HDI in Africa Map 2023

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
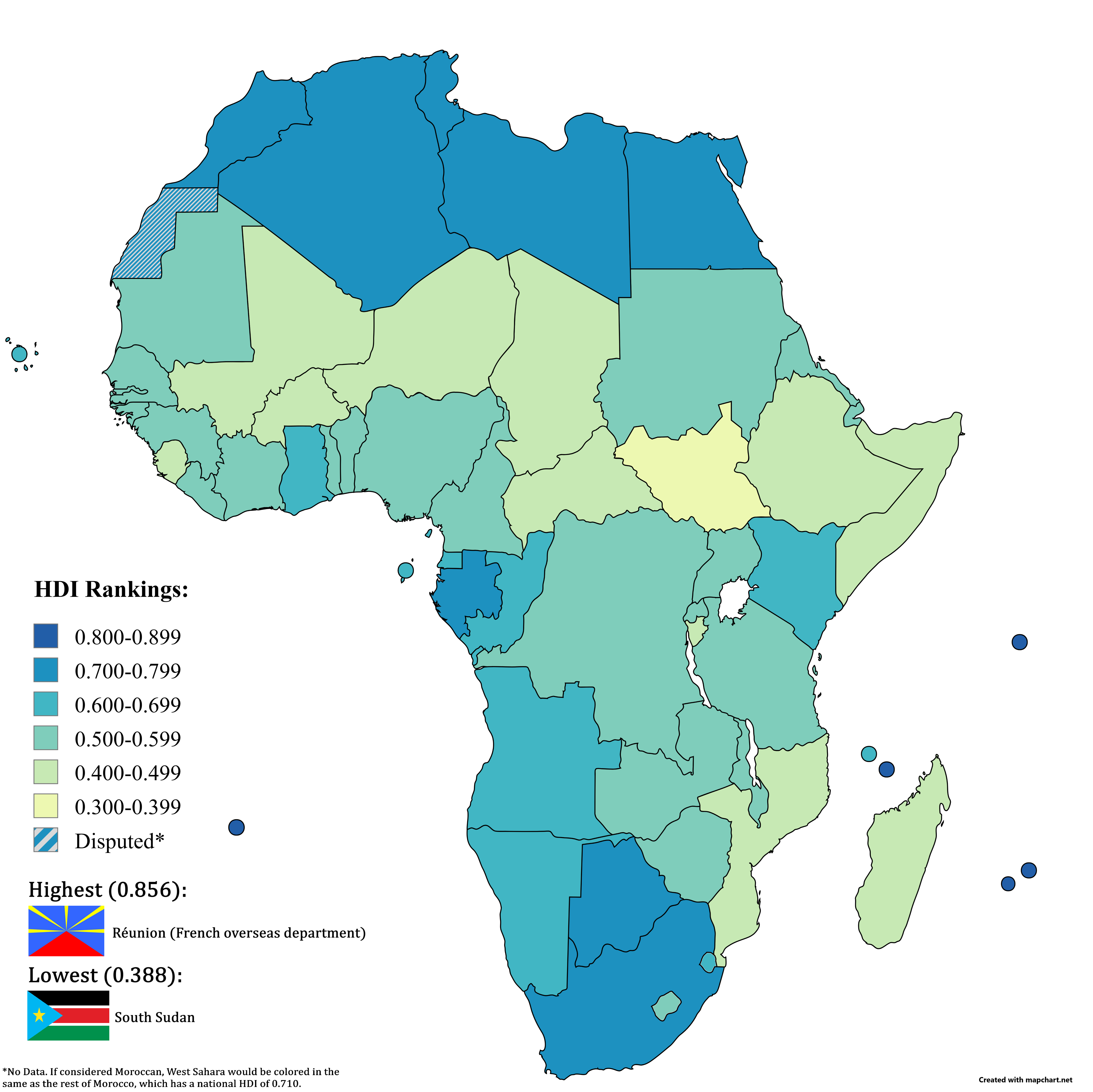
What This Map Shows
The "HDI in Africa (2023 Data)" map provides a comprehensive overview of the Human Development Index (HDI) across African nations. This visualization highlights the varying levels of human development throughout the continent, with Seychelles leading the way as the country with the highest HDI score of 0.848, followed closely by other nations. The HDI is a crucial metric that combines indicators of life expectancy, education, and per capita income to assess the overall development and quality of life in different countries. This map serves not only as a geographical representation but also as a tool for understanding the socio-economic landscape of Africa.
Deep Dive into Human Development Index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic used to rank countries based on human development levels. It was introduced by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in 1990 as a response to the limitations of using only economic indicators like GDP to evaluate the progress of nations. The HDI encompasses three main dimensions: health (measured by life expectancy at birth), education (measured by mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling), and standard of living (measured by gross national income per capita).
In Africa, the HDI scores reveal significant disparities in development. For instance, countries like Seychelles, Mauritius, and Algeria rank high with scores above 0.7, indicating a higher quality of life, better education systems, and improved health care. In contrast, nations such as Niger and the Central African Republic have much lower HDI scores, reflecting challenges like poverty, limited access to education, and inadequate healthcare services.
Interestingly, Seychelles stands out not just for its HDI score but also for its unique socio-economic structure. As an island nation, it has invested heavily in tourism and education, which has contributed to its high ranking. On the other hand, countries with lower HDI scores often grapple with issues such as political instability, economic challenges, and environmental factors that hinder development. For example, Niger, despite being rich in resources like uranium, faces significant hurdles due to climate change, which affects agricultural productivity and leads to food insecurity.
The concept of HDI encourages a more holistic view of development. It emphasizes that economic growth alone does not equate to improved living standards. Countries with similar GDP figures may have drastically different HDI scores, showcasing the importance of addressing social and health-related issues alongside economic metrics.
Regional Analysis
When examining the HDI across different regions of Africa, notable patterns emerge. North Africa generally showcases higher HDI scores compared to Sub-Saharan Africa, largely due to better educational systems and healthcare infrastructure. For instance, countries like Tunisia and Egypt score relatively high on the HDI, thanks to their long-standing investments in education and health.
In contrast, Central Africa struggles significantly with low HDI scores. Countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Chad face severe challenges, including high mortality rates, low education levels, and economic instability. The ongoing conflict and political unrest in these regions further exacerbate these issues.
West Africa presents a mixed picture. Nations like Ghana and Nigeria show promising HDI scores, largely attributed to economic growth and educational initiatives. However, the region also includes countries like Sierra Leone and Liberia, which have lower scores due to the aftereffects of civil war and ongoing health crises, such as Ebola outbreaks.
Interestingly, Southern Africa has some of the highest and lowest HDI scores on the continent. While countries like South Africa and Botswana rank high, nations like Lesotho and Swaziland face challenges such as high HIV/AIDS prevalence, which impacts life expectancy and overall development.
Significance and Impact
Understanding HDI in Africa is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and development partners. The HDI not only highlights the disparities in development but also serves as a call to action for addressing the underlying issues that hinder progress. Improving HDI scores can lead to better health outcomes, enhanced educational opportunities, and ultimately, a more prosperous society.
Moreover, as Africa continues to grow economically, investing in human capital becomes increasingly important. Countries that prioritize education, healthcare, and social services often experience sustainable growth and stability. Future projections suggest that if current trends continue, we may see improvements in HDI across African nations, particularly as more governments recognize the importance of investing in their people.
In conclusion, the HDI map of Africa in 2023 is a crucial tool for understanding the diverse developmental landscape of the continent. By focusing on human development rather than solely economic indicators, we can work towards a more equitable future for all African nations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 25, 2025
- Views
- 74
Comments
Loading comments...