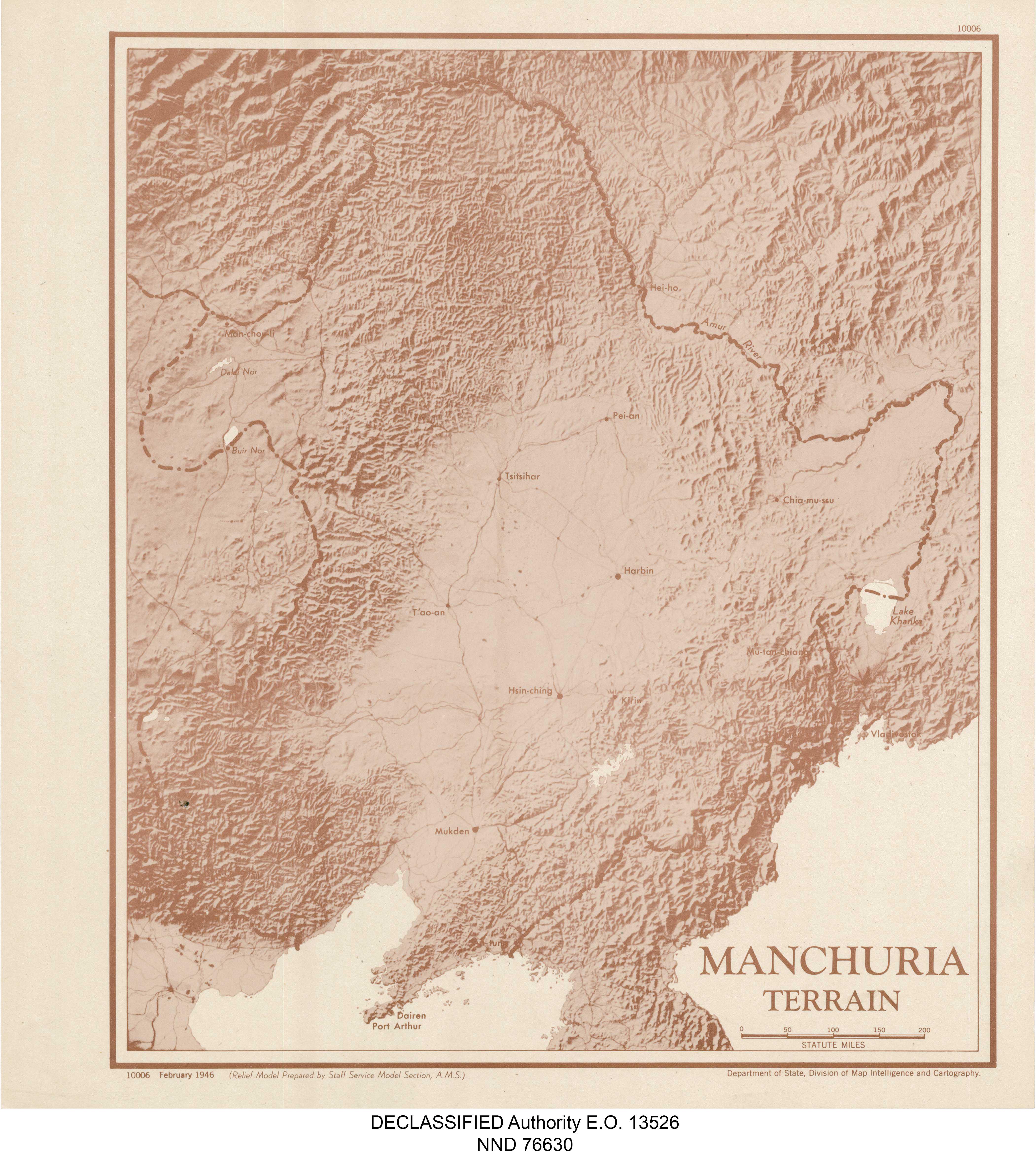
Manchuria Terrain Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
The "Manchuria Terrain Map" provides a detailed visualization of the topographical features of the Manchuria region, which encompasses parts of northeastern China, eastern Mongolia, and the Russian Far East. This map highlights key geographical elements such as mountains, plains, and river systems, offering insights into how these features shape the landscape and influence human activities. The terrain of Manchuria is diverse, with various elevations and landforms that contribute to its ecological richness.
Deep Dive into Manchuria's Terrain
Manchuria's terrain is a compelling subject, shaped by its unique geological history and climatic conditions. The region is predominantly characterized by its vast plains, mountains, and river valleys. The Greater Khingan Range runs along the western edge of Manchuria, presenting a rugged landscape that contrasts sharply with the low-lying areas to the east.
What's fascinating is that the mountains not only define the physical geography but also influence the climate, creating a rain shadow effect that affects agricultural practices in the region. The eastern part of Manchuria features the fertile Songhua River basin, which supports extensive agriculture, including rice and soybeans. In contrast, the western regions are less fertile, dominated by forested areas and grasslands where pastoralism is more common.
The Amur River, one of the longest rivers in the world, forms a natural border between Russia and China, flowing through this diverse terrain. This river is crucial for transportation and trade, as well as for the ecosystems that depend on its waters. The river's tributaries, such as the Ussuri and the Sungari, create complex watersheds that support a variety of flora and fauna.
Interestingly, the combination of plains and mountains creates microclimates within the region. This variability allows for a rich biodiversity, making Manchuria home to several endemic species, including the Siberian tiger and the Amur leopard. The ecological importance of the terrain cannot be understated, as it plays a vital role in conservation efforts and biodiversity protection.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the terrain of Manchuria by regions reveals significant variations in land use and ecological features. For instance, the Northeast Plain, which includes parts of Heilongjiang Province, is renowned for its agricultural productivity. Here, the flat landscape and fertile soil create ideal conditions for large-scale farming, making it a vital food production area for China.
In contrast, the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, which lies to the west, is characterized by a more arid climate and rugged terrain. The area is predominantly grassland, suitable for sheep herding and nomadic lifestyles. The differences in terrain influence not only the economy but also the cultural practices of the inhabitants.
Another notable area is the Hulunbuir grassland, famous for its sweeping plains and rich biodiversity. This region contrasts sharply with the mountainous areas of the Greater Khingan Range, where dense forests dominate. The diversity in terrain leads to a variety of ecological niches, supporting different animal species and plant communities.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the terrain of Manchuria is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it informs land use planning and resource management, essential for sustainable development in the region. As populations grow and climate change impacts agricultural productivity, knowledge of the terrain can help mitigate adverse effects.
Moreover, the topography has historical significance; the region served as a corridor for migration and trade between China and Russia, impacting cultural exchanges and economic development. Today, the terrain continues to influence geopolitical dynamics, particularly concerning resource allocation and environmental conservation efforts.
Looking ahead, the future of Manchuria's terrain will likely be shaped by ongoing environmental challenges, including deforestation, land degradation, and climate change. Monitoring these changes through detailed mapping and analysis will be vital for preserving the region's natural heritage and ensuring that it remains a vibrant area for future generations.
In conclusion, the "Manchuria Terrain Map" not only highlights the intricate landscape of this diverse region but also underscores the importance of understanding geography in addressing real-world issues. Whether for agriculture, conservation, or cultural heritage, the terrain of Manchuria is a vital aspect of its identity and future.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 31, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...