Voting Rights for Women in Europe Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
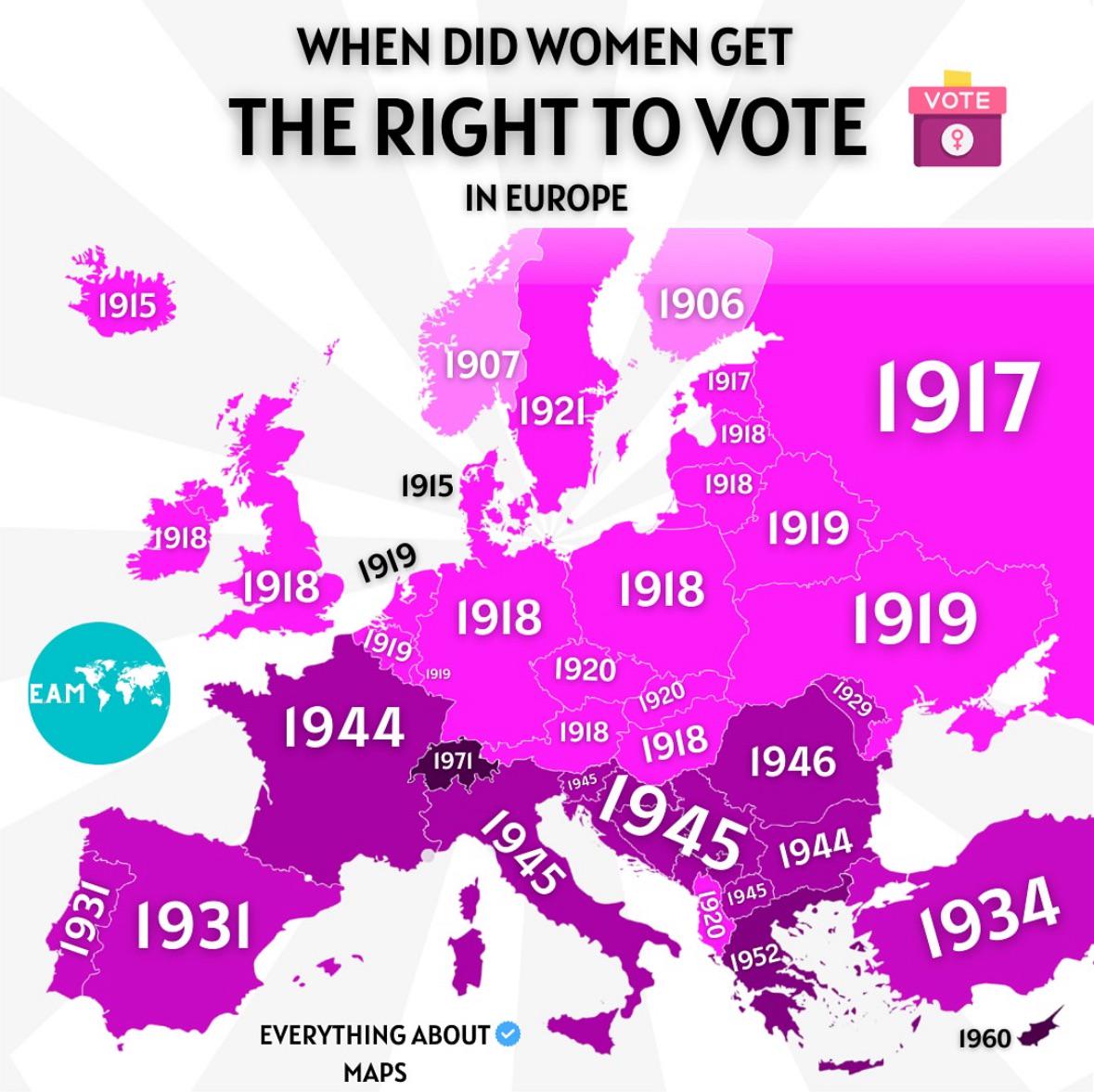
What This Map Shows
The map titled "When Did Women Get The Right To Vote in Europe" provides a comprehensive overview of the timeline of women's suffrage across various European countries. It highlights the specific years when women gained the legal right to vote, offering a visual representation of progress in gender equality throughout the continent. By examining this map, one can quickly discern the disparities in voting rights timelines among different nations, reflecting broader social and political contexts that influenced these milestones.
Deep Dive into Women's Suffrage in Europe
Women's suffrage is not just a historical footnote; it represents a pivotal shift in societal norms and political landscapes. The movement for women's voting rights gained momentum in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, influenced by factors such as industrialization, the rise of the feminist movement, and the aftermath of World War I, which significantly altered traditional roles in many societies. Interestingly, the pace of this change varied widely across Europe.
In the early 1900s, Finland became a pioneer in women's rights, allowing women to vote in 1906. This was a significant leap, as it marked Finland as the first European country to extend voting rights to women on equal terms with men. Following Finland, countries like Norway and Denmark soon followed suit, with women gaining the vote in 1913 and 1915, respectively.
However, it wasn't a uniform movement. In the United Kingdom, women over the age of 30 gained the right to vote in 1918, but it wasn't until 1928 that women could vote on equal terms with men. This delay showcased the complexities of the suffrage movement, shaped by class distinctions and political resistance. Meanwhile, in countries like Switzerland, women had to wait until 1971 to vote at the federal level, highlighting stark contrasts in the progression of women's rights across Europe.
The interwar period saw a rise in women's suffrage in several other European nations, including Germany and Austria, where women gained voting rights in 1918. However, the onset of World War II caused significant setbacks in many countries, as political focus shifted towards survival rather than suffrage. After the war, many nations resumed the path towards gender equality, but with varying degrees of success.
It's fascinating to note that the timeline of women's voting rights is interconnected with broader movements for civil rights and social justice. In countries like France, women had to wait until 1944 to vote, a reflection of the political upheavals and social attitudes of the time. The eventual granting of voting rights paved the way for women's greater involvement in politics and governance, influencing policies and societal norms in the decades that followed.
Regional Analysis
When examining the map, regional differences in the timelines of women's suffrage become quite evident. For instance, Northern European countries generally led the way in granting voting rights, with the Scandinavian nations being among the first to recognize women's rights. In contrast, Southern European countries like Italy and Spain did not extend these rights until the mid-20th century, underscoring the influence of cultural and political factors unique to each region.
In Eastern Europe, the aftermath of World War I and subsequent political changes played a significant role in shaping women's suffrage. For example, in Poland, women were granted the right to vote in 1918, shortly after regaining independence. However, in other countries, such as Hungary, women did not achieve full voting rights until after the fall of communism in the late 20th century.
Interestingly, the map also highlights the ongoing disparities even at the present day. While most European countries have established gender equality in voting, the political participation of women remains uneven, with many nations still struggling to achieve equal representation in government.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the timeline of women's voting rights in Europe is crucial for contextualizing the ongoing discussions about gender equality and representation in politics today. The struggles for suffrage were not merely about voting; they were about the recognition of women as equal participants in society. This historical context sheds light on the current challenges women face in political spheres, from underrepresentation to gender-based violence in politics.
Current trends indicate a growing awareness of the need for gender parity in governance. Various European nations are implementing quotas and initiatives aimed at increasing women's representation in political offices. However, the journey is far from complete. The historical timeline of voting rights serves as a reminder of how far we've come and how much further we need to go to achieve true equality.
As we look to the future, the progress made in women's suffrage can inspire ongoing advocacy for women's rights not just in Europe, but globally. The map serves as a historical document, reminding us of the struggles endured and the victories achieved, while also highlighting the work that remains to be done in the pursuit of gender equality in every aspect of life.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 15, 2025
- Views
- 192
Comments
Loading comments...