The Great Wall of China Map

Marcus Rodriguez
Historical Geography Expert
Marcus Rodriguez specializes in historical cartography and geographic data analysis. With a background in both history and geography, he brings unique...
Geographic Analysis
What This Map Shows
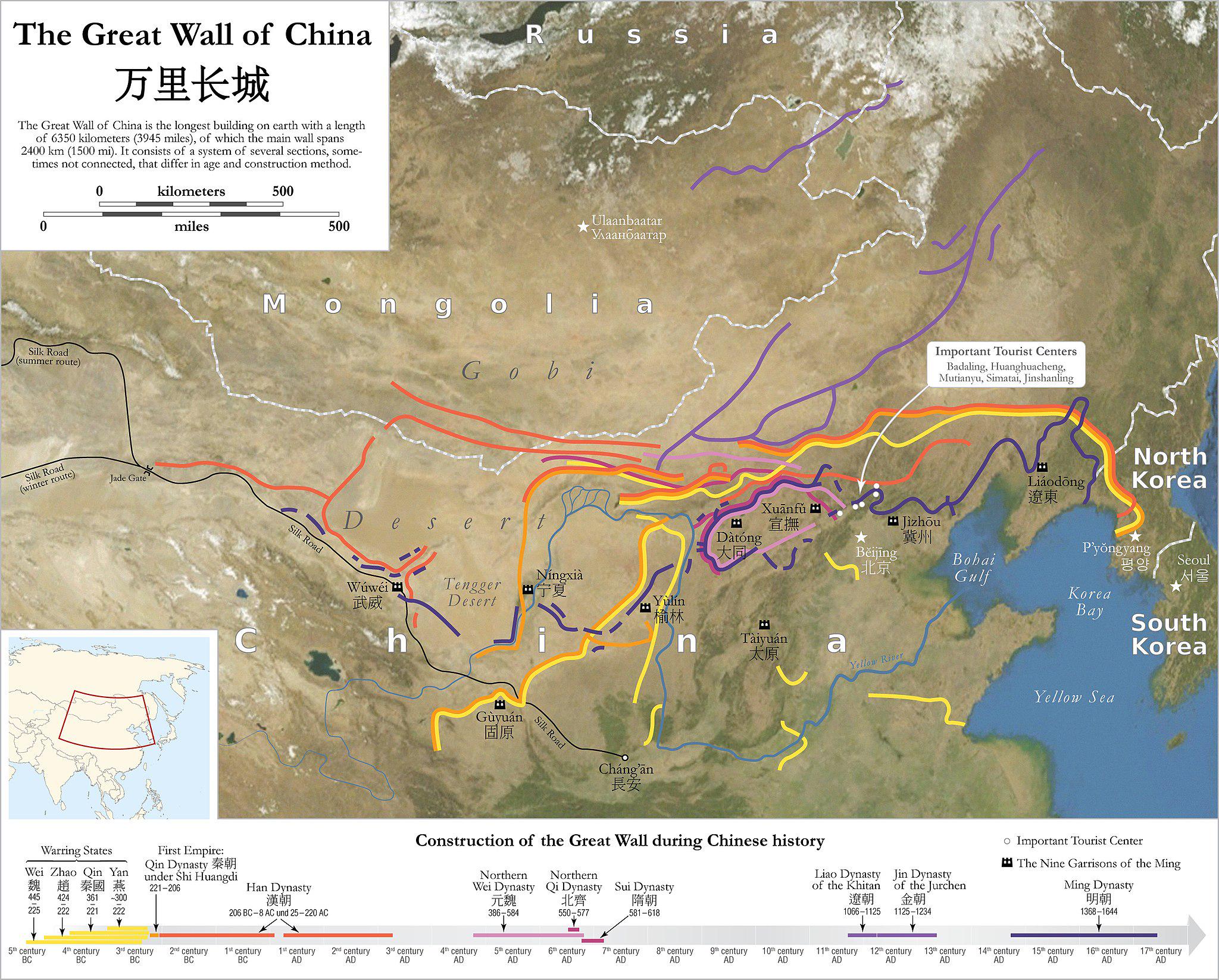
The visualization titled "The Great Wall of China Map" provides a comprehensive overview of the historical and geographical expanse of one of the most iconic structures in the world. This map not only delineates the various sections of the Great Wall but also highlights significant features, including watchtowers, fortresses, and the surrounding landscapes that have played a crucial role in the Wall’s historical significance.
Deep Dive into the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China, stretching over 13,000 miles, is more than just a remarkable feat of engineering; it is a testament to the historical resilience of the Chinese civilization. Originally constructed to protect various Chinese states and empires from invasions by nomadic groups from the north, the Great Wall is a complex network of walls, trenches, and natural barriers that were built over several dynasties, with the earliest sections dating back to the 7th century BC.
Interestingly, the Wall is not a single continuous structure but rather a series of walls and fortifications built by different dynasties, most notably the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644). The Ming sections, which are best preserved and most commonly associated with the Wall, were constructed using bricks and stone, offering a stark contrast to the earlier earth and wood walls.
What's fascinating is that the Wall's construction was not just about defense; it also served as a means of border control, allowing for the regulation of trade and immigration along the Silk Road. The Wall's strategic placement in rugged terrain reveals the ancient Chinese understanding of geography and military tactics.
Today, the Great Wall is not only a UNESCO World Heritage site but also one of the most visited monuments in the world, attracting millions of tourists annually. In 2019 alone, over 10 million visitors explored its various sections, contributing to the local economy while also raising concerns about preservation and environmental impact.
The map illustrates various segments of the Wall, including popular sites like Badaling and Mutianyu, which are well-restored and easily accessible to tourists. However, many lesser-known sections, such as those in Gubeikou and Jiankou, remain wild and rugged, providing a glimpse into the Wall's ancient past.
Regional Analysis
The Great Wall traverses a variety of landscapes, from arid deserts in the west to lush forests in the east. In the west, the Wall extends into the Gobi Desert, where the harsh climate and sparse population make the structure less accessible. Here, the Wall is often constructed from tamped earth and is less well-preserved, reflecting the territorial challenges faced by ancient builders.
In contrast, the eastern sections of the Wall, particularly around Beijing, have been heavily restored and are surrounded by urban development. This area experiences significant tourism, and the local economy has adapted to cater to the influx of visitors. The stark difference in preservation and accessibility of the Wall in these regions raises questions about conservation practices and the balance between tourism and heritage preservation.
Significance and Impact
The Great Wall of China is more than just a historical monument; it symbolizes the enduring spirit of Chinese civilization and its capacity for resilience and adaptation. The Wall has also become a potent cultural icon, representing national pride and unity. However, it faces challenges from environmental degradation, tourism pressures, and the effects of climate change.
Have you noticed that as climate patterns shift, so do the environmental conditions surrounding the Wall? Increased rainfall and erosion threaten the structural integrity of many sections, particularly those that are less frequently maintained. Current trends indicate a growing awareness of the need for sustainable tourism practices, ensuring that future generations can appreciate this marvel of human ingenuity.
The future of the Great Wall lies in a delicate balance between preserving its historical integrity and accommodating the modern world's demands. As we look forward, ongoing conservation efforts and responsible tourism practices will play a crucial role in safeguarding this monumental structure for years to come.
Visualization Details
- Published
- October 21, 2025
- Views
- 32
Comments
Loading comments...