Ancient Indian Geography Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
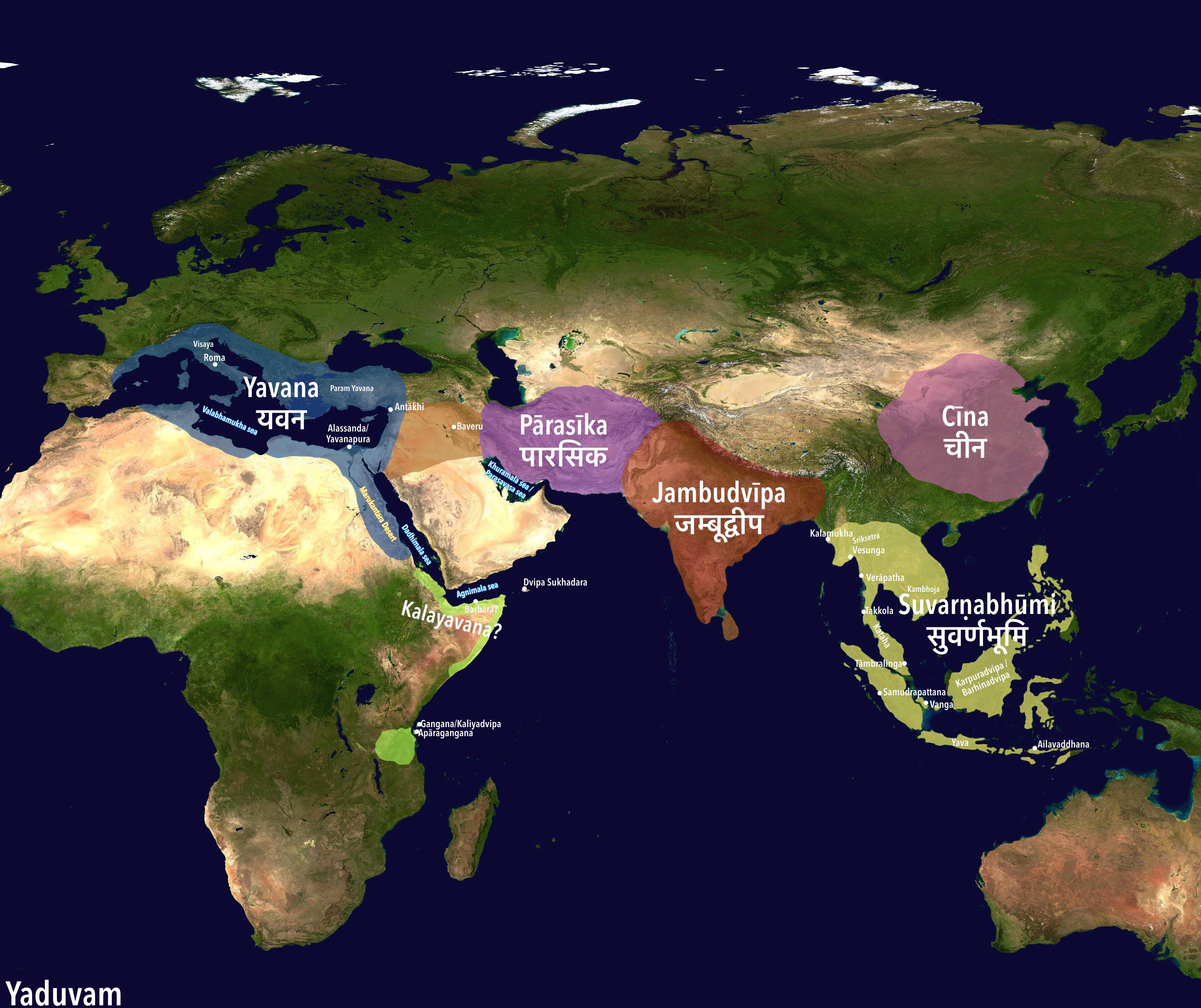
What This Map Shows
The visualization titled "The World as Known to Ancient Indians" provides a fascinating glimpse into the geographical perceptions and knowledge of ancient Indian civilizations. This map illustrates not only the locations of various regions, cities, and countries known to these early scholars but also highlights the trade routes, cultural exchanges, and interactions that were prominent in their understanding of the world. By examining this map, we can gain insight into how ancient Indians viewed their environment and the world beyond their immediate surroundings, which was rich with diverse cultures and landscapes.
Deep Dive into Ancient Indian Geography
Interestingly, the ancient Indian understanding of geography was deeply intertwined with their culture, mythology, and trade. The subcontinent's geographical knowledge was shaped by various sources, including ancient texts like the "Mahabharata" and "Ramayana," as well as works by scholars like Aryabhata and Varahamihira. These texts contain references to vast landscapes, rivers, mountains, and the surrounding regions known to ancient Indians.
One of the most significant geographical features noted in ancient Indian maps is the presence of major river systems. The Indus River, the Ganges, and the Brahmaputra were not just vital for agriculture and sustenance; they were also central to the cultural and spiritual life of the people. The Indus Valley civilization, which flourished around 2500 BCE, relied on the Indus River for irrigation and trade, showcasing how geography influenced societal development. Moreover, these rivers were often considered sacred, further emphasizing their importance in the cultural landscape.
Moreover, ancient Indian cartographers had a remarkable understanding of the mountains that bordered their land. The Himalayas, revered as the abode of the gods, were regarded as a natural barrier and a source of numerous rivers. The ancient texts often depicted these mountains not just as physical barriers but as mystical entities that shaped the spiritual dimension of Indian geography. This perspective illustrates how geography was not merely a physical science but also a reflection of the worldview held by ancient Indians.
Trade routes also played a crucial role in the geographical understanding of ancient Indians. The Silk Road, which connected India to Central Asia and beyond, facilitated not only the exchange of goods but also the transfer of knowledge and culture. Ancient maps often depicted these routes, indicating the significance of trade in expanding the geographical horizons of Indian civilizations. Interestingly, the trade interactions led to a mutual exchange of ideas, resulting in advancements in various fields, including astronomy, mathematics, and medicine.
Regional Analysis
When we delve deeper into the regions represented on the map, we can see distinct geographical features that influenced the development of various cultures. For instance, the southern region of India, with its coastal access, was predominantly engaged in maritime trade. Cities like Kochi and Calicut became crucial ports, facilitating trade with the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
In contrast, northern India, characterized by its fertile plains and proximity to the Himalayas, nurtured agrarian societies. The Ganges plain, for example, was a cradle of civilization due to its rich alluvial soil, allowing for the growth of settlements and kingdoms. The ancient knowledge of these regions was not uniform; rather, it varied based on local resources, climate, and interactions with neighboring cultures.
Interestingly, the ancient Indians also had a grasp of the geographical features beyond their immediate borders. The maps often included regions such as Persia, the Arabian Peninsula, and even parts of Africa, demonstrating an early awareness of the interconnectedness of civilizations. This geographical understanding was essential for facilitating diplomatic relations and trade agreements, which were crucial for the prosperity of ancient Indian states.
Significance and Impact
The significance of understanding the ancient Indian geographical perspective goes beyond mere historical interest; it has real-world implications today. The map serves as a reminder of how civilizations have interacted over millennia, shaping cultures and societies. In a world that is increasingly globalized, reflecting on these ancient connections can provide valuable insights into contemporary international relations and trade practices.
Moreover, current trends in geography education can benefit from this ancient knowledge. Understanding how ancient civilizations comprehended their world can guide modern approaches to teaching geography, emphasizing the importance of cultural context. As we look to the future, it is essential to recognize the interplay between geography and culture, as it continues to influence geopolitical dynamics today.
In conclusion, the map of "The World as Known to Ancient Indians" serves as a window into a rich tapestry of knowledge that shaped one of the world's oldest civilizations. By exploring this geographical perspective, we not only honor the legacy of ancient scholars but also enrich our understanding of the complexities of human interaction with the environment.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 11, 2025
- Views
- 102
Comments
Loading comments...