Original Language of Every New Zealand Districts Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
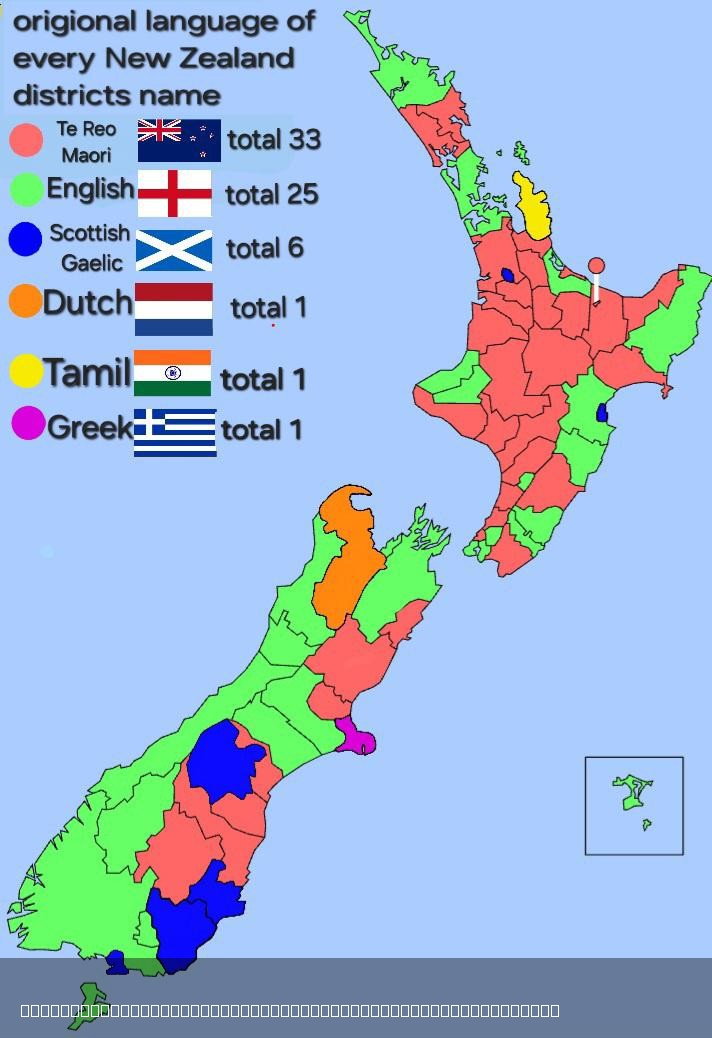
What This Map Shows
This map provides a detailed visualization of the original languages associated with the names of every district in New Zealand. It highlights how the cultural and linguistic heritage of the indigenous Māori people, along with other influences, have shaped the nomenclature of these regions. Each district name carries a story, often reflecting the geographical features, historical events, or the people that inhabit these areas. By looking at this map, we can gain insight into the rich tapestry of languages that contribute to New Zealand's identity.
Deep Dive into New Zealand's Linguistic Heritage
New Zealand is a unique blend of cultures, with its indigenous Māori language, te reo Māori, at the forefront. The Māori people have a profound connection to the land, and this is vividly reflected in their language. Names of places often describe the natural features of the area or commemorate significant historical figures or events. For instance, the name "Auckland" is derived from the Māori word "Akarana," which refers to the city's natural harbor.
Interestingly, the influence of European settlers in the 19th century also left its mark, resulting in a dual-language environment. Many places have names that are adaptations of Māori words, anglicized for easier pronunciation by settlers. This blending of languages reflects a broader narrative of colonization, cultural exchange, and adaptation.
Beyond the Māori language, New Zealand also has communities that speak other languages, including English, Samoan, Mandarin, and French, among others. These languages speak to the diverse immigrant populations that have settled in New Zealand over the years. For example, the district of "Wellington" is not only the capital of New Zealand but also a hub for various cultures and languages, making it a melting pot of linguistic heritage.
What’s fascinating is how the evolution of language in New Zealand continues to unfold. The Māori language has seen a resurgence in recent decades, partly due to governmental initiatives and community efforts to preserve it. Today, many districts are not just named after their historical roots but are also being revitalized through cultural programs that promote te reo Māori.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map reveals distinct regions where specific languages dominate. In the northern parts of New Zealand, such as Northland and Auckland, the Māori influence is strong, with many district names rooted in te reo Māori. Areas like "Hokianga" and "Kaipara" connect deeply with Māori history and culture, showcasing the language's role in place-making.
In contrast, in the central regions, English names have become more prevalent, particularly in areas with higher European settlement. Districts such as "Palmerston North" and "Napier" reflect this shift, where names often commemorate British figures or heritage.
Interestingly, the South Island presents a different linguistic landscape. Here, the Māori names often describe geographical features, such as "Wakatipu" (meaning 'the place where the river meets') and "Otago," which refers to a place of great value. These names highlight the natural beauty of the area while also paying homage to the Māori connection to the land.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the original languages of New Zealand's district names is crucial for appreciating the country's cultural heritage. It highlights the importance of language as a living entity that continues to evolve and adapt. As globalization increasingly intermingles cultures, recognizing and preserving indigenous languages becomes essential not just for heritage but for identity as well.
Current trends show a growing movement towards revitalizing te reo Māori across all levels of society, including education, government, and media. Schools are now incorporating Māori language education into their curricula, and local councils are promoting bilingual signage. This shift not only honors the Māori culture but also fosters a sense of unity among New Zealand's diverse population.
In conclusion, the original languages of New Zealand's district names serve as a window into the country's past and a reflection of its ongoing journey towards cultural inclusivity. As we study these names, we are reminded of the stories they tell and the rich heritage they represent, making this map more than just a geographical tool—it's a narrative of identity and resilience.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 7, 2025
- Views
- 96
Comments
Loading comments...