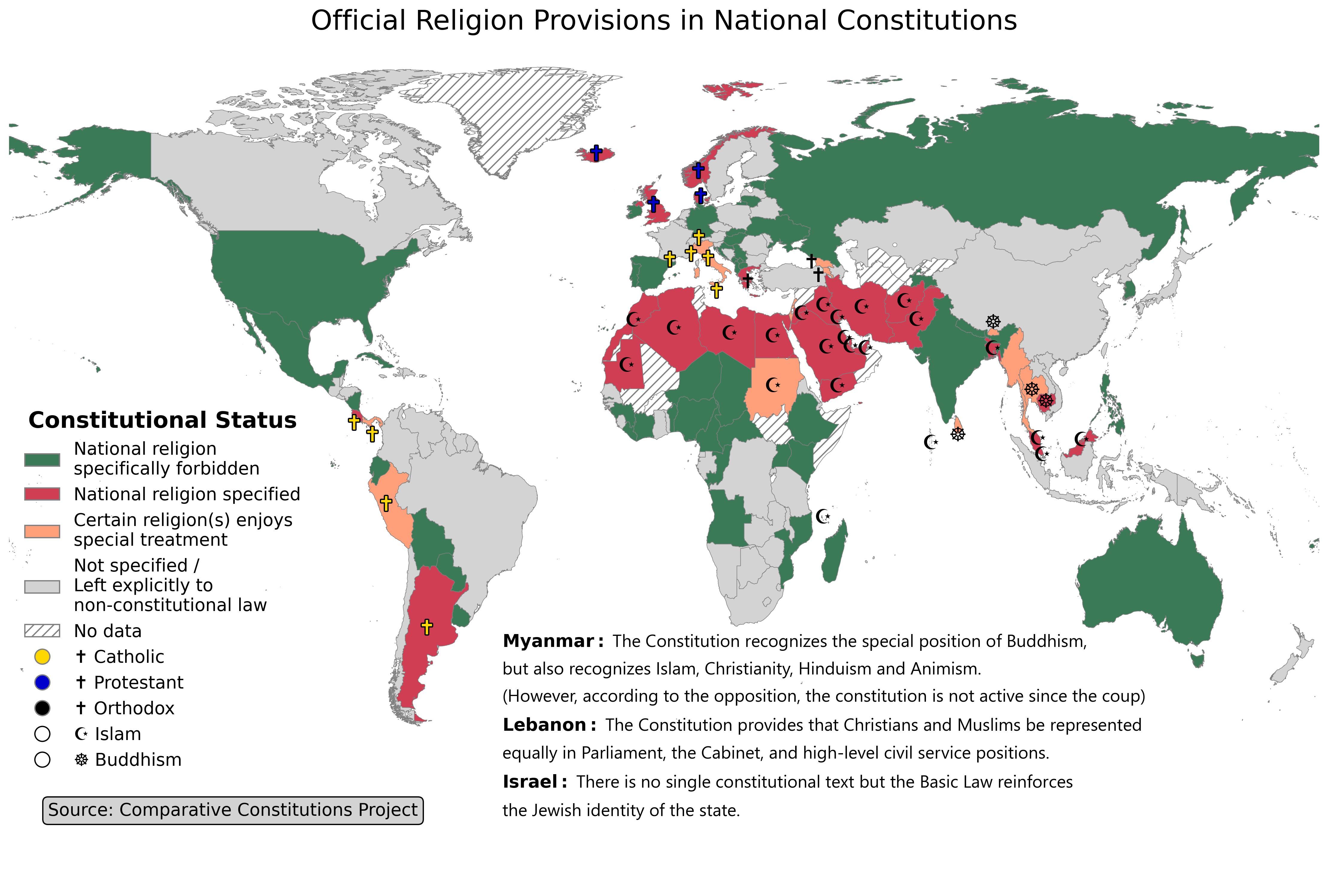
Map of Countries with National Religion Laws

Alex Cartwright
Senior Cartographer & GIS Specialist
Alex Cartwright is a renowned cartographer and geographic information systems specialist with over 15 years of experience in spatial analysis and data...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates which countries have constitutions that either name or forbid a national religion. It provides a clear visual representation of how different nations approach the intersection of religion and state governance. By examining the legal frameworks established in these countries, we can gain insight into the broader implications for religious freedom and cultural identity.
Deep Dive into National Religion Laws
National religion laws are a vital aspect of a country's constitution, reflecting its historical, cultural, and social dynamics. Interestingly, about 13% of the world's nations have constitutions that recognize a specific religion as the national faith. This can significantly influence the legal rights of individuals, government policies, and even the daily lives of citizens.
Countries like Saudi Arabia and Iran explicitly name Islam as a state religion, which shapes their legal systems and governance. In these nations, Islamic law (Sharia) plays a central role in the judicial system, influencing everything from family law to criminal justice. For instance, in Saudi Arabia, the absence of a written legal code means that Sharia law is interpreted by judges, leading to a unique legal landscape that is intertwined with religious doctrine.
On the other hand, some countries, such as the United States and France, explicitly forbid the establishment of a national religion. This is rooted in the principle of secularism, which aims to separate religion from governmental affairs. The First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution guarantees freedom of religion and prohibits the government from establishing a national religion. Similarly, France's 1905 law on the Separation of the Churches and the State emphasizes the neutrality of the state in religious matters.
What's fascinating is that these legal distinctions can lead to varying levels of religious freedom and pluralism within each country. In secular nations, individuals can practice any religion—or none at all—without fear of government interference. This creates a diverse religious landscape where multiple faiths coexist. However, in countries where a national religion is established, minority religions may face discrimination or limitations on their practices.
Regional Analysis
When analyzing the map, we can observe distinct regional patterns in how countries approach national religion laws. In the Middle East and parts of North Africa, many nations have laws enshrining Islam as the state religion. For example, Egypt's constitution recognizes Islam as the religion of the state and Islamic law as the primary source of legislation. This can lead to tensions between secular citizens and those who advocate for strict adherence to religious law.
In contrast, many European countries, particularly in Western Europe, embrace secularism and have constitutions that forbid the establishment of a national religion. Countries like Germany and Italy highlight this trend, allowing for a multitude of religious practices while ensuring that no single faith is favored over others. This creates an environment where diverse beliefs can flourish, but it also raises questions about how to address the needs of religious communities in a predominantly secular society.
In Asia, the approach varies widely. For instance, India maintains a secular constitution that promotes equal respect for all religions, despite being a predominantly Hindu nation. Conversely, countries like Bhutan have Buddhism entrenched in their national identity, influencing governance and policies. This diversity reflects how culture, history, and societal values shape the relationship between religion and state in different regions.
Significance and Impact
Understanding national religion laws is crucial for several reasons. First, these laws directly affect human rights and freedoms. In countries where a national religion is established, individuals who adhere to minority faiths may experience legal challenges, social exclusion, or persecution. This can lead to broader societal tensions and conflicts, impacting national stability and harmony.
Moreover, these laws influence international relations. Countries with strict religious laws may face criticism from the international community regarding their human rights records, prompting discussions about diplomacy and foreign aid. In contrast, nations that promote religious freedom may strengthen their global standing and foster better international relationships.
Looking to the future, the trend towards secularism in many parts of the world suggests a potential shift in how national religions are viewed. As globalization brings diverse cultures and beliefs into closer contact, the dialogue around religious freedom and state governance will likely continue to evolve. This could result in a reevaluation of existing laws and policies, leading to a more inclusive approach to religion in governance.
Overall, the relationship between national religion laws and governance remains a complex and dynamic aspect of global geography, influencing everything from individual rights to international relations.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 21, 2025
- Views
- 80
Comments
Loading comments...