Cincinnati Abandoned Subway Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
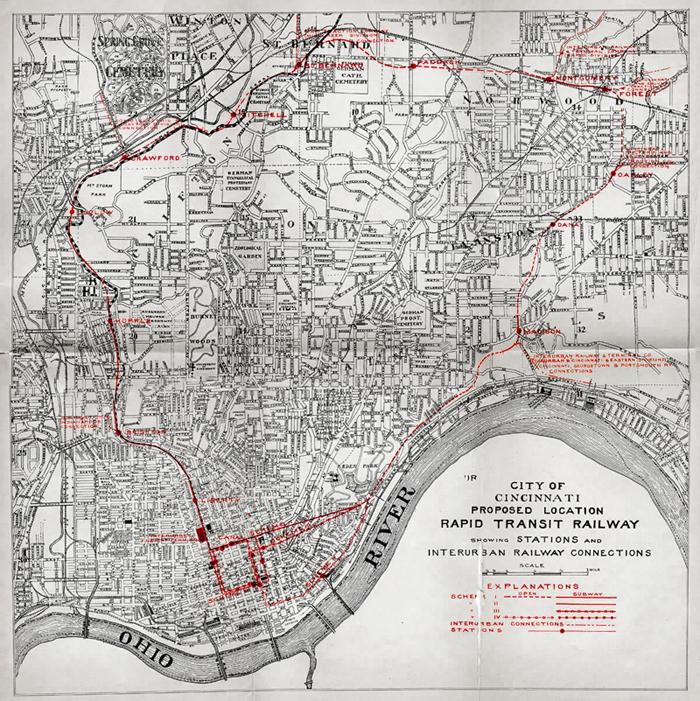
The Cincinnati Abandoned Subway Map, created in 1914 by Edwards & Baldwin, illustrates the ambitious yet ultimately unrealized subway system proposed for the city of Cincinnati, Ohio. Designed to alleviate traffic congestion and enhance public transportation, this map details the planned routes, station locations, and the envisioned connections between various neighborhoods and key urban areas. However, what stands out is not just the map's technical details but its reflection of the city’s historical ambition and the social context of early 20th-century urban planning.
Deep Dive into Cincinnati's Transportation History
Transportation has always been a crucial aspect of urban development, and Cincinnati's history is no exception. The proposed subway network was part of a broader vision to modernize the city and cater to its growing population. In the early 1900s, Cincinnati experienced significant population growth, with many residents flocking to the city for work in its bustling industries. The idea behind the subway was to provide a fast, efficient means for commuters to navigate the urban landscape.
Interestingly, Cincinnati was not alone in its subway ambitions; cities like New York and Chicago were also investing heavily in their transit systems during this period. However, the Cincinnati subway plan faced numerous challenges, including financial difficulties and political opposition. Despite these obstacles, the 1914 map serves as a testament to the city planners' vision and the practical realities they faced.
The proposed subway routes spanned approximately 22 miles, connecting communities from the suburbs into the downtown area. Each line was strategically planned to serve densely populated neighborhoods, ensuring accessibility to workplaces, schools, and entertainment venues. The importance of such a network cannot be overstated, as it would have transformed commuting patterns and potentially alleviated the notorious traffic congestion that Cincinnati still faces today.
However, by the mid-1920s, the plans for the subway were abandoned. The Great Depression and shifts in public transportation preferences, such as the rise of automobiles, contributed to the decline of the subway project. Today, remnants of the abandoned subway tunnels exist beneath the city, serving as a fascinating glimpse into what could have been.
Regional Analysis
When examining the proposed subway routes on the Cincinnati Abandoned Subway Map, it becomes evident how different neighborhoods would have been impacted. For example, the planned route extending from the Over-the-Rhine district down to the riverfront highlights the intention to connect some of the most vibrant areas of the city. Over-the-Rhine, known for its historic architecture and cultural significance, would have benefitted greatly from improved transit. Conversely, neighborhoods like Avondale and College Hill would have seen enhanced access to downtown jobs and amenities, potentially altering their economic trajectories.
Additionally, the proposed connections to suburbs such as Hyde Park and Pleasant Ridge indicate a foresight in suburban development trends. If these routes had been implemented, they might have influenced the demographic makeup of these areas, possibly leading to a more integrated urban-suburban fabric.
Significance and Impact
The Cincinnati Abandoned Subway Map holds more than just a historical significance; it reflects a critical moment in urban planning and public transportation history. Understanding this proposed subway system allows us to appreciate the challenges cities face when developing infrastructure. The lessons learned from Cincinnati's experience can be applied to current urban planning initiatives, particularly as cities grapple with modern transportation issues, such as traffic congestion and sustainability.
Today, Cincinnati continues to explore ways to enhance its public transportation system. Interestingly, there are discussions around expanding the current streetcar system and improving bus services to meet the needs of a growing population. The legacy of the abandoned subway project serves as a reminder of the importance of vision and adaptability in urban planning. As cities evolve, the balance between innovative public transportation solutions and financial realities remains a pivotal challenge for planners and policymakers.
In conclusion, the Cincinnati Abandoned Subway Map is not merely a relic of a failed project; it encapsulates the aspirations and realities of early 20th-century urban life. It invites us to reflect on how infrastructure shapes our experiences in a city and the ongoing quest for effective public transportation solutions that can meet the needs of diverse communities.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 22, 2025
- Views
- 84
Comments
Loading comments...