Indo-European Languages Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
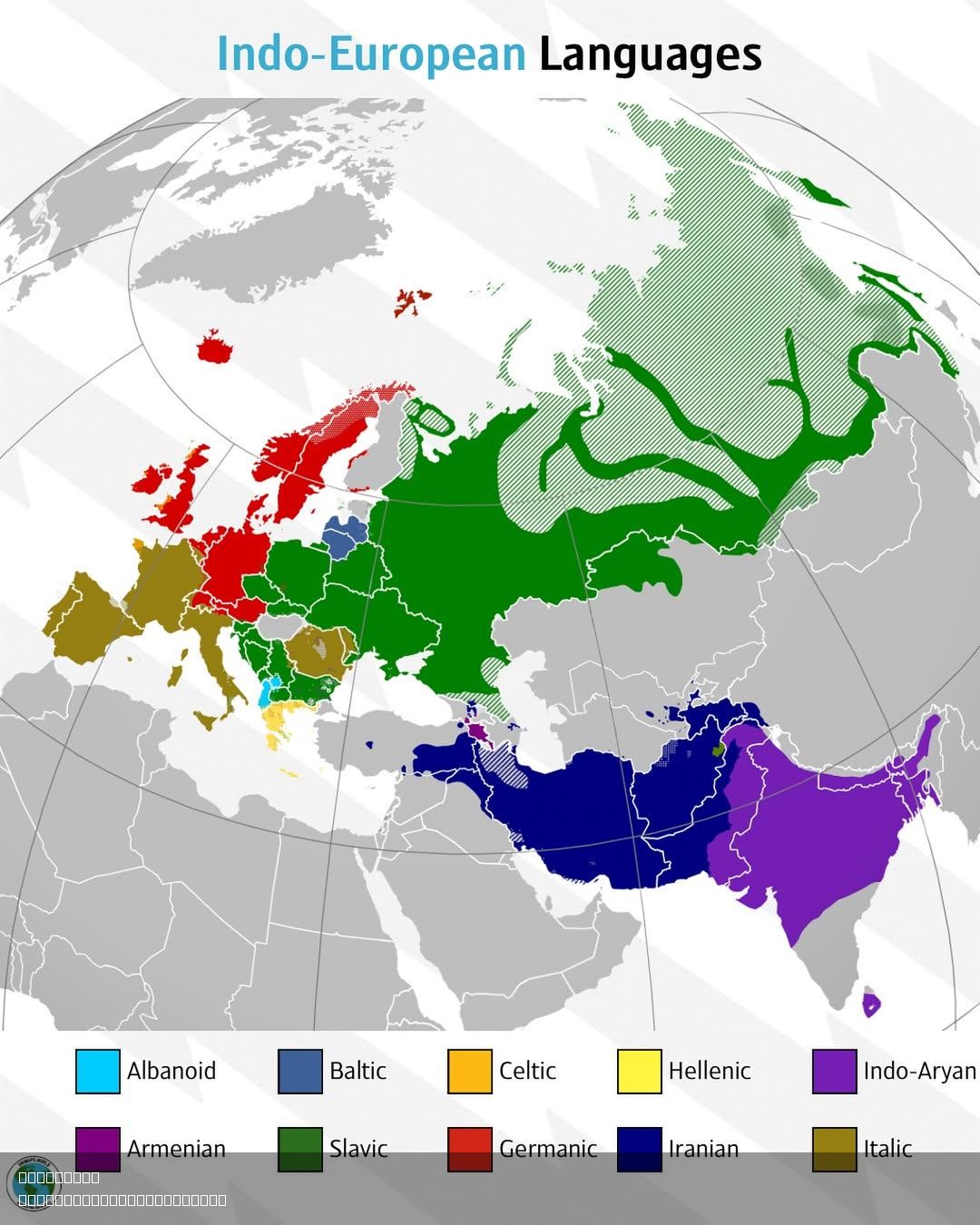
What This Map Shows
The "Indo-European Languages Map" provides a detailed visualization of the linguistic distribution of Indo-European languages across Europe, parts of Asia, and even extending to regions in the Americas and Oceania. This map highlights the various branches of the Indo-European language family, showcasing not just where these languages are spoken but also their historical and cultural significance. From English to Hindi, the map illustrates how interconnected these languages are, as well as the geographic diversity in language use.
Deep Dive into Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European language family is one of the world's largest and most widely distributed linguistic families. It encompasses several key branches, including Germanic, Romance, Slavic, Indo-Iranian, Celtic, and others. Interestingly, the roots of this language family can be traced back to a common ancestor known as Proto-Indo-European, which is believed to have been spoken around 4500 to 2500 BCE in the steppes of modern-day Ukraine and Russia.
The Germanic branch includes languages such as English, German, Dutch, Swedish, and Norwegian. English, in particular, has become a global lingua franca, heavily influenced by Norman French and Latin due to historical conquests and governance. Did you know that more than 1.5 billion people speak English worldwide?
The Romance languages, which evolved from Latin, include Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, and Romanian. This branch is particularly prevalent in Southern Europe and Latin America. For instance, Spanish is the second most spoken language globally, a testament to the colonial expansion of Spain in the 16th century.
The Slavic languages, such as Russian, Polish, Czech, and Bulgarian, predominantly occupy Eastern Europe. Russian, as the largest Slavic language, is notable for its rich literary tradition and has over 250 million speakers.
Meanwhile, the Indo-Iranian branch includes languages like Hindi, Bengali, Persian, and Urdu, primarily spoken in South Asia and parts of the Middle East. Hindi, for example, is one of the official languages of India and is spoken by over 500 million people.
Interestingly, the diversity within the Indo-European languages is not merely linguistic but also cultural. Many of these languages carry unique traditions, idioms, and worldviews that reflect the history of the peoples who speak them. For instance, the word for 'mother' in Sanskrit is 'mātṛ,' which is similar to 'mater' in Latin and 'mother' in English, showcasing the shared roots of these languages.
Regional Analysis
Examining the map, we can see the concentration of Indo-European languages in specific regions. In Western Europe, the Romance languages dominate, with French and Spanish being the most prevalent. This region has a rich history of language development influenced by trade, conquest, and cultural exchange. Interestingly, in countries like Belgium and Switzerland, multiple languages coexist, reflecting the complex historical and political backgrounds of these nations.
In Eastern Europe, the Slavic languages are prominent, with Russian being widely spoken not just in Russia but also in former Soviet states. Ukrainian and Polish also have significant numbers of speakers, and the map illustrates how these languages spread through migration and historical events.
South Asia showcases a different linguistic tapestry, where Indo-Iranian languages flourish. Hindi, Urdu, and Bengali dominate the linguistic landscape, with Hindi not only serving as a primary language in India but also influencing numerous regional dialects. The map underscores the intricate web of language relationships that exist due to historical migrations and cultural exchanges.
Significance and Impact
Understanding the distribution of Indo-European languages is crucial for several reasons. First, it sheds light on historical migrations and the spread of cultures. Language is often a vehicle for cultural identity, and by studying linguistic patterns, we can gain insights into the movements and interactions of peoples throughout history.
Moreover, in today's globalized world, the impact of these languages is profoundly felt in international business, diplomacy, and education. English's status as a global lingua franca facilitates communication across diverse cultures, but it also raises questions about linguistic imperialism and the preservation of minority languages. Have you noticed how many languages are slowly fading away? According to UNESCO, a language dies approximately every two weeks, emphasizing the need for awareness and preservation efforts.
Looking toward the future, trends such as technological advancements in language translation and learning may further influence linguistic landscapes. As globalization continues to shape communication, the dynamics of language use will undoubtedly evolve, making it an exciting area of study for linguists and geographers alike.
In summary, the "Indo-European Languages Map" is not just a visual representation; it is a gateway to understanding the rich tapestry of human history and cultural exchange that these languages embody. The continued study of these languages will provide valuable insights into our shared heritage and the future of communication in an increasingly interconnected world.
Visualization Details
- Published
- August 6, 2025
- Views
- 110
Comments
Loading comments...