Migration of Dutch Cars During Summer Holiday Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
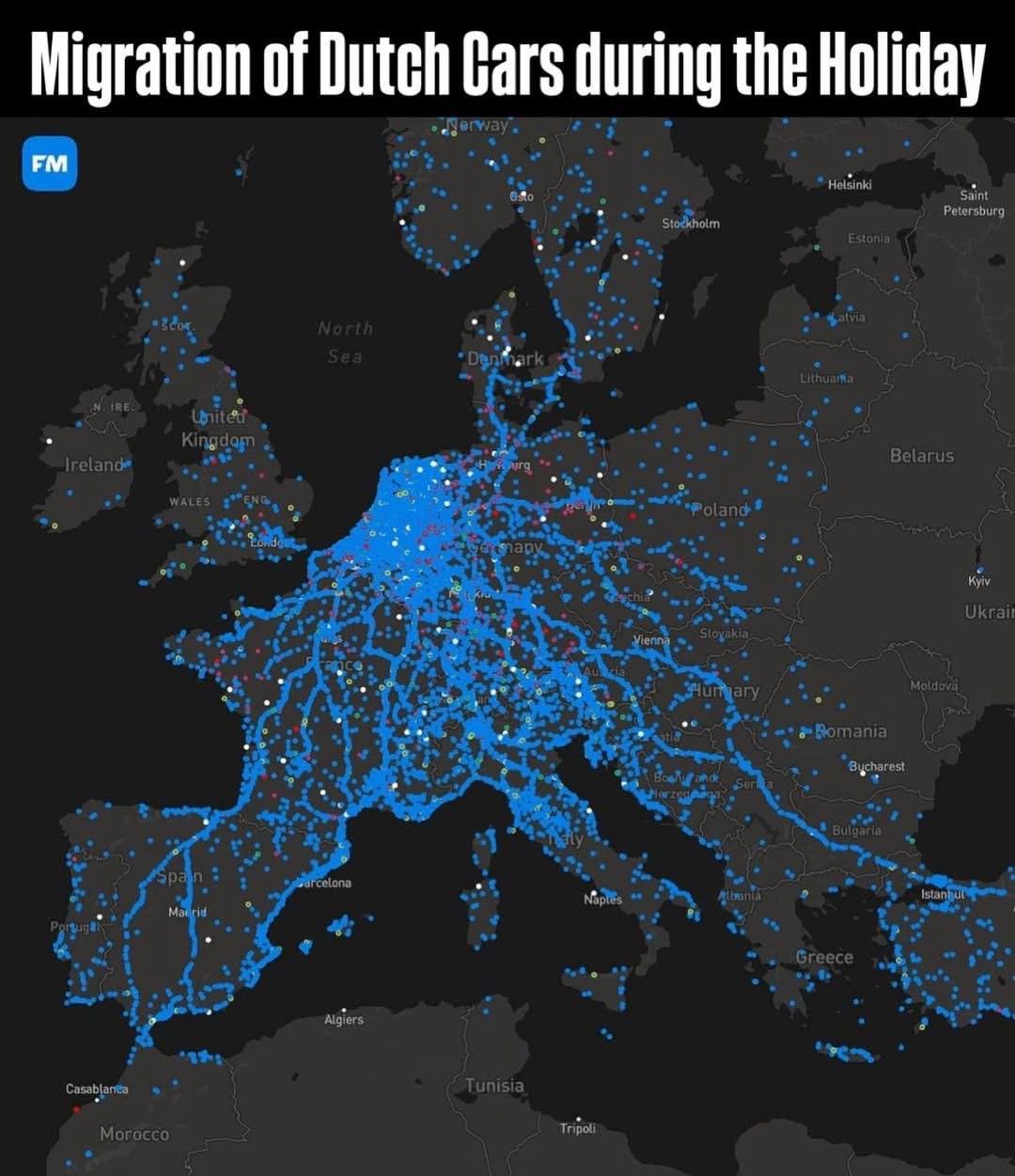
What This Map Shows
The "Migration of Dutch Cars During Summer Holiday Map" provides a detailed visualization of how Dutch vehicles travel during the peak summer vacation months. It showcases the flow of cars from urban centers to popular holiday destinations, both domestically and internationally. This map captures essential trends in travel patterns, revealing how regions in the Netherlands are connected to the movement of people seeking leisure and relaxation during the summer break.
Deep Dive into Dutch Summer Travel Patterns
Summer in the Netherlands is synonymous with vacation time, and this migration of cars offers a fascinating glimpse into how Dutch residents prioritize leisure. The trend generally peaks in late July and early August when families and individuals alike take to the roads to enjoy the sun, sea, and scenic landscapes. The most popular destinations include coastal areas such as Zeeland, the Dutch Wadden Islands, and various camping sites throughout the country.
Interestingly, the map highlights the significant impact of geographical features on travel behavior. For example, proximity to the North Sea makes places like Scheveningen and Zandvoort particularly attractive, leading to a higher concentration of vehicles heading towards these coastal towns. In fact, statistics show that during the summer holidays, traffic to beach destinations can increase by over 30% compared to non-holiday periods.
Another noteworthy aspect is the cross-border travel patterns revealed by the map. Many Dutch vacationers also take road trips to neighboring countries, particularly Belgium and Germany. The allure of cities like Antwerp and Cologne or the picturesque landscapes of the Ardennes is hard to resist. The map indicates that routes connecting to these countries see a significant increase in car traffic, with the A12 and A1 highways being the most frequented during the summer months.
Have you ever wondered why certain routes see more traffic than others? Factors such as road infrastructure, travel time, and even cultural preferences play a crucial role in shaping these patterns. For instance, the A28, which leads to the northern provinces, tends to be less congested than routes heading to the south, despite being equally popular among vacationers. This discrepancy can be attributed to the types of destinations each route offers, as well as the preferences of Dutch families who often favor the southern coasts for their summer retreats.
Regional Analysis
Breaking down the map regionally, we observe distinct variations in travel patterns. For instance, the migration of cars from the Randstad—home to major cities like Amsterdam, The Hague, and Rotterdam—shows a pronounced tendency toward the coastal regions of Zeeland and South Holland. The A58 highway, which connects these urban areas to the coast, experiences some of the highest traffic volumes during the summer months.
On the other hand, regions such as Friesland and Groningen see a different pattern. While these northern provinces are popular for their natural beauty and rural charm, they attract visitors primarily from within the region rather than from the densely populated Randstad. This localized travel trend can be attributed to the appeal of water sports and outdoor activities that are prevalent in these areas.
Interestingly, the map also reveals the internal movement within the Netherlands. Cities like Utrecht and Eindhoven, positioned centrally, facilitate travel to both northern and southern destinations equally. This centrality makes them critical hubs during the summer migration, as they serve as starting points for vacationers heading toward both the coast and the countryside.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the migration of Dutch cars during the summer holiday is more than just academic curiosity; it has real-world implications for infrastructure planning, environmental considerations, and tourism marketing. For instance, local governments can use this data to optimize traffic management and improve road safety during peak travel times. Furthermore, knowing the most trafficked routes allows for targeted investments in infrastructure, such as road expansions or service areas.
Additionally, the environmental impact of increased car travel during the summer cannot be overlooked. With a growing emphasis on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints, many Dutch citizens are now advocating for more eco-friendly travel options, such as carpooling or using public transportation. Interestingly, this shift in mindset could reshape future travel patterns and even influence how holiday marketing is approached in the years to come.
In conclusion, the map depicting the migration of Dutch cars during summer serves as a valuable tool for understanding not only travel habits but also broader societal trends. As we look toward the future, staying attuned to these patterns will be essential in fostering more sustainable and enjoyable travel experiences for everyone.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 14, 2025
- Views
- 86
Comments
Loading comments...