Europe and North America's 10-Year Yields Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
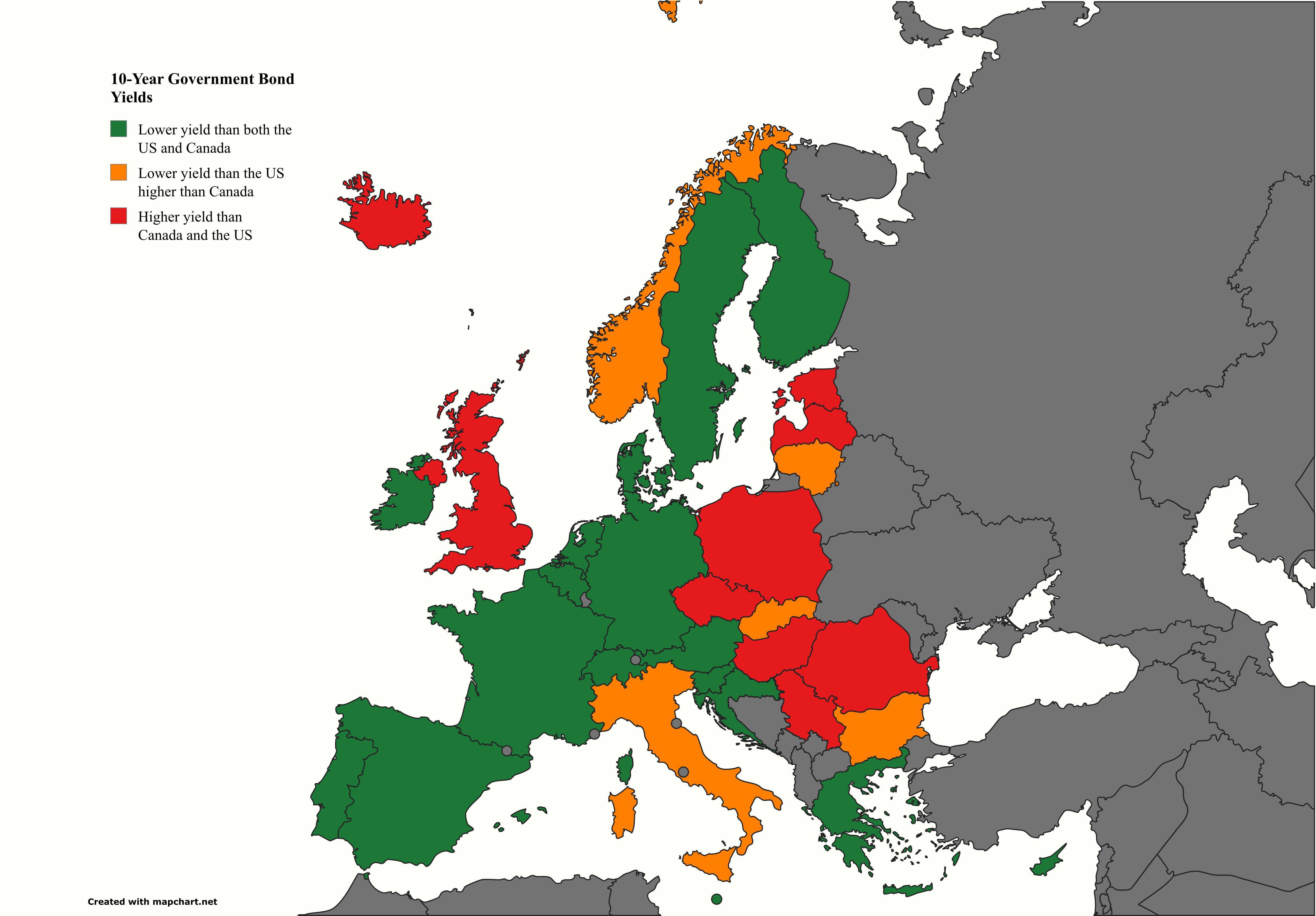
What This Map Shows
This map presents a comparative visualization of the 10-year government bond yields across Europe, the United States, and Canada over the past decade. By examining the divergence and convergence of these yields, the map provides insights into the economic health and fiscal policies of various countries in these regions. A bond yield is an important economic indicator, reflecting the return investors can expect from purchasing government debt, and is often viewed as a gauge of economic stability and confidence.
Deep Dive into 10-Year Government Bond Yields
Understanding 10-year government bond yields is crucial for grasping the broader economic landscape. These yields serve as a benchmark for interest rates across the economy, influencing everything from mortgage rates to corporate borrowing costs. When yields rise, it usually indicates that investors are expecting stronger economic growth, leading to inflation, while falling yields often point towards economic uncertainty or recession fears.
The differences in bond yields can be attributed to several factors, including inflation expectations, central bank policies, and overall economic conditions. For instance, in Europe, the European Central Bank (ECB) has maintained a policy of low interest rates to stimulate economic growth post-2008 financial crisis. Consequently, many European countries, especially those in the Eurozone, have experienced consistently low yields, reflecting investor confidence in stable economies, albeit with varying degrees of growth.
Interestingly, countries like Greece have seen significant fluctuations in their yields due to political instability and economic challenges. In contrast, nations such as Germany, known for their fiscal discipline, benefit from lower yields, which indicates a higher level of investor trust.
On the other side of the Atlantic, the United States and Canada have experienced their own yield dynamics. The U.S. has historically seen higher yields compared to its European counterparts, reflecting a more robust economic growth outlook. However, this trend can vary; for example, in times of economic uncertainty, such as during the COVID-19 pandemic, yields in the U.S. dropped sharply as investors flocked to safer assets.
Canada's bond yields tend to mirror those of the U.S. due to the close economic ties between the two nations. However, Canadian yields are often slightly lower, influenced by the country's stable economy and lower inflation rates.
Regional Analysis
Looking more closely at the regions represented on the map, we can see distinct patterns emerging. In Southern Europe, countries like Spain and Italy have had relatively high bond yields compared to their Northern counterparts, driven by economic recovery challenges and varying investor confidence levels. For example, Italy's bond yields have been historically higher due to concerns over political stability and economic growth.
In contrast, the Nordic countries, particularly Sweden and Finland, have demonstrated lower yields, reflecting their strong fiscal policies and economic resilience. These nations have benefited from robust economic performance and low unemployment rates, which bolster investor confidence.
Meanwhile, in North America, the U.S. shows a notable yield trend that often reacts to Federal Reserve policies. Changes in interest rates and economic forecasts can lead to quick adjustments in bond yields. For instance, when the Fed indicated potential rate hikes in response to inflation concerns, yields spiked as investors anticipated higher returns on future bonds. Canada, while closely following U.S. trends, often shows a lag due to its own economic policies and market conditions.
Significance and Impact
Why does understanding these bond yields matter? The implications are vast and profound. Investors, policymakers, and economists all rely on bond yield trends to make informed decisions. For example, rising yields may signal a booming economy, but they can also indicate increasing inflation rates, which could prompt central banks to tighten monetary policy. Conversely, falling yields might suggest economic troubles ahead, leading to lower borrowing costs but potentially stalling economic growth.
Furthermore, the disparities in yields between regions can affect international investment flows. Countries with lower yields might attract more foreign investment, while those with higher yields may face capital outflows as investors seek better returns elsewhere.
As the global economy continues to evolve, keeping an eye on these bond yields is crucial for anticipating future trends. With ongoing geopolitical uncertainties and economic shifts, the landscape of government bond yields will likely remain a key focal point for analysts and investors alike. Have you noticed how these trends reflect broader economic narratives? Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone interested in global finance and economics.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 13, 2025
- Views
- 126
Comments
Loading comments...