve, the historical significance of such regions reminds us of the interconnectedness of cultures and economies.
Furthermore, current trends in archaeology and historical research are bringing to light more about the Regency's impact on trade networks across the Mediterranean. As scholars delve deeper into the intricacies of this historical period, we gain insights that not only inform us about the past but also help us understand the present dynamics of cultural and economic exchanges in the region.
In conclusion, the "Map of the Regency of Algiers c.1800 A.D." is more than just a visual representation; it encapsulates a pivotal moment in North African history, revealing the intricate tapestry of trade, culture, and geography that continues to shape the region today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 31, 2025
- Views
- 118
Comments
Loading comments...