Expansion of Semitic Scripts Map

David Chen
Data Visualization Specialist
David Chen is an expert in transforming complex geographic datasets into compelling visual narratives. He combines his background in computer science ...
Geographic Analysis
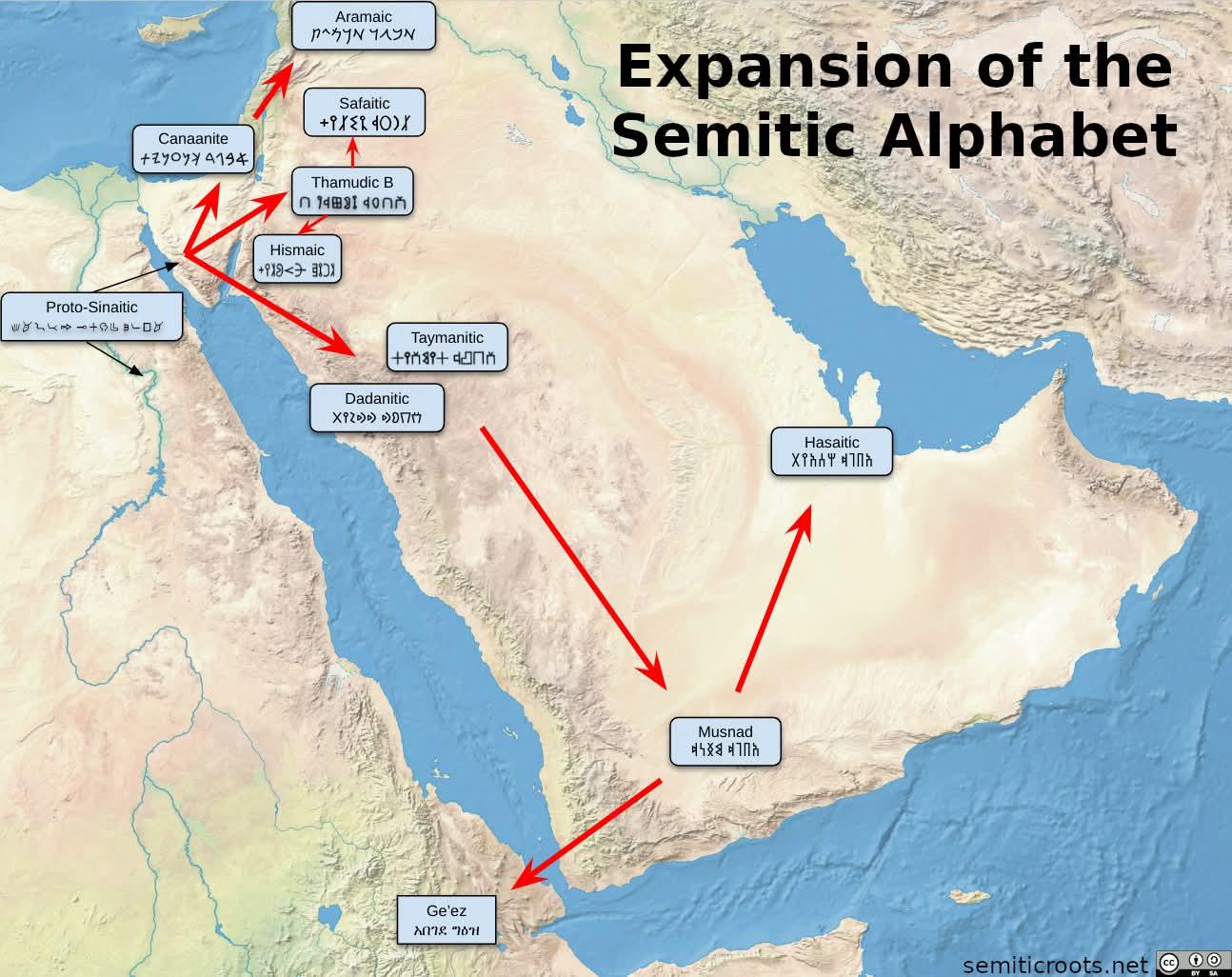
What This Map Shows
This map illustrates the historical and geographical spread of Semitic scripts across various regions, highlighting the linguistic and cultural influence of Semitic languages over millennia. The visualization provides a clear representation of how these scripts evolved and adapted, reflecting the migrations and interactions of Semitic peoples throughout history. From ancient inscriptions in the Levant to modern adaptations in different parts of the world, this map encapsulates a significant aspect of human communication and culture.
Deep Dive into Semitic Scripts
Semitic scripts are a group of writing systems that have their roots in the ancient Semitic languages, which include Hebrew, Arabic, Aramaic, and Phoenician, among others. These scripts are fascinating not only for their historical significance but also for their enduring impact on the languages and cultures we see today. The origins of these scripts can be traced back over 3,000 years, with the earliest examples found in inscriptions from the ancient Near East.
Interestingly, the Phoenician script is often credited as one of the first alphabetic scripts, influencing many other writing systems, including Greek and Latin. The map reflects this influence, showing how Phoenician traders spread their writing system across the Mediterranean, leading to the development of various alphabets. For instance, the Greek alphabet was derived from Phoenician characters, and this lineage can be seen in modern European scripts.
Hebrew and Arabic scripts, also depicted on the map, evolved from earlier Semitic scripts and have become integral to the cultures of the Jewish and Arab peoples, respectively. The Hebrew script, which has undergone several transformations, is still used today in Israel and among Jewish communities worldwide. Meanwhile, Arabic script has expanded far beyond its original geographical boundaries, adapting to various languages across North Africa and the Middle East, such as Persian, Urdu, and Pashto.
What's fascinating is that while these scripts share a common ancestry, they have diverged significantly in their usage and style. For example, Arabic script is cursive and written from right to left, while Hebrew is more angular and also written from right to left but has distinct vowel markings that vary from Arabic. This divergence highlights the adaptability of Semitic scripts in different cultural contexts and their role in fostering communication.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can see distinct patterns of script expansion across different regions. In the Levant, for example, the Hebrew script has deep historical roots, closely linked to Jewish history and religious texts. Cities like Jerusalem and Safed have been central to the preservation and evolution of Hebrew language and script.
In contrast, the Arabic script predominantly flourishes in North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Countries like Egypt and Saudi Arabia showcase the script's significance in Islamic culture, where it serves as the medium for the Quran and countless literary works. The map indicates the spread of Arabic due to trade and conquest, illustrating how the script has been adopted by various cultures and languages, adapting to local phonetics and scripts.
An intriguing example of this adaptation can be found in the Maghrebi script, which is a style of Arabic writing used in North Africa. The regional variations in script demonstrate how Semitic scripts are not static; they evolve and change with the societies that use them.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the expansion of Semitic scripts is crucial for several reasons. First, it sheds light on the historical movements of people and the exchanges of ideas across cultures. Scripts are more than mere symbols; they represent the thoughts, beliefs, and identities of the people who use them. The spread of Semitic scripts reflects the interconnectedness of civilizations throughout history.
Moreover, in our globalized world, the implications of script evolution are evident in how languages are maintained or transformed. As technology advances, we see new forms of writing, such as digital communication, impacting how Semitic languages are used today. The preservation of these scripts is vital for cultural heritage and identity, especially in regions where languages are at risk of extinction.
Looking ahead, the future of Semitic scripts appears to hinge on the balance between modernization and tradition. With increasing digitalization, how will these scripts adapt to new mediums? Will they continue to thrive in their traditional forms, or will they evolve further under the influence of technology? These questions invite deeper exploration into the ongoing journey of Semitic scripts and their role in shaping human history.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 9, 2025
- Views
- 124
Comments
Loading comments...