English vs German Speakers by County Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
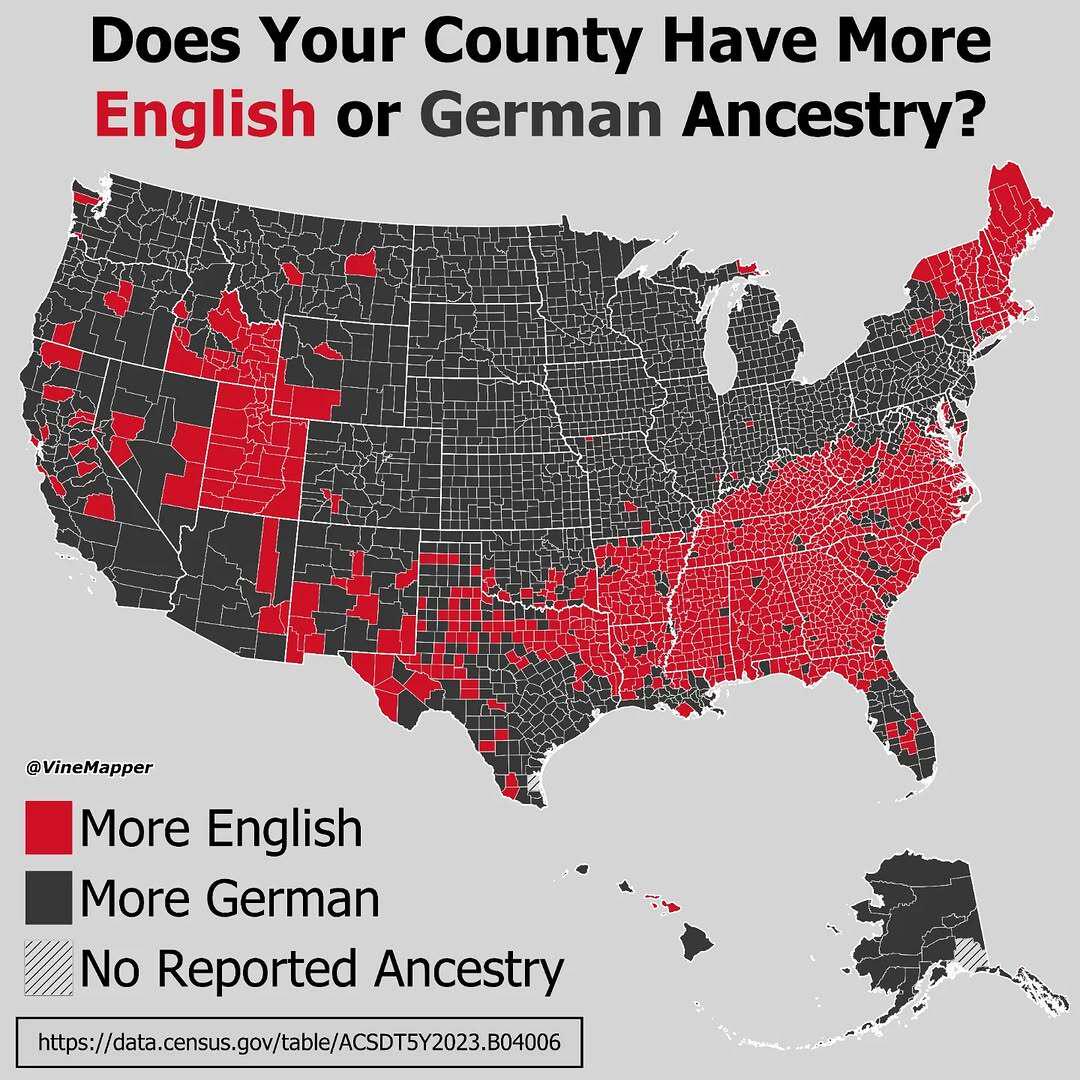
What This Map Shows
The map titled "Does Your County Have More English or German?" provides a visual representation of the linguistic landscape across various counties in the United States. It distinctly illustrates the proportion of residents who primarily speak English compared to those who speak German at home. This visualization invites us to consider the historical and cultural influences that have shaped these language distributions over time.
Language is an essential aspect of cultural identity, and understanding the prevalence of English and German speakers can reveal much about migration patterns, settlement histories, and even economic interactions. As we dive deeper into the topic, we can uncover how these languages reflect the diverse tapestry of American society.
Deep Dive into Language Distribution
Language distribution is influenced by a multitude of factors including immigration patterns, historical settlement, and community cohesion. The United States, often termed a melting pot, has seen waves of immigrants from different countries, each bringing their languages and cultures along. German immigrants, in particular, played a significant role in shaping American society from the 18th century onward.
Interestingly, German was the second most spoken language in the U.S. during the early 20th century. Many German-speaking communities established themselves in the Midwest, particularly in states like Wisconsin, Minnesota, and Pennsylvania. Today, while the number of German speakers may have declined due to assimilation and language shift, pockets of German-speaking populations still exist.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, around 1.1 million people reported speaking German at home as of the latest surveys. This figure, while significantly lower than that of English speakers (over 239 million), highlights the enduring presence of the German language in certain areas. The map showcases counties such as Adams County in Pennsylvania, where German speakers still represent a notable demographic, illustrating a legacy of immigration and cultural retention.
The linguistic dynamics also reflect broader demographic trends. For example, urban areas typically have higher proportions of English speakers, often due to their diverse populations and the influx of migrants from various backgrounds. On the other hand, rural areas may retain more of their historical linguistic identities, as seen in certain counties where German heritage is still celebrated through community events and cultural festivals.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map closely, we can see distinct regional patterns in the distribution of English and German speakers. In the Midwest, counties in states like Wisconsin and Ohio show a notable number of German speakers. For instance, Sheboygan County in Wisconsin has historically had a strong German influence, reflected in its cultural festivals and community organizations focused on German heritage.
Conversely, in the southern states, such as Texas, the map reveals a dominance of English speakers, reflecting the demographic shifts and the historical influx of English-speaking populations. Interestingly, some counties in Texas also showcase a blend of languages due to the state's diverse immigrant communities, which adds a layer of complexity to the linguistic landscape.
Moreover, counties in the Northeast, particularly in Pennsylvania, reveal a mix of both English and German speakers. Areas like Lancaster County are famous for their Amish communities, many of whom speak Pennsylvania Dutch, a derivative of German. This unique situation illustrates how language can coexist and evolve within specific cultural contexts.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of English versus German speakers is more than just a linguistic exercise; it has real-world implications for community engagement, education, and cultural preservation. Language shapes our identities, influences our social interactions, and affects how communities function. For instance, counties with a higher percentage of German speakers may prioritize cultural events that celebrate their heritage, which can lead to greater community cohesion and identity.
Moreover, as the U.S. becomes increasingly multicultural, the dynamics of language use are evolving. Trends show a growing interest in bilingual education, and communities are recognizing the importance of heritage languages. This is particularly relevant in areas with significant German-speaking populations, as they strive to maintain their cultural legacy while integrating into the broader society.
Looking ahead, projections suggest that language use will continue to shift, influenced by immigration patterns, educational policies, and generational changes. As younger generations emerge, the challenge will be to balance cultural retention with the realities of an ever-evolving linguistic landscape. The significance of the language map goes beyond mere numbers; it serves as a reminder of the rich cultural history that continues to shape our communities today.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 20, 2025
- Views
- 96
Comments
Loading comments...