Somalia Piracy Threat Map 2005-2010

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
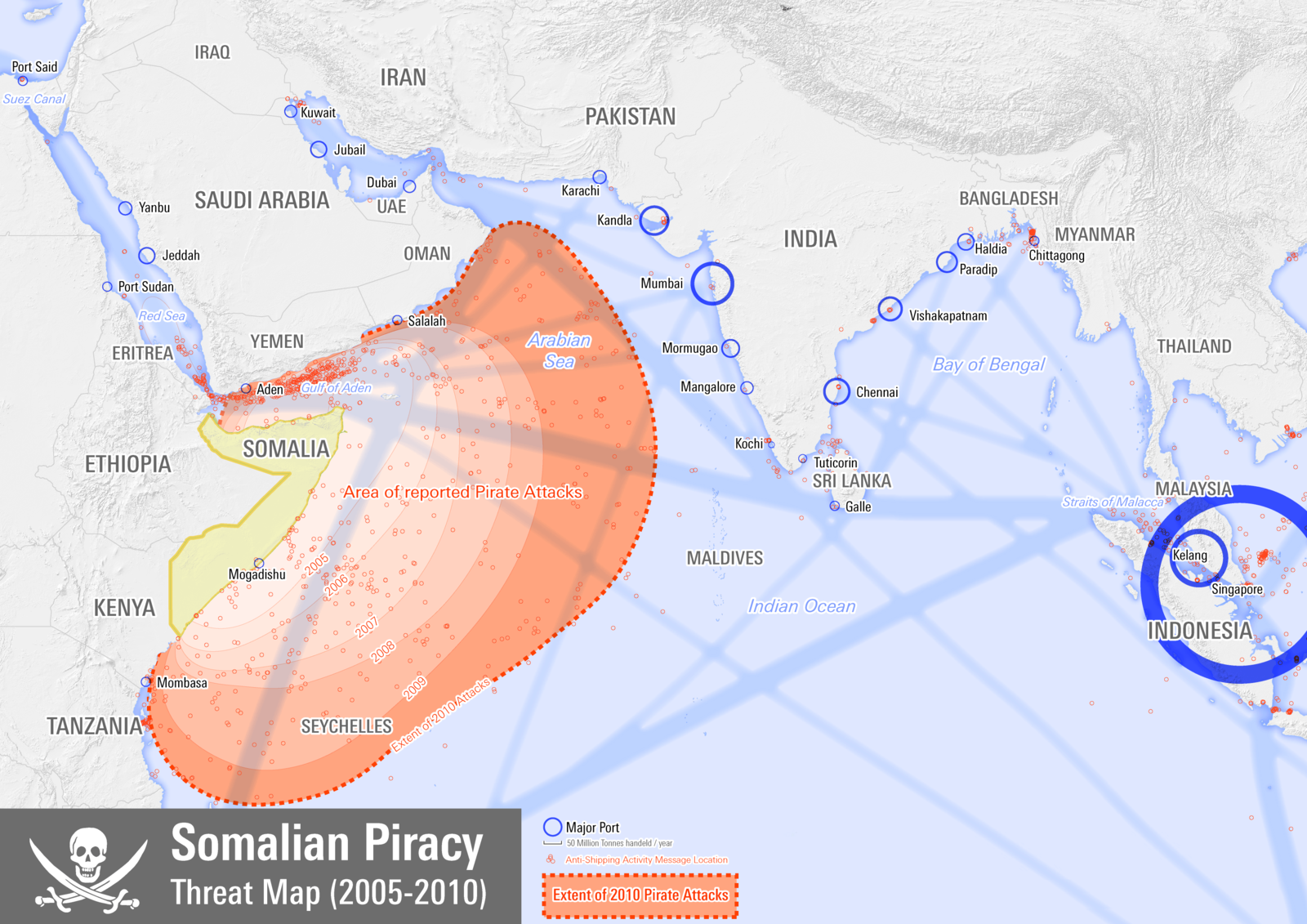
What This Map Shows
The "Somalia Piracy Threat Map 2005-2010" compellingly illustrates the surge in piracy incidents along the coast of Somalia during this tumultuous period. It highlights not only the geographical hotspots where piracy was prevalent but also provides insight into the maritime routes that were particularly vulnerable to attacks. The visualization serves as a stark reminder of the challenges faced by maritime trade in this region and the significant implications for international shipping routes.
Transitioning from the visualization itself to the topic of piracy, it's crucial to understand the broader context: why did Somalia become a hotspot for piracy, and how did this phenomenon affect global trade and security?
Deep Dive into Piracy Off the Coast of Somalia
Piracy off the coast of Somalia began to escalate in the early 2000s, primarily driven by a combination of economic hardship, political instability, and lack of effective governance in the region. Somalia, once a thriving nation, descended into chaos following the civil war that erupted in the early 1990s. With a collapsed economy and rampant unemployment, many Somalis turned to piracy as a means of survival.
Interestingly, piracy in this context was not merely opportunistic theft; it was often framed as a form of protest against illegal fishing and toxic dumping by foreign vessels in Somali waters. Pirates claimed that they were defending their territorial waters from exploitation. However, this justification didn’t mitigate the impact on international shipping, which faced serious threats from armed attacks, hijacking, and ransom demands.
Statistics indicate that between 2005 and 2010, Somali pirates attacked more than 200 vessels, with successful hijackings resulting in millions of dollars in ransom payments. The International Maritime Bureau reported that the waters off the Somali coast became the most dangerous in the world for shipping during these years. What's fascinating is that even though Somalia was landlocked in conflict, it managed to disrupt global maritime trade significantly.
The piracy not only affected shipping companies but also led to increased insurance costs, rerouting of vessels, and heightened security measures. This included the deployment of naval forces from various countries, including the United States, European Union, and NATO, in an effort to patrol the waters and reduce piracy incidents.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the piracy incidents by regions shown on the map reveals distinct patterns. The majority of attacks occurred in the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean, notably in areas such as the Somali Basin. For instance, regions like Puntland became notorious for their piracy operations, with pirates operating out of small coastal towns such as Eyl and Harardhere.
In contrast, despite the ongoing issues, the southern coastal regions of Somalia saw fewer incidents, possibly due to the limited presence of organized pirate groups there. Interestingly, the map also shows the international response, where naval patrols were concentrated in the most affected areas, creating a protective corridor for vessels traveling through these volatile waters.
The effectiveness of these multinational naval forces eventually led to a decline in piracy incidents post-2010. However, sporadic attacks continued, indicating that while the immediate threat diminished, underlying issues remained unaddressed.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the phenomenon of piracy off the coast of Somalia is crucial, not just for maritime security, but for broader discussions on international law, maritime rights, and the socio-economic conditions that drive individuals towards piracy. The implications of these events are profound, as they highlight how political instability can have far-reaching consequences beyond national borders.
In recent years, there has been a notable decrease in piracy incidents, attributed to increased naval presence and effective anti-piracy measures. However, the underlying conditions that led to piracy remain largely unaddressed. Have you noticed that even as international efforts have quelled piracy, the reasons for its rise—such as poverty and lack of governance—persist?
Looking forward, the challenge lies in addressing the root causes of piracy through sustainable development in Somalia. As global trade continues to evolve, so too must our strategies to ensure safe maritime routes that do not merely react to piracy but proactively tackle the socio-economic issues at their heart. The Somali piracy crisis serves as a critical case study in the interplay between local conditions and global commerce, a reminder that the oceans are as much a part of our interconnected world as the land itself.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 25, 2025
- Views
- 68
Comments
Loading comments...